Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is a key factor in clinical assessment during a dental examination?
Which of the following is a key factor in clinical assessment during a dental examination?
- Number of teeth present
- Presence of orthodontic appliances
- Tooth restorable (correct)
- Patient's age
Fluctuation felt by palpating a swollen mucobuccal fold indicates a chronic dentoalveolar abscess.
Fluctuation felt by palpating a swollen mucobuccal fold indicates a chronic dentoalveolar abscess.
False (B)
What is the purpose of the percussion test in dental assessments?
What is the purpose of the percussion test in dental assessments?
To reveal sensitivity in teeth and detect inflammation in the periodontal ligament.
A significant difference in mobility compared to the contralateral tooth might indicate __________ disease.
A significant difference in mobility compared to the contralateral tooth might indicate __________ disease.
Match the following dental assessment techniques with their significance:
Match the following dental assessment techniques with their significance:
Reversible pulp inflammation indicates that the pulp is incapable of healing.
Reversible pulp inflammation indicates that the pulp is incapable of healing.
What type of radiographs are typically taken to diagnose pulpitis?
What type of radiographs are typically taken to diagnose pulpitis?
In the case of reversible pulpitis, the pulp is capable of __________.
In the case of reversible pulpitis, the pulp is capable of __________.
Match the following terms with their definitions:
Match the following terms with their definitions:
Which symptom is NOT typically associated with reversible pulpitis?
Which symptom is NOT typically associated with reversible pulpitis?
What kind of examination should be performed on a child with a dental complaint?
What kind of examination should be performed on a child with a dental complaint?
The symptom of __________ pain can occur when the inter dental gingiva is inflamed due to food impaction.
The symptom of __________ pain can occur when the inter dental gingiva is inflamed due to food impaction.
What type of radiograph is recommended for assessing root length and pathology in paedodontics?
What type of radiograph is recommended for assessing root length and pathology in paedodontics?
Thermal testing is always conclusive in diagnosing dental conditions.
Thermal testing is always conclusive in diagnosing dental conditions.
What is the primary indicator for performing a pulpotomy?
What is the primary indicator for performing a pulpotomy?
In cases of irreversible pulpitis, the recommended procedure is _________.
In cases of irreversible pulpitis, the recommended procedure is _________.
Match the following dental conditions with the appropriate management options:
Match the following dental conditions with the appropriate management options:
Which of the following is a symptom of a tooth requiring extraction?
Which of the following is a symptom of a tooth requiring extraction?
An unrestorable tooth with symptomatic sepsis can still be treated with a vital pulpotomy.
An unrestorable tooth with symptomatic sepsis can still be treated with a vital pulpotomy.
For a tooth with occlusal caries and symptoms, the appropriate treatment choice is ________.
For a tooth with occlusal caries and symptoms, the appropriate treatment choice is ________.
Flashcards
Clinical assessment for paedodontics
Clinical assessment for paedodontics
Checking for abscesses, mobility, swelling, tenderness, restorable teeth, extent of gum damage, and sites of cavities.
Palpation in dental assessment
Palpation in dental assessment
Feeling for swelling (fluctuation) or bony changes by touching the affected area in a childs mouth to detect abscesses.
Mobility test in dentistry
Mobility test in dentistry
Comparing a suspected tooth's movement with its opposite tooth to identify potential pulpal problems.
Percussion test in dentistry
Percussion test in dentistry
Signup and view all the flashcards
Importance of gentle percussion
Importance of gentle percussion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reversible Pulp Inflammation
Reversible Pulp Inflammation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vital Pulp
Vital Pulp
Signup and view all the flashcards
Irreversible Pulpitis
Irreversible Pulpitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Necrotic Pulp
Necrotic Pulp
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clinical Diagnosis
Clinical Diagnosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chief Complaint
Chief Complaint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulp Therapy Indications
Pulp Therapy Indications
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pain Simulation - Food Impaction
Pain Simulation - Food Impaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radiographic Assessment in Paedodontics
Radiographic Assessment in Paedodontics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Operative Diagnosis (Pulp)
Operative Diagnosis (Pulp)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulpotomy
Pulpotomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vital Pulpotomy
Vital Pulpotomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Non-vital Pulpotomy
Non-vital Pulpotomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Caries Removal (Indirect)
Caries Removal (Indirect)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Occlusal Caries
Occlusal Caries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proximal Caries
Proximal Caries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Chief Complaint
- Patients experience pain while eating, but the pain subsides after a few minutes without taking pain relievers.
Examination
- A physical examination of the patient's mouth is performed.
Investigations
- Periapical radiograph: X-ray image taken focused on the area around the tooth's root.
- Bitewing radiograph: X-ray image taken from the side of the upper and lower teeth.
Diagnosis
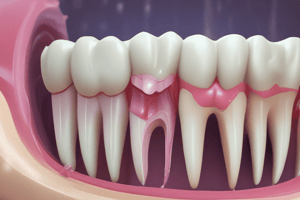
- Reversible pulp inflammation: Inflammation of the dental pulp, which can resolve.
Pulpal Therapy
- The treatment plan depends on whether the pulp is vital or nonvital.
- Normal pulp: Symptom-free and responsive to vitality tests, and is capable of healing.
- Reversible pulpitis: Pulp can heal.
- Symptomatic or asymptomatic irreversible pulpitis: Vital inflamed pulp is incapable of healing, or necrotic pulp.
Clinical Diagnosis
- Comprehensive medical history: Reviewing the patient's past and present medical history, including dental history.
- Current symptoms and chief complaint: Including symptoms related to the mouth.
- Subjective evaluation of the area associated with current symptoms: Involves questioning the child and parent on location, intensity, duration, stimulus, relief, and spontaneity of the symptoms.
Clinical assessment
- Assessing for abscess, abnormal mobility, swelling, and tenderness to percussion.
- Assessing the extent of marginal ridge breakdown from caries.
- Reviewing missing or fractured restorations.
Palpation
- Detecting fluctuation (swelling) and bone destruction, which may result from a dentoalveolar abscess.
Mobility
- Comparing the suspicious tooth's mobility with its counterpart. A significant difference might indicate pulp disease.
Percussion Test
- Sensitivity to percussion may indicate inflamed periodontal ligament (acute apical periodontitis).
- Percussion should be gentle to prevent discomfort for the patient.
Electrical and Thermal Assessments
- These are not typically definitive indicators for pulp issues.
Radiographic Assessment
- High-quality bitewing radiographs are used to determine root length, perifurcational pathology, and internal resorption.
Operative Diagnosis
- Acute inflammation and pain.
- Exposed pulp tissue, with continuous bleeding.
Pulpotomy in Primary Teeth Treatment Objectives
- Eliminating potential infections.
- Keeping the tooth stable.
- Maintaining space for the permanent tooth.
- Retaining primary teeth if permanent ones are congenitally absent.
Indications for Pulpotomy
- Deep caries without pulp exposure.
- Carious or traumatic pulp exposure with temporary thermal/chemical stimulated pain.
- Physiological tooth mobility.
- Normal soft tissues; no percussion sensitivity (excluding food impaction cases).
- Intact continuous ligament space; intact periapical and/or furcation bone.
Conflicting Factors in Diagnosis of Pulp Status
- Pulp hemorrhage color is not a definitive indicator for pulp histological status.
- Excessive bleeding may indicate degenerative changes.
- A significant portion of teeth with carious pulp exposures have normal pulps while a significant portion of teeth with deep caries and no pulp exposure have abnormal pulps.
Successful Pulp Therapy Requirements
- Patient cooperation.
- Using LA (local anesthesia).
- Employing rubber dams.
- Implementing postoperative restoration.
- Conducting follow-ups.
Steps in Pulpotomy
- Local anesthesia and isolation.
- Caries removal, exposing the pulp chamber/cavity.
- Removing the roof of the pulp chamber, but avoiding deeper penetration, only laterally.
- Removing the coronal pulp using a large spoon excavator or bur.
- Applying saline solution on the cotton pellet for 1 minute.
- Applying medicine to the radicular pulp on a cotton pledget for 15 seconds.
- Checking for bleeding and removing the cotton pledget.
- Filling the pulp chamber (using ZOE cement), condensing it with a damp cotton pledget.
- Applying a coronal restoration using a SSC material.
Materials for Pulpotomy
- Ferric sulfate.
- MTA.
Ferric Sulfate
- Current gold standard.
- Applied to the radicular pulp.
Safe Burs
- Tungsten carbide endodontic burs and diamond burs are used.
Additional Issues to be Aware of
- Perforating the floor of the pulp chamber.
- Problems with the pulp floor (approximately at the gingival margin).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.