Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the most common cause of diaper dermatitis?
What is the most common cause of diaper dermatitis?
- Allergic reaction
- Irritation from urine (correct)
- Fungal infection
- Bacterial infection
Which condition is characterized by the presence of satellite pustules?
Which condition is characterized by the presence of satellite pustules?
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Candidiasis (correct)
- Irritant contact dermatitis
- Histiocytosis
In which form of dermatitis is the skin often spared in the folds?
In which form of dermatitis is the skin often spared in the folds?
- Candidiasis
- Irritant contact dermatitis (correct)
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Psoriasis
Which dermatitis is notably associated with cradle cap?
Which dermatitis is notably associated with cradle cap?
What can indicate isolated seborrheic diaper dermatitis?
What can indicate isolated seborrheic diaper dermatitis?
Which of the following is a rare cause of diaper dermatitis that may present with petechiae?
Which of the following is a rare cause of diaper dermatitis that may present with petechiae?
Which type of dermatitis rarely requires a biopsy?
Which type of dermatitis rarely requires a biopsy?
Psoriasis is characterized by which distinctive finding that may occur in diaper dermatitis?
Psoriasis is characterized by which distinctive finding that may occur in diaper dermatitis?
What is the primary purpose of a biopsy in difficult cases of skin conditions?
What is the primary purpose of a biopsy in difficult cases of skin conditions?
Which barrier is NOT mentioned as effective for treating diaper rash?
Which barrier is NOT mentioned as effective for treating diaper rash?
What is the typical age of onset for atopic dermatitis in children?
What is the typical age of onset for atopic dermatitis in children?
What is the significance of a family history in the context of atopic dermatitis?
What is the significance of a family history in the context of atopic dermatitis?
Which of the following statements best differentiates atopic dermatitis from other conditions referred to as eczema?
Which of the following statements best differentiates atopic dermatitis from other conditions referred to as eczema?
What mixture is often used when anti-candida agents are combined with anti-inflammatory agents?
What mixture is often used when anti-candida agents are combined with anti-inflammatory agents?
How is the distribution of atopic dermatitis lesions thought to change as children age?
How is the distribution of atopic dermatitis lesions thought to change as children age?
Which protein mutation is associated with atopic dermatitis according to recent data?
Which protein mutation is associated with atopic dermatitis according to recent data?
What role do filaggrins play in epithelial cells?
What role do filaggrins play in epithelial cells?
What is the predominant cytokine profile in acute lesions of atopic dermatitis?
What is the predominant cytokine profile in acute lesions of atopic dermatitis?
How does elevated IgE levels in patients often correlate with atopic dermatitis?
How does elevated IgE levels in patients often correlate with atopic dermatitis?
What is primarily responsible for exacerbating atopic dermatitis in many patients?
What is primarily responsible for exacerbating atopic dermatitis in many patients?
What is essential in the treatment of atopic dermatitis?
What is essential in the treatment of atopic dermatitis?
Which type of moisturizers are recommended for repairing the skin barrier in atopic dermatitis treatment?
Which type of moisturizers are recommended for repairing the skin barrier in atopic dermatitis treatment?
When should topical steroids for atopic dermatitis ideally be used?
When should topical steroids for atopic dermatitis ideally be used?
What is a primary advantage of T-lymphocyte inhibitors over steroids?
What is a primary advantage of T-lymphocyte inhibitors over steroids?
Which dietary allergens are commonly associated with exacerbating atopic dermatitis in children?
Which dietary allergens are commonly associated with exacerbating atopic dermatitis in children?
What is the typical presentation of neonatal acne?
What is the typical presentation of neonatal acne?
What two factors are thought to contribute to the etiology of infantile acne?
What two factors are thought to contribute to the etiology of infantile acne?
Which treatment options have been reported effective for infantile acne?
Which treatment options have been reported effective for infantile acne?
Which condition is characterized by erythema and thick, yellowish, greasy scales on the scalp of infants?
Which condition is characterized by erythema and thick, yellowish, greasy scales on the scalp of infants?
What is generally understood about the long-term risk of adolescents developing severe acne who had infantile acne?
What is generally understood about the long-term risk of adolescents developing severe acne who had infantile acne?
Flashcards
Diaper dermatitis
Diaper dermatitis
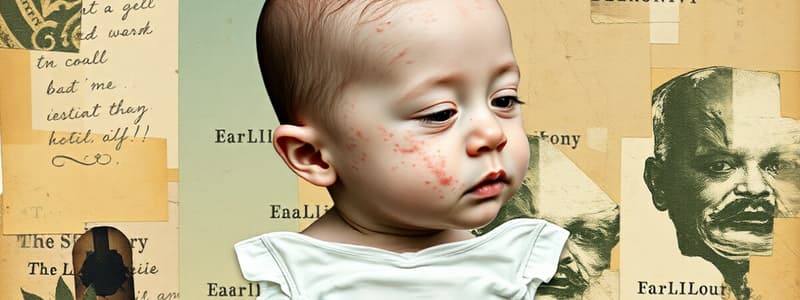
A common condition in babies, usually due to irritation from urine, stool, or moisture. It typically causes redness, itching, and sometimes pain in the diaper area.
Irritant contact dermatitis
Irritant contact dermatitis
An inflammation of the skin caused by direct contact with irritating substances, like urine or stool.
Candida diaper dermatitis
Candida diaper dermatitis
A fungal infection that often coexists with diaper dermatitis, usually showing up as tiny white or yellow bumps on a red base, often around the edges of the diaper area. These bumps are called satellite pustules.
Seborrheic diaper dermatitis
Seborrheic diaper dermatitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Psoriatic diaper dermatitis
Psoriatic diaper dermatitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Histiocytosis in diaper dermatitis
Histiocytosis in diaper dermatitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atopic dermatitis and diaper area
Atopic dermatitis and diaper area
Signup and view all the flashcards
When to biopsy diaper dermatitis
When to biopsy diaper dermatitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Candidiasis in Diaper Dermatitis
Candidiasis in Diaper Dermatitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seborrheic Dermatitis in the Diaper Area
Seborrheic Dermatitis in the Diaper Area
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atopic Dermatitis in Infants
Atopic Dermatitis in Infants
Signup and view all the flashcards
Filaggrin
Filaggrin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atopic Triad
Atopic Triad
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biopsy for Diaper Dermatitis
Biopsy for Diaper Dermatitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Swab Culture for Candida
Swab Culture for Candida
Signup and view all the flashcards
What's the role of filaggrin in skin?
What's the role of filaggrin in skin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is atopic dermatitis?
What is atopic dermatitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the immune system in atopic dermatitis?
What is the role of the immune system in atopic dermatitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How can hygiene affect atopic dermatitis?
How can hygiene affect atopic dermatitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the connection between Staphylococcus and atopic dermatitis?
What is the connection between Staphylococcus and atopic dermatitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the importance of moisturizers in treating atopic dermatitis?
What is the importance of moisturizers in treating atopic dermatitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How are topical steroids used in atopic dermatitis treatment?
How are topical steroids used in atopic dermatitis treatment?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are topical immunomodulators (TIMS) and how are they used in atopic dermatitis?
What are topical immunomodulators (TIMS) and how are they used in atopic dermatitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
T-lymphocyte inhibiting medications (TIMS)
T-lymphocyte inhibiting medications (TIMS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infantile acne
Infantile acne
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pityrosporum
Pityrosporum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cradle cap (seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp)
Cradle cap (seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Androgenic hormones
Androgenic hormones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spontaneous resolution
Spontaneous resolution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Diaper Dermatitis
- Diaper dermatitis is common in children of diaper-wearing age.
- It encompasses several potentially co-occurring skin conditions (diseases).
- Irritation (e.g., urine, stool) is a common cause.
- Irritant contact dermatitis: Skin becomes more sensitive to irritation, particularly spared in skin folds.
- Candidiasis (yeast infection): Commonly coexists; characterized by pustules (satellite pustules).
- Seborrheic dermatitis: Involves skin folds, without satellite pustules. Often associated with cradle cap.
- Psoriasis: Rarely causes diaper dermatitis; silvery scale is sometimes observed.
- Histiocytosis: Very rare cause, presenting with severe rash, often petechiae.
- Atopic dermatitis: Typically spares the diaper area.
Diagnosis and Management
- Biopsy is rarely needed unless histiocytosis is suspected.
- Investigations might include a swab culture to test for Candida.
- Frequent diaper changes to minimize moisture.
- Barrier pastes (e.g., zinc oxide) block irritants.
Early Atopic Dermatitis
- Prevalence is increasing.
- Strong familial component, with atopic triad (dermatitis, asthma, and allergies).
- "Eczema" is often used interchangeably, but includes other conditions (dry skin, contact dermatitis).
- Most involve face and extremities.
- Characterized by bright red, scaly, and weeping lesions.
- Possible genetic mutation in filaggrin (protein in epithelial cells maintaining skin barrier).
- Th-2 phenotype in acute; Th-1 in chronic lesions.
- Increased IgE and eosinophilia.
- Hygiene hypothesis: Lower exposure to infectious agents, lower prevalence of AD.
Infantile Acne
- Occurs in up to 50% of infants.
- Presents as inflammatory papules (pustules).
- Can persist up to a year.
- Possibly related to androgenic hormones from mother, and/or, Pityrosporum overgrowth.
Cradle Cap
- Common in infants.
- Erythematous, thick, yellowish, greasy scales on the scalp, potentially extending to the forehead and neck.
- Relates to overgrowth of Pityrosporum yeast and subsequent inflammation.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.