Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which type of endodontic infection is characterized by microorganisms introduced during treatment, between appointments, and after root canal obturation?
Which type of endodontic infection is characterized by microorganisms introduced during treatment, between appointments, and after root canal obturation?
- Intraradicular infection
- Secondary infection (correct)
- Extraradicular infection
- Primary infection
What is the main characteristic of persistent endodontic infection?
What is the main characteristic of persistent endodontic infection?
- Resistant to irrigation and medication (correct)
- Consists of mainly anaerobic bacteria
- Occurs in the periradicular area
- Caused by necrotic pulp
Which type of microorganisms are primarily responsible for secondary endodontic infections?
Which type of microorganisms are primarily responsible for secondary endodontic infections?
- Obligate anaerobes
- Facultative micro-organisms (correct)
- G+ve facultative anaerobic
- Fungi (Candida Albicans)
What is the main impact of extraradicular infection in the periradicular area?
What is the main impact of extraradicular infection in the periradicular area?
What is the term for free floating single microorganisms inside the root canal that can cause infection?
What is the term for free floating single microorganisms inside the root canal that can cause infection?
Which cellular component of microorganisms protects bacteria from phagocytosis?
Which cellular component of microorganisms protects bacteria from phagocytosis?
What makes bacterial biofilms resistant to antimicrobial agents?
What makes bacterial biofilms resistant to antimicrobial agents?
What is the main function of neutralizing enzymes secreted by microorganisms?
What is the main function of neutralizing enzymes secreted by microorganisms?
What is the main component of outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria, released after death of the microorganism, and known for activating the complement system?
What is the main component of outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria, released after death of the microorganism, and known for activating the complement system?
What type of irritant may lead to pulpal irritation due to pressure, friction, and heat?
What type of irritant may lead to pulpal irritation due to pressure, friction, and heat?
Which type of pulp changes is characterized by a soft solid cheesy like mass known as caseation?
Which type of pulp changes is characterized by a soft solid cheesy like mass known as caseation?
What is the typical response to percussion in the examination of retrogressive pulp changes?
What is the typical response to percussion in the examination of retrogressive pulp changes?
In which condition does inflammation in the pulp initiate resorption of adjacent hard tissues?
In which condition does inflammation in the pulp initiate resorption of adjacent hard tissues?
What is the appropriate treatment for previously treated pulp according to the text?
What is the appropriate treatment for previously treated pulp according to the text?
Which educational aim of the lecture includes detailing the etiology and progress of pulp and periapical injuries?
Which educational aim of the lecture includes detailing the etiology and progress of pulp and periapical injuries?
What is the main aim in the category of 'previously treated pulp' according to the text?
What is the main aim in the category of 'previously treated pulp' according to the text?
Which reading material is advised for students who want to read about 'problems in endodontics'?
Which reading material is advised for students who want to read about 'problems in endodontics'?
What response is expected at high current sensitivity test in retrogressive pulp changes?
What response is expected at high current sensitivity test in retrogressive pulp changes?
What does atrophy refer to in retrogressive pulp changes?
What does atrophy refer to in retrogressive pulp changes?
Which type of pulp changes includes deposition of calcium salts in dead or degenerated tissue?
Which type of pulp changes includes deposition of calcium salts in dead or degenerated tissue?
What is the main cause of pulp and periradicular infection?
What is the main cause of pulp and periradicular infection?
Which classification of pulp inflammation is based on the severity and duration of the condition?
Which classification of pulp inflammation is based on the severity and duration of the condition?
Which of the following is NOT a pathway of pulp and periradicular infection?
Which of the following is NOT a pathway of pulp and periradicular infection?
What is the definition of reversible pulpitis?
What is the definition of reversible pulpitis?
What are the signs and symptoms of irreversible pulpitis?
What are the signs and symptoms of irreversible pulpitis?
What is the most common cause of ingress of bacteria to the pulp?
What is the most common cause of ingress of bacteria to the pulp?
Which condition is a special form of chronic pulpitis that occurs in molar teeth of children and young adults?
Which condition is a special form of chronic pulpitis that occurs in molar teeth of children and young adults?
Which type of irritant is NOT a cause of ingress of bacteria to pulp?
Which type of irritant is NOT a cause of ingress of bacteria to pulp?
Which stage of irreversible pulpitis involves hot and cold stimuli causing pain due to C & A delta fibers?
Which stage of irreversible pulpitis involves hot and cold stimuli causing pain due to C & A delta fibers?
Which type of injury is NOT detailed in the educational aims of the lecture?
Which type of injury is NOT detailed in the educational aims of the lecture?
What is the response to the ingress of bacteria to the pulp?
What is the response to the ingress of bacteria to the pulp?
What is the primary treatment for reversible pulpitis?
What is the primary treatment for reversible pulpitis?
What is the differential diagnosis between reversible and irreversible pulpitis?
What is the differential diagnosis between reversible and irreversible pulpitis?
What is the main cause of direct pulp exposure?
What is the main cause of direct pulp exposure?
What are the clinical features of chronic closed pulpitis?
What are the clinical features of chronic closed pulpitis?
What is responsible for ingress of bacteria to lateral canals?
What is responsible for ingress of bacteria to lateral canals?
Which type of irritant is NOT listed as a main irritant of the pulp?
Which type of irritant is NOT listed as a main irritant of the pulp?
What type of infection did the lecture focus on?
What type of infection did the lecture focus on?
What is the main function of neutralizing enzymes secreted by microorganisms?
What is the main function of neutralizing enzymes secreted by microorganisms?
What is the main impact of extraradicular infection in the periradicular area?
What is the main impact of extraradicular infection in the periradicular area?
What type of irritant may lead to pulpal irritation due to pressure, friction, and heat?
What type of irritant may lead to pulpal irritation due to pressure, friction, and heat?
What is responsible for ingress of bacteria to lateral canals?
What is responsible for ingress of bacteria to lateral canals?
What does atrophy refer to in retrogressive pulp changes?
What does atrophy refer to in retrogressive pulp changes?
Which type of endodontic infection is characterized by microorganisms introduced during treatment, between appointments, and after root canal obturation?
Which type of endodontic infection is characterized by microorganisms introduced during treatment, between appointments, and after root canal obturation?
What is the differential diagnosis between reversible and irreversible pulpitis?
What is the differential diagnosis between reversible and irreversible pulpitis?
Which reading material is advised for students who want to read about 'problems in endodontics'?
Which reading material is advised for students who want to read about 'problems in endodontics'?
What is the main characteristic of persistent endodontic infection?
What is the main characteristic of persistent endodontic infection?
Which stage of irreversible pulpitis involves hot and cold stimuli causing pain due to C & A delta fibers?
Which stage of irreversible pulpitis involves hot and cold stimuli causing pain due to C & A delta fibers?
What type of infection did the lecture focus on?
What type of infection did the lecture focus on?
What is the main cause of direct pulp exposure?
What is the main cause of direct pulp exposure?
Which condition is characterized by the formation of pus draining through a sinus tract?
Which condition is characterized by the formation of pus draining through a sinus tract?
What is the characteristic radiographic feature that differentiates periapical granuloma from chronic periapical abscess?
What is the characteristic radiographic feature that differentiates periapical granuloma from chronic periapical abscess?
Which treatment involves root canal treatment, surgical removal of the cyst, and apicectomy?
Which treatment involves root canal treatment, surgical removal of the cyst, and apicectomy?
What is the main characteristic radiographic feature of condensing osteitis?
What is the main characteristic radiographic feature of condensing osteitis?
What is the primary cause of a periapical granuloma?
What is the primary cause of a periapical granuloma?
Which condition is diagnosed based on a well-defined periapical radiolucency surrounded by radioopaque margins?
Which condition is diagnosed based on a well-defined periapical radiolucency surrounded by radioopaque margins?
What is the typical response to percussion in the examination of periapical granuloma?
What is the typical response to percussion in the examination of periapical granuloma?
Which reading material is advised for students to read about the details of endodontic infections?
Which reading material is advised for students to read about the details of endodontic infections?
What is the main cause of direct pulp exposure?
What is the main cause of direct pulp exposure?
What type of irritant may lead to pulpal irritation due to pressure, friction, and heat?
What type of irritant may lead to pulpal irritation due to pressure, friction, and heat?
What are the clinical features of chronic closed pulpitis?
What are the clinical features of chronic closed pulpitis?
What is responsible for ingress of bacteria to lateral canals?
What is responsible for ingress of bacteria to lateral canals?
What makes bacterial biofilms resistant to antimicrobial agents?
What makes bacterial biofilms resistant to antimicrobial agents?
What type of irritant is NOT listed as a main irritant of the pulp?
What type of irritant is NOT listed as a main irritant of the pulp?
What is the differential diagnosis between reversible and irreversible pulpitis?
What is the differential diagnosis between reversible and irreversible pulpitis?
Which type of endodontic infection is characterized by microorganisms introduced during treatment, between appointments, and after root canal obturation?
Which type of endodontic infection is characterized by microorganisms introduced during treatment, between appointments, and after root canal obturation?
What is the main impact of extraradicular infection in the periradicular area?
What is the main impact of extraradicular infection in the periradicular area?
Which type of infection did the lecture focus on?
Which type of infection did the lecture focus on?
What is the response to the ingress of bacteria to the pulp?
What is the response to the ingress of bacteria to the pulp?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
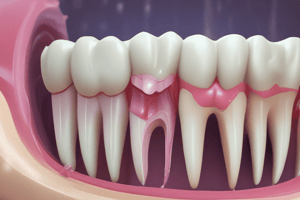
Endodontic Infections
- Iatrogenic infection: microorganisms introduced during treatment, between appointments, and after root canal obturation
- Persistent endodontic infection: characterized by failure of treatment to eliminate infection
- Secondary endodontic infections: caused by anaerobic microorganisms
- Extraradicular infection: causes bone resorption and formation of a periapical lesion
- Free-floating single microorganisms inside the root canal: can cause infection
- Bacterial biofilms: resistant to antimicrobial agents due to complex structure
- Lipopolysaccharide (LPS): protects bacteria from phagocytosis
- Neutralizing enzymes: secreted by microorganisms to break down antimicrobial agents
- Outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria: releases lipopolysaccharide (LPS) after death, activating the complement system
Pulpal Irritation and Inflammation
- Pressure, friction, and heat: types of irritants that can cause pulpal irritation
- Retrogressive pulp changes: pulp changes caused by irritation, characterized by atrophy
- Caseation: soft, solid, cheesy-like mass characteristic of retrogressive pulp changes
- Inflammation: leads to resorption of adjacent hard tissues
- Reversible pulpitis: characterized by pain in response to stimuli, but returns to normal
- Irreversible pulpitis: characterized by prolonged pain, not responsive to stimuli
- Direct pulp exposure: caused by cavity, trauma, or decay
- Chronic closed pulpitis: characterized by asymptomatic, chronic inflammation
- Lateral canals: ingress of bacteria through lateral canals causes infection
Periapical Infections
- Periapical granuloma: chronic periapical infection, characterized by radiolucent area surrounded by radioopaque margins
- Chronic periapical abscess: characterized by formation of pus draining through a sinus tract
- Apical cyst: characterized by a well-defined periapical radiolucency surrounded by radioopaque margins
- Condensing osteitis: characterized by radiographic feature of increased bone density around the apex
- Periapical infection: primary cause of periapical granuloma
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.