Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the characteristic feature of a Cyclostomata's mouth?
What is the characteristic feature of a Cyclostomata's mouth?
- It has a sucking mouth (correct)
- It has a cartilaginous cranium
- It has paired fins
- It has jaws
How do Cyclostomes carry out respiration?
How do Cyclostomes carry out respiration?
- Through their scales
- Through their gill slits (correct)
- Through their paired fins
- Through their caudal fin
What is the purpose of the caudal fin in a lamprey?
What is the purpose of the caudal fin in a lamprey?
- To facilitate respiration
- To help with propulsion and steering in the water (correct)
- To sense the environment
- To defend against predators
What is the habitat of Cyclostomes?
What is the habitat of Cyclostomes?
What happens to Cyclostomes after spawning?
What happens to Cyclostomes after spawning?
What is Petromyzon an example of?
What is Petromyzon an example of?
What is unique about the body of Cyclostomes?
What is unique about the body of Cyclostomes?
What is the function of the gill slits in Cyclostomes?
What is the function of the gill slits in Cyclostomes?
What is the shape of the mouth in Cyclostomes?
What is the shape of the mouth in Cyclostomes?
What is the characteristic of the vertebral column in Cyclostomes?
What is the characteristic of the vertebral column in Cyclostomes?
What is the genus of hagfish, which is an example of Cyclostomata?
What is the genus of hagfish, which is an example of Cyclostomata?
What happens to the larvae of Cyclostomes after metamorphosis?
What happens to the larvae of Cyclostomes after metamorphosis?
What is the characteristic of the cranium in Cyclostomes?
What is the characteristic of the cranium in Cyclostomes?
What is the function of the gill slits in Cyclostomes?
What is the function of the gill slits in Cyclostomes?
What is the typical habitat of Cyclostomes during their adult life?
What is the typical habitat of Cyclostomes during their adult life?
What is the characteristic of the body of Cyclostomes?
What is the characteristic of the body of Cyclostomes?
What is the genus of lamprey, which is an example of Cyclostomata?
What is the genus of lamprey, which is an example of Cyclostomata?
What is unique about the circulatory system of Cyclostomes?
What is unique about the circulatory system of Cyclostomes?
What is the primary function of the gill slits in Cyclostomes?
What is the primary function of the gill slits in Cyclostomes?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the body of Cyclostomes?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the body of Cyclostomes?
What is the purpose of Cyclostomes' migration to freshwater?
What is the purpose of Cyclostomes' migration to freshwater?
What is the characteristic of the dorsal fin in lampreys?
What is the characteristic of the dorsal fin in lampreys?
What is the fate of Cyclostomes after spawning?
What is the fate of Cyclostomes after spawning?
Which of the following is an example of Cyclostomata?
Which of the following is an example of Cyclostomata?
What is the main function of the gill slits in Cyclostomes?
What is the main function of the gill slits in Cyclostomes?
What is unique about the body of Cyclostomes?
What is unique about the body of Cyclostomes?
Where do Cyclostomes typically migrate to for spawning?
Where do Cyclostomes typically migrate to for spawning?
What is the characteristic of the vertebral column in Cyclostomes?
What is the characteristic of the vertebral column in Cyclostomes?
What is the typical number of dorsal fins in lampreys?
What is the typical number of dorsal fins in lampreys?
What happens to the larvae of Cyclostomes after metamorphosis?
What happens to the larvae of Cyclostomes after metamorphosis?
What is the primary function of the circular mouth in Cyclostomes?
What is the primary function of the circular mouth in Cyclostomes?
What is the purpose of the cartilaginous vertebral column in Cyclostomes?
What is the purpose of the cartilaginous vertebral column in Cyclostomes?
What is unique about the circulatory system of Cyclostomes?
What is unique about the circulatory system of Cyclostomes?
Why do Cyclostomes migrate to freshwater?
Why do Cyclostomes migrate to freshwater?
What is the typical body shape of Cyclostomes?
What is the typical body shape of Cyclostomes?
What is the function of the gill slits in Cyclostomes?
What is the function of the gill slits in Cyclostomes?
What is the primary function of the sucking mouth in Cyclostomes?
What is the primary function of the sucking mouth in Cyclostomes?
What is the characteristic of the body of Cyclostomes that allows them to move efficiently in the water?
What is the characteristic of the body of Cyclostomes that allows them to move efficiently in the water?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of Cyclostomes?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of Cyclostomes?
What is the purpose of the unique migration pattern of Cyclostomes?
What is the purpose of the unique migration pattern of Cyclostomes?
What is the significance of the gill slits in Cyclostomes?
What is the significance of the gill slits in Cyclostomes?
What is the characteristic of the dorsal fin in lampreys, which is an example of Cyclostomata?
What is the characteristic of the dorsal fin in lampreys, which is an example of Cyclostomata?
What is the main reason why Cyclostomes migrate to freshwater?
What is the main reason why Cyclostomes migrate to freshwater?
What is the function of the caudal fin in lampreys?
What is the function of the caudal fin in lampreys?
What is unique about the skeletal system of Cyclostomes?
What is unique about the skeletal system of Cyclostomes?
What is the characteristic of the circulatory system of Cyclostomes?
What is the characteristic of the circulatory system of Cyclostomes?
What is the primary function of the gill slits in Cyclostomes?
What is the primary function of the gill slits in Cyclostomes?
What is the fate of Cyclostomes after they spawn?
What is the fate of Cyclostomes after they spawn?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Characteristics of Cyclostomata
- Cyclostomata is a class of Chordata
- All living members of Cyclostomata are ectoparasites
- Cyclostomes have an elongated body
- Cyclostomes have 6-15 pairs of gill slits used for respiration
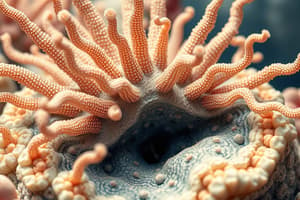
- Cyclostomes have a circular, sucking mouth without jaws
- Cyclostomes' bodies lack scales and paired fins
- Cyclostomes have a cartilaginous cranium and vertebral column
Physical Characteristics of Lampreys and Hagfish
- Lampreys typically have one or two dorsal fins along their back
- Caudal Fin in lamprey is located at the tail end, helping with propulsion and steering
- Petromyzon is the genus of lamprey, an example of Cyclostomata
- Myxine is the genus of hagfish, an example of Cyclostomata
Life Cycle and Habitat
- Cyclostomes are marine, but migrate to freshwater for spawning
- Cyclostomes die within a few days after spawning
- Cyclostomes' larvae return to the ocean after metamorphosis
Characteristics of Cyclostomata
- Cyclostomata is a class of Chordata
- All living members of Cyclostomata are ectoparasites
- Cyclostomes have an elongated body
- Cyclostomes have 6-15 pairs of gill slits used for respiration
- Cyclostomes have a circular, sucking mouth without jaws
- Cyclostomes' bodies lack scales and paired fins
- Cyclostomes have a cartilaginous cranium and vertebral column
Physical Characteristics of Lampreys and Hagfish
- Lampreys typically have one or two dorsal fins along their back
- Caudal Fin in lamprey is located at the tail end, helping with propulsion and steering
- Petromyzon is the genus of lamprey, an example of Cyclostomata
- Myxine is the genus of hagfish, an example of Cyclostomata
Life Cycle and Habitat
- Cyclostomes are marine, but migrate to freshwater for spawning
- Cyclostomes die within a few days after spawning
- Cyclostomes' larvae return to the ocean after metamorphosis
Characteristics of Cyclostomata
- Cyclostomata is a class of Chordata
- All living members of Cyclostomata are ectoparasites
- Cyclostomes have an elongated body
- Cyclostomes have 6-15 pairs of gill slits used for respiration
- Cyclostomes have a circular, sucking mouth without jaws
- Cyclostomes' bodies lack scales and paired fins
- Cyclostomes have a cartilaginous cranium and vertebral column
Physical Characteristics of Lampreys and Hagfish
- Lampreys typically have one or two dorsal fins along their back
- Caudal Fin in lamprey is located at the tail end, helping with propulsion and steering
- Petromyzon is the genus of lamprey, an example of Cyclostomata
- Myxine is the genus of hagfish, an example of Cyclostomata
Life Cycle and Habitat
- Cyclostomes are marine, but migrate to freshwater for spawning
- Cyclostomes die within a few days after spawning
- Cyclostomes' larvae return to the ocean after metamorphosis
Characteristics of Cyclostomata
- Cyclostomata is a class of Chordata
- All living members of Cyclostomata are ectoparasites
- Cyclostomes have an elongated body
- Cyclostomes have 6-15 pairs of gill slits used for respiration
- Cyclostomes have a circular, sucking mouth without jaws
- Cyclostomes' bodies lack scales and paired fins
- Cyclostomes have a cartilaginous cranium and vertebral column
Physical Characteristics of Lampreys and Hagfish
- Lampreys typically have one or two dorsal fins along their back
- Caudal Fin in lamprey is located at the tail end, helping with propulsion and steering
- Petromyzon is the genus of lamprey, an example of Cyclostomata
- Myxine is the genus of hagfish, an example of Cyclostomata
Life Cycle and Habitat
- Cyclostomes are marine, but migrate to freshwater for spawning
- Cyclostomes die within a few days after spawning
- Cyclostomes' larvae return to the ocean after metamorphosis
Characteristics of Cyclostomata
- Cyclostomata is a class of Chordata
- All living members of Cyclostomata are ectoparasites
- Cyclostomes have an elongated body
- Cyclostomes have 6-15 pairs of gill slits used for respiration
- Cyclostomes have a circular, sucking mouth without jaws
- Cyclostomes' bodies lack scales and paired fins
- Cyclostomes have a cartilaginous cranium and vertebral column
Physical Characteristics of Lampreys and Hagfish
- Lampreys typically have one or two dorsal fins along their back
- Caudal Fin in lamprey is located at the tail end, helping with propulsion and steering
- Petromyzon is the genus of lamprey, an example of Cyclostomata
- Myxine is the genus of hagfish, an example of Cyclostomata
Life Cycle and Habitat
- Cyclostomes are marine, but migrate to freshwater for spawning
- Cyclostomes die within a few days after spawning
- Cyclostomes' larvae return to the ocean after metamorphosis
Characteristics of Cyclostomata
- Cyclostomata is a class of Chordata
- All living members of Cyclostomata are ectoparasites
- Cyclostomes have an elongated body
- Cyclostomes have 6-15 pairs of gill slits used for respiration
- Cyclostomes have a circular, sucking mouth without jaws
- Cyclostomes' bodies lack scales and paired fins
- Cyclostomes have a cartilaginous cranium and vertebral column
Physical Characteristics of Lampreys and Hagfish
- Lampreys typically have one or two dorsal fins along their back
- Caudal Fin in lamprey is located at the tail end, helping with propulsion and steering
- Petromyzon is the genus of lamprey, an example of Cyclostomata
- Myxine is the genus of hagfish, an example of Cyclostomata
Life Cycle and Habitat
- Cyclostomes are marine, but migrate to freshwater for spawning
- Cyclostomes die within a few days after spawning
- Cyclostomes' larvae return to the ocean after metamorphosis
Characteristics of Cyclostomata
- Cyclostomata is a class of Chordata
- All living members of Cyclostomata are ectoparasites
- Cyclostomes have an elongated body
- Cyclostomes have 6-15 pairs of gill slits used for respiration
- Cyclostomes have a circular, sucking mouth without jaws
- Cyclostomes' bodies lack scales and paired fins
- Cyclostomes have a cartilaginous cranium and vertebral column
Physical Characteristics of Lampreys and Hagfish
- Lampreys typically have one or two dorsal fins along their back
- Caudal Fin in lamprey is located at the tail end, helping with propulsion and steering
- Petromyzon is the genus of lamprey, an example of Cyclostomata
- Myxine is the genus of hagfish, an example of Cyclostomata
Life Cycle and Habitat
- Cyclostomes are marine, but migrate to freshwater for spawning
- Cyclostomes die within a few days after spawning
- Cyclostomes' larvae return to the ocean after metamorphosis
Characteristics of Cyclostomata
- Cyclostomata is a class of Chordata
- All living members of Cyclostomata are ectoparasites
- Cyclostomes have an elongated body
- Cyclostomes have 6-15 pairs of gill slits used for respiration
- Cyclostomes have a circular, sucking mouth without jaws
- Cyclostomes' bodies lack scales and paired fins
- Cyclostomes have a cartilaginous cranium and vertebral column
Physical Characteristics of Lampreys and Hagfish
- Lampreys typically have one or two dorsal fins along their back
- Caudal Fin in lamprey is located at the tail end, helping with propulsion and steering
- Petromyzon is the genus of lamprey, an example of Cyclostomata
- Myxine is the genus of hagfish, an example of Cyclostomata
Life Cycle and Habitat
- Cyclostomes are marine, but migrate to freshwater for spawning
- Cyclostomes die within a few days after spawning
- Cyclostomes' larvae return to the ocean after metamorphosis
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.