Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the two major implications of diets?
What are the two major implications of diets?
- They treat obesity and are used to reduce cholesterol
- They treat asthma and are used to reduce inflammation
- They treat diabetes and are used to mobilize fluid
- They treat hypertension and are used to mobilize fluid (correct)
What is the basic functional unit of the kidney?
What is the basic functional unit of the kidney?
- Glomerulus
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Nephrons (correct)
What is the primary function of the glomerulus?
What is the primary function of the glomerulus?
- Filtration of small molecules (correct)
- Reabsorption of sodium and chloride
- Maintenance of acid-base balance
- Active secretion of metabolic waste
What is the purpose of the Loop of Henle?
What is the purpose of the Loop of Henle?
What are the three basic functions of the kidney?
What are the three basic functions of the kidney?
What is the process by which the kidney excretes metabolic waste?
What is the process by which the kidney excretes metabolic waste?
What type of molecules do not undergo filtration in the glomerulus?
What type of molecules do not undergo filtration in the glomerulus?
What is the main mechanism of action of diuretics?
What is the main mechanism of action of diuretics?
What is the purpose of the transport compounds in the kidney?
What is the purpose of the transport compounds in the kidney?
Where do Loop diuretics work in the nephron?
Where do Loop diuretics work in the nephron?
What is the prototype drug of the Lute diuretics?
What is the prototype drug of the Lute diuretics?
What percentage of sodium chloride is filtered in the Loop of Henle?
What percentage of sodium chloride is filtered in the Loop of Henle?
What is the therapeutic goal of using Lasix?
What is the therapeutic goal of using Lasix?
What is the duration of action of Lasix?
What is the duration of action of Lasix?
Why should you be cautious when using Lasix in patients with cardiovascular disease?
Why should you be cautious when using Lasix in patients with cardiovascular disease?
What is an example of an osmotic diuretic?
What is an example of an osmotic diuretic?
Why should Lasix be avoided in pregnant women?
Why should Lasix be avoided in pregnant women?
What is the Beers criteria related to?
What is the Beers criteria related to?
What is the effect of the potassium sparing diuretic on sodium reabsorption?
What is the effect of the potassium sparing diuretic on sodium reabsorption?
What is the primary therapeutic goal of using the potassium sparing diuretic?
What is the primary therapeutic goal of using the potassium sparing diuretic?
Why is the potassium sparing diuretic contraindicated in elevated potassium levels?
Why is the potassium sparing diuretic contraindicated in elevated potassium levels?
What is a common adverse effect of the potassium sparing diuretic?
What is a common adverse effect of the potassium sparing diuretic?
What is the reason for monitoring potassium levels when using the potassium sparing diuretic?
What is the reason for monitoring potassium levels when using the potassium sparing diuretic?
What is the duration of action of the potassium sparing diuretic?
What is the duration of action of the potassium sparing diuretic?
What is the advantage of Las diuretics in patient populations with renal impairment?
What is the advantage of Las diuretics in patient populations with renal impairment?
What is the equivalent dose of Vmax to 40 mg of Las?
What is the equivalent dose of Vmax to 40 mg of Las?
What is a potential adverse effect of Las diuretics?
What is a potential adverse effect of Las diuretics?
What is the interaction between Las diuretics and potassium-sparing diuretics?
What is the interaction between Las diuretics and potassium-sparing diuretics?
What is the primary mechanism of action of thiazide diuretics?
What is the primary mechanism of action of thiazide diuretics?
What is a characteristic of thiazide diuretics compared to loop diuretics?
What is a characteristic of thiazide diuretics compared to loop diuretics?
What is the minimum glomerular filtration rate required for thiazide diuretics to be effective?
What is the minimum glomerular filtration rate required for thiazide diuretics to be effective?
What is a potential adverse effect of thiazide diuretics on electrolyte levels?
What is a potential adverse effect of thiazide diuretics on electrolyte levels?
What is the effect of thiazide diuretics on uric acid levels?
What is the effect of thiazide diuretics on uric acid levels?
Why is it important to monitor patients' blood pressure when taking thiazide diuretics?
Why is it important to monitor patients' blood pressure when taking thiazide diuretics?
What is the time frame for diuresis to peak with Lex?
What is the time frame for diuresis to peak with Lex?
What is a common adverse effect of Lex and Loop Diuretics?
What is a common adverse effect of Lex and Loop Diuretics?
What is the purpose of teaching patients to do daily weights at home?
What is the purpose of teaching patients to do daily weights at home?
What is the mechanism of action of Spironolactone?
What is the mechanism of action of Spironolactone?
What is the primary use of Potassium-sparing Diuretics?
What is the primary use of Potassium-sparing Diuretics?
What is a unique feature of Spironolactone's dosing and administration?
What is a unique feature of Spironolactone's dosing and administration?
What is a potential interaction between Spironolactone and other medications?
What is a potential interaction between Spironolactone and other medications?
What is the black box warning associated with Spironolactone?
What is the black box warning associated with Spironolactone?
What is the primary difference between Spironolactone and Tramiprosate?
What is the primary difference between Spironolactone and Tramiprosate?
What should patients be educated on when taking Spironolactone?
What should patients be educated on when taking Spironolactone?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Diets and Their Implications
- Diets have two major implications: treating hypertension and mobilizing fluid in patients with liver failure, kidney disease, or heart failure.
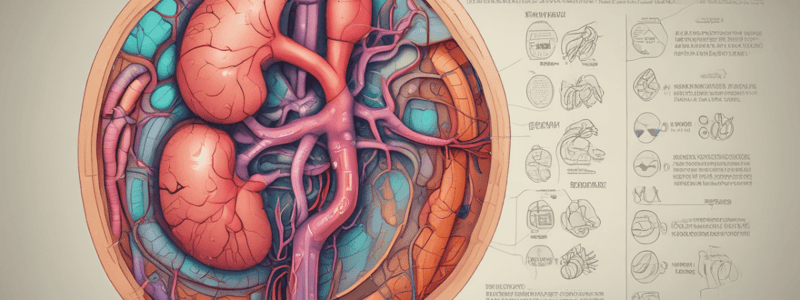
- The kidney's basic functional unit is the nephron, which has four functionally distinct regions: glomerulus, proximal convoluted tubule, Loop of Henle, and distal convoluted tubule.
- The kidney serves three basic functions: cleansing extracellular fluid, maintaining extracellular fluid volume, and excreting metabolic waste and foreign substances.
Filtration, Reabsorption, and Secretion
- Filtration occurs at the glomerulus, where small molecules like electrolytes, amino acids, glucose, and drugs are filtered.
- Larger molecules like lipids and proteins remain in the bloodstream.
- Reabsorption and secretion occur in the proximal convoluted tubule and distal convoluted tubule, respectively.
Diuretics
- Diuretics share a common mechanism of action: blocking sodium and chloride reabsorption, causing excretion and diuresis.
- There are four main categories of diuretics:
- Loop diuretics (e.g., Furosemide, Torsemide, Bumetanide)
- Thiazide diuretics (e.g., Hydrochlorothiazide)
- Osmotic diuretics (e.g., Mannitol)
- Potassium-sparing diuretics (e.g., Spironolactone, Triamterene)
Loop Diuretics
- Loop diuretics are the most effective and produce the most significant loss of fluid and electrolytes.
- They work in the Loop of Henle, blocking sodium and chloride reabsorption.
- Examples of loop diuretics:
- Furosemide (Lasix)
- Used for rapid mobilization of fluid, hypertension, and edema
- Acts in the G segment of the ascending limb of the Loop of Henle
- Produces profound diuresis
- Adverse effects: hypotension, hypokalemia, hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, and increased LD and triglycerides
- Furosemide (Lasix)
Thiazide Diuretics
- Thiazide diuretics are less potent than loop diuretics and work in the early segment of the distal convoluted tubule.
- They increase renal excretion of sodium, chloride, potassium, and water, and can elevate plasma levels of uric acid and glucose.
- Examples of thiazide diuretics:
- Hydrochlorothiazide
- Used for hypertension, edema, and congestive heart failure
- Acts in the early segment of the distal convoluted tubule
- Produces milder diuresis
- Adverse effects: similar to loop diuretics, plus photo sensitivity and hyperuricemia
- Hydrochlorothiazide
Potassium-Sparing Diuretics
- Potassium-sparing diuretics work by blocking the action of aldosterone in the distal nephrons, resulting in retention of potassium and excretion of sodium.
- Examples of potassium-sparing diuretics:
- Spironolactone (Aldactone)
- Used for hypertension, edema, and congestive heart failure
- Acts as an aldosterone antagonist
- Counteracts potassium wasting effects of other diuretics
- Adverse effects: hyperkalemia, nausea, vomiting, and blood dyscrasias
- Triamterene
- Used for hypertension, edema, and congestive heart failure
- Acts by direct inhibition of sodium-potassium exchange
- Counteracts potassium wasting effects of other diuretics
- Adverse effects: hyperkalemia, nausea, vomiting, and blood dyscrasias
- Spironolactone (Aldactone)
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.