Podcast
Questions and Answers
Peri-implant mucositis is primarily characterized by inflammation of the soft tissues surrounding a dental implant, without which of the following?
Peri-implant mucositis is primarily characterized by inflammation of the soft tissues surrounding a dental implant, without which of the following?
- Loss of supporting bone (correct)
- Visual signs of soft-tissue inflammation
- Increased probing depths
- Presence of bleeding upon probing
What is the estimated occurrence rate of peri-implant mucositis in patients with dental implants?
What is the estimated occurrence rate of peri-implant mucositis in patients with dental implants?
- 80% of patients and 50% of implant sites (correct)
- 20% of patients and 10% of implant sites
- 10% of patients and 20% of implant sites
- 50% of patients and 80% of implant sites
Which of the following is crucial for diagnosing peri-implantitis, distinguishing it from peri-implant mucositis?
Which of the following is crucial for diagnosing peri-implantitis, distinguishing it from peri-implant mucositis?
- Radiographic evidence of bone loss (correct)
- Presence of bleeding on probing
- Visual signs of inflammation
- Increased probing depths
What is a key characteristic of peri-implantitis progression?
What is a key characteristic of peri-implantitis progression?
Which of the following diagnostic criteria is shared by both peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis?
Which of the following diagnostic criteria is shared by both peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis?
The inflammation seen in peri-implant mucositis is induced by:
The inflammation seen in peri-implant mucositis is induced by:
A clinician notes increased probing depths, bleeding on probing, and visual signs of inflammation around a dental implant. A radiograph reveals no bone loss. Which condition is most likely?
A clinician notes increased probing depths, bleeding on probing, and visual signs of inflammation around a dental implant. A radiograph reveals no bone loss. Which condition is most likely?
Peri-implant mucositis is considered reversible if:
Peri-implant mucositis is considered reversible if:
What is the primary function of the implant body?
What is the primary function of the implant body?
Why is titanium or titanium alloy commonly used for implant bodies?
Why is titanium or titanium alloy commonly used for implant bodies?
What is the role of the implant abutment?
What is the role of the implant abutment?
What is a primary advantage of using ceramics like zirconia as an alternative to titanium for implant components?
What is a primary advantage of using ceramics like zirconia as an alternative to titanium for implant components?
Why is the sequence of using drills with increasing diameters important during the preparation of the osteotomy site?
Why is the sequence of using drills with increasing diameters important during the preparation of the osteotomy site?
What is the primary function of the dental hygienist in the context of dental implants?
What is the primary function of the dental hygienist in the context of dental implants?
Which component of a dental implant system serves as the 'root' of the implant?
Which component of a dental implant system serves as the 'root' of the implant?
During the implant placement surgery, the implant body can be covered with gingiva or left exposed to the oral cavity. What factor might influence this decision?
During the implant placement surgery, the implant body can be covered with gingiva or left exposed to the oral cavity. What factor might influence this decision?
What are 'peri-implant tissues'?
What are 'peri-implant tissues'?
What is the primary function of the abutment in an endosteal dental implant?
What is the primary function of the abutment in an endosteal dental implant?
A dental technician notices scratches on a newly received titanium abutment. What property of titanium makes it susceptible to this?
A dental technician notices scratches on a newly received titanium abutment. What property of titanium makes it susceptible to this?
A patient is considering different tooth replacement options. Which of the following is a benefit unique to dental implants compared to traditional removable dentures?
A patient is considering different tooth replacement options. Which of the following is a benefit unique to dental implants compared to traditional removable dentures?
Why is biocompatibility of the abutment important for a dental implant's success?
Why is biocompatibility of the abutment important for a dental implant's success?
Which of the following is a key characteristic of the implant body that contributes to the long-term success of a dental implant?
Which of the following is a key characteristic of the implant body that contributes to the long-term success of a dental implant?
Besides replacing individual teeth, what other function can a dental implant serve?
Besides replacing individual teeth, what other function can a dental implant serve?
How do dental implants help in maintaining the integrity of the jawbone after tooth loss?
How do dental implants help in maintaining the integrity of the jawbone after tooth loss?
What is the most reliable clinical indicator for determining implant failure?
What is the most reliable clinical indicator for determining implant failure?
Which radiographic finding is most indicative of a failing dental implant?
Which radiographic finding is most indicative of a failing dental implant?
Why should dental professionals use light force when probing around dental implants?
Why should dental professionals use light force when probing around dental implants?
What would be the most appropriate initial treatment for a failing implant exhibiting inflammation and bleeding on probing, without mobility?
What would be the most appropriate initial treatment for a failing implant exhibiting inflammation and bleeding on probing, without mobility?
A dental implant was placed too close to an adjacent natural tooth. What potential complication is most likely to arise as a result of this placement?
A dental implant was placed too close to an adjacent natural tooth. What potential complication is most likely to arise as a result of this placement?
When should initial probing be performed around a newly placed and restored dental implant?
When should initial probing be performed around a newly placed and restored dental implant?
A patient presents with a dental implant that exhibits a wedge-shaped radiolucency on the mesial aspect. What does this radiographic finding suggest?
A patient presents with a dental implant that exhibits a wedge-shaped radiolucency on the mesial aspect. What does this radiographic finding suggest?
What is the rationale behind using plastic probes around dental implants?
What is the rationale behind using plastic probes around dental implants?
Which of the following materials used for subgingival scaling is characterized by its slender design and sharpenability?
Which of the following materials used for subgingival scaling is characterized by its slender design and sharpenability?
What is the recommended initial maintenance frequency for a patient following the restoration of a dental implant?
What is the recommended initial maintenance frequency for a patient following the restoration of a dental implant?
Which of the following factors warrants a more frequent dental implant maintenance schedule?
Which of the following factors warrants a more frequent dental implant maintenance schedule?
Why is routine polishing generally not recommended for dental implants, abutments, and related components?
Why is routine polishing generally not recommended for dental implants, abutments, and related components?
Which air abrasive powder is considered safe and effective for air polishing on rough implant surfaces?
Which air abrasive powder is considered safe and effective for air polishing on rough implant surfaces?
What is the most important factor in preventing peri-implant disease?
What is the most important factor in preventing peri-implant disease?
During a dental implant maintenance visit, which assessment is crucial for evaluating the functional integration and potential complications of the implant?
During a dental implant maintenance visit, which assessment is crucial for evaluating the functional integration and potential complications of the implant?
A patient presents with inflammation around a dental implant, but reports consistent and thorough self-care practices. What is the MOST appropriate next step for the dental professional?
A patient presents with inflammation around a dental implant, but reports consistent and thorough self-care practices. What is the MOST appropriate next step for the dental professional?
What is a primary self-care challenge associated with fixed prosthetic crowns?
What is a primary self-care challenge associated with fixed prosthetic crowns?
Why are interdental brushes recommended for patients with dental implants?
Why are interdental brushes recommended for patients with dental implants?
When caring for a removable implant-supported prosthesis, what is a crucial factor to consider?
When caring for a removable implant-supported prosthesis, what is a crucial factor to consider?
What is the most important consideration when selecting self-care devices for a patient with dental implants?
What is the most important consideration when selecting self-care devices for a patient with dental implants?
What is the best method for cleaning the underside of a metal bar connecting implant abutments?
What is the best method for cleaning the underside of a metal bar connecting implant abutments?
Why is biofilm control particularly important for patients with dental implants?
Why is biofilm control particularly important for patients with dental implants?
Which type of toothbrush is generally considered safe and effective for cleaning titanium implant surfaces?
Which type of toothbrush is generally considered safe and effective for cleaning titanium implant surfaces?
A patient with an implant-supported overdenture complains of persistent bad breath. Besides professional cleaning, what home care recommendation is most appropriate?
A patient with an implant-supported overdenture complains of persistent bad breath. Besides professional cleaning, what home care recommendation is most appropriate?
Flashcards
Dental Implant
Dental Implant
A nonbiologic device surgically inserted into the jawbone to replace a tooth or provide support for a multiunit prosthesis.
Dental Hygienist's Role
Dental Hygienist's Role
Plays an important role in patient education and professional maintenance of dental implants.
Dental Implant System Function
Dental Implant System Function
Can replace individual or multiple teeth by supporting a fixed bridge or removable denture.
Implant Body
Implant Body
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abutment
Abutment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Implant Body (Fixture)
Implant Body (Fixture)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abutment
Abutment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abutment Material
Abutment Material
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prosthetic crown/prosthesis
Prosthetic crown/prosthesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Titanium or titanium alloy
Titanium or titanium alloy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zirconia
Zirconia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Implant Abutment
Implant Abutment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteotomy Site
Osteotomy Site
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osseointegration
Osseointegration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peri-Implant Tissues
Peri-Implant Tissues
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peri-Implant Mucositis
Peri-Implant Mucositis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peri-Implant Mucositis: Reversibility
Peri-Implant Mucositis: Reversibility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diagnosing Peri-Implant Mucositis
Diagnosing Peri-Implant Mucositis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peri-Implantitis
Peri-Implantitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peri-Implantitis Characteristics
Peri-Implantitis Characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diagnosing Peri-Implantitis
Diagnosing Peri-Implantitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peri-implantitis: Clinical Signs
Peri-implantitis: Clinical Signs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Criteria for Peri-Implantitis Diagnosis
Criteria for Peri-Implantitis Diagnosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peri-implant Soft Tissue Indicators of a Failing Implant
Peri-implant Soft Tissue Indicators of a Failing Implant
Signup and view all the flashcards
Implant Mobility
Implant Mobility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radiographic Signs of a Failing Implant
Radiographic Signs of a Failing Implant
Signup and view all the flashcards
Treatment Modalities for Failing Implants
Treatment Modalities for Failing Implants
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nonsurgical Periodontal Instrumentation
Nonsurgical Periodontal Instrumentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subgingival Air Polishing
Subgingival Air Polishing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Initial Probing
Initial Probing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Probing Technique Around Implants
Probing Technique Around Implants
Signup and view all the flashcards
Titanium scalers
Titanium scalers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polymer scalers
Polymer scalers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Implant maintenance factors
Implant maintenance factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Initial implant maintenance
Initial implant maintenance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Long-term implant maintenance
Long-term implant maintenance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Routine implant polishing
Routine implant polishing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Air polishing implants
Air polishing implants
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patient self-care for implants
Patient self-care for implants
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peri-implant disease
Peri-implant disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fixed prosthetic crown
Fixed prosthetic crown
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flossing a crown
Flossing a crown
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tools for fixed prosthetic care
Tools for fixed prosthetic care
Signup and view all the flashcards
Removable implant prosthesis
Removable implant prosthesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Implant maintenance: Simplicity
Implant maintenance: Simplicity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cleaning a metal bar
Cleaning a metal bar
Signup and view all the flashcards
Implant Materials
Implant Materials
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- A dental implant is a nonbiologic device surgically inserted into the jawbone, replacing a tooth or providing support for multiunit prosthesis.
- A dental hygienist plays an important role in patient education and dental implant maintenance.
- Dental implants replace individual or multiple teeth, supporting fixed bridges or removable dentures.
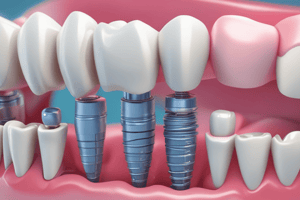
Anatomy of an Endosteal Dental Implant
- The implant body is the "root" of the implant surgically placed in the living alveolar bone.
- The abutment is a titanium post attaching to the implant body.
- The abutment protrudes partially or fully through the gingival tissue and supports the crown or denture, biocompatible with the body.
- The components of the implant system are the implant body/fixture, abutment, and prosthetic crown/prosthesis.
- The implant body is surgically placed into living alveolar bone and acts as the "root" of the implant.
- Implant body are usually made of titanium or titanium alloy, lightweight, biocompatible, noncorrosive, and poor conductors.
- Titanium implant body might be softer than other dental restorative metals, easily scratched, and can cause inflammatory reactions.
- Ceramics like zirconia serve as alternative materials, with better outcomes for patients with thin gingival phenotype.
- The implant abutment is a metal post that connects the prosthesis to the implant body, secured in place, and protrudes into the oral cavity.
- Implant abutments can be made of titanium or zirconia (ceramic).
Peri-Implant Tissues
- Hard and soft tissues that surround the implant.
- Junctional epithelium attaches to the implant or abutment surface which serves as a biologic seal.
- Connective tissue runs parallel to the implant or abutment, or encircles the structure.
- No periodontal ligament or cementum exists.
- Alveolar bone is in direct osseointegration contact with the implant.
- Epithelium adapts to the abutment post or implant, creating a cuff-like perimucosal biological seal, functioning as a barrier between the implant and oral cavity.
- The sulcus is lined by sulcular epithelium, and the junctional epithelium surrounds the implant abutment or collar.
- The implant surface lacks cementum.
- On natural teeth, supragingival fibers brace the gingival margin and periodontal ligament suspends the tooth in its socket, and fibers are a barrier to infection.
- Supragingival fiber bundles support healthy gingiva against the abutment.
- There are no periodontal ligament fibers.
- Periodontal probe passes easily through the inflamed peri-implant soft tissues to apical connective tissue or close to peri-implant alveolar bone.
- Osseointegration is the direct contact of living bone with the implant body surface.
- Criteria includes absence of clinical mobility, no discomfort/pain, no increased bone loss, and <0.2mm of bone loss annually after the first year to determine success.
Peri-Implant Health
- Characterized by the absence of erythema, bleeding on probing, swelling, and suppuration.
- There are no visual differences between healthy peri-implant tissues and healthy periodontal tissues.
- Probing depths may be deeper at a healthy implant site.
Peri-Implant Mucositis
- Plaque biofilm-induced inflammation of soft tissues with no loss of supporting bone, localized around the dental implant.
- It occurs in 80% of patients and 50% of sites, reversing when etiologic factors are removed.
- Diagnosis requires visual soft tissue inflammation signs, bleeding and/or suppuration upon probing, increased probing depths, and absence of bone loss.
- Features knifed-edge tissue, rounded and thickened tissue, and no signs of significant pathology.
Peri-Implantitis
- It is periodontitis affecting soft and hard tissues surrounding functioning osseointegrated dental implant.
- Characterized by plaque biofilm-induced inflammation and progressive alveolar bone loss.
- Onset may occur early during follow-up, progressing in a nonlinear, accelerating pattern.
- A diagnosis comes through detecting radiographic bone loss around implant that range from 6.61% to 47%. Residual cement could also suggest peri-implantitis.
- Other diagnostic criteria include visual signs of inflammation, bleeding and/or suppuration, progressive bone loss comparing baseline to 12 months, or lack of baseline information showing radiographic evidence ≥ 3mm / probing depths ≥ 6mm.
- Bone resorption occurs after tooth loss, which leads to hard-tissue deficiencies.
- Contributing factors include loss of periodontal support, endodontic infections, thin buccal bone plates, extraction with additional trauma, traumatic injury systemic diseases impairing normal bone remodeling, pneumatization of maxillary sinus.
- Peri-implant mucositis results primarily from biofilm-induced infection and is considered a precursor to peri-implantitis.
- Peri-implantitis is a result of overwhelming bacterial infection, progresses similar to periodontitis, but no single microorganism implicated as the causative agent.
Risk Factors
- History of previous periodontal disease
- Poor plaque biofilm control and lack of regular maintenance therapy
- Smoking
- Residual cement
- Biomechanical forces and overload
- Spatial placement of implants
- Implants can fail because of ill fitting prosthesis that result in occlusal interference with protrusive movements.
- Positioning of implants to close together or to far facially.
- Soft tissue indicators of a failing implant include peri-implant pocket, bleeding after probing, and suppuration.
- Implant mobility is the best indicator for implant failure.
- Radiographic signs include vertical destruction of crestal bone, wedge-shaped defects, and bone loss.
- Available treatment methods include nonsurgical periodontal instrumentation, antiseptics/ chlorhexidine, local and/or systemic antibiotics, and access flap surgery & bone grafting.
- There is no standard protocol.
- Using nonsurgical periodontal instrumentation with local minocycline or chlorhexidine can he helpful.
- Subgingival glycine air powder polishing to remove biofilm may reduce inflammation.
Probing
- Initial to asess peri-implant tissues after the final restoration is installed; some surgeons avoid any until healing is complete after abutment connection.
- It is recommened to use light force since the peri mucosal seal is weakly adherent to the titanium surface.
- Plastic probes are often preferred, but metal probes are okay if pressure is kept light.
Bleeding and Suppuration
- Indicators of peri-implant tissue inflammation and improve biofilm removal.
- The presence of bleeding or increased probing depth warrants radiographic assessment.
- All locations must be recorded.
- Radiographs should be taken prior to cementation and when implant crown is on.
- It is also recommended to take post-prosthetic insertion x-ray when cement is present and to include follow-up approximately once a year.
- Baseline radiographs include placing initial implant, placing final prosthesis, and during implant maintenance.
Goals of Maintenance Therapy
- Maintenance of alveolar bone support
- Control of inflammation
- Healthy implant
- Fully functional neighboring teeth
Dental Appointment Maintenance
- Modern implants can be difficult to recognize so the exact locations must be documented in the chart clearly.
- Update radiographs annually prior to instrumentation
- Supragingival scaling with traditional instruments
- Subgingival scaling with titanium metals/instruments.
- Individualized treatment plans depends on previous examinations, evaluation of peri-implant tissue health/stability, any occlusal issues, self care assessments, and a radiographic examination.
- A 3-month maintenance interval for the first year and then every 3 to 6 months unless there is less bone support.
- Patients with fixed or removable, supported restorations - should see someone every 6 months.
- Meticulous care is vital for long-term implant care so instruction in self-care techniqes for natural/ supported teeth should alwasy me demonstrated.
- The material compatible with dental implants.
- Air is an important component of the oral aids used.
- Do not use routine implants, abutments, but improve titanium that would only be surface.
- Use dental abrasives for rough implants (glycine is always great!)
- Preventing care is important because neglect/poor plaque controls the source of the infection.
- Fixed prosthetic crowns sit over implants.
- Patients challenge with adaptation in the crowns when they mimic natural tooth function.
- Patients need to use floss along margins.
- Restore to resemble to be used to fix with dentures and complex prostheses.
- Standard soft toothbrush.
- Power toothbrush with titanium
- Interdental brushes for biofilm removal.
- Floss and irrigators subgingivally. Antimicrobial to care for everything at the end.
- Traditional dentures.
- O-rings and magnets, with clips.
- Removable.
- Tools: Titanium!
- Fewer devices!
- Selective easy to use!
- Tufted floss to use to clean or gauze
- Tufted is helpful!
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.