Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the general shape of the cubital fossa?
What is the general shape of the cubital fossa?
- Rectangular
- Square
- Circular
- Triangular (correct)
Which of the following structures forms the base (superior boundary) of the cubital fossa?
Which of the following structures forms the base (superior boundary) of the cubital fossa?
- Lateral border of the pronator teres muscle
- Medial border of the brachioradialis muscle
- Imaginary line between the epicondyles of the humerus (correct)
- Bicipital aponeurosis
Which muscle's medial border contributes to the lateral boundary of the cubital fossa?
Which muscle's medial border contributes to the lateral boundary of the cubital fossa?
- Biceps brachii
- Brachioradialis (correct)
- Brachialis
- Pronator teres
What structure is located medially as part of the floor of the cubital fossa?
What structure is located medially as part of the floor of the cubital fossa?
Which nerve and its branch pass through the cubital fossa?
Which nerve and its branch pass through the cubital fossa?
Which of the following structures does NOT pass through the cubital fossa?
Which of the following structures does NOT pass through the cubital fossa?
The superficial fascia of the cubital fossa contains which vein?
The superficial fascia of the cubital fossa contains which vein?
What is the correct order of the contents within the cubital fossa from lateral to medial?
What is the correct order of the contents within the cubital fossa from lateral to medial?
The medial border of which muscle forms the lateral boundary of the cubital fossa?
The medial border of which muscle forms the lateral boundary of the cubital fossa?
What is the primary nerve that innervates the majority of the anterior compartment of the forearm?
What is the primary nerve that innervates the majority of the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which of the following is NOT a muscle within the superficial layer of the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which of the following is NOT a muscle within the superficial layer of the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which muscle assists in pronation of the forearm and contributes to forming the medial border of the cubital fossa?
Which muscle assists in pronation of the forearm and contributes to forming the medial border of the cubital fossa?
What action is primarily associated with the flexor carpi radialis?
What action is primarily associated with the flexor carpi radialis?
Which nerve innervates the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle?
Which nerve innervates the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle?
What is the insertion point for the flexor carpi ulnaris?
What is the insertion point for the flexor carpi ulnaris?
Which muscle of the anterior forearm is sometimes absent in some individuals?
Which muscle of the anterior forearm is sometimes absent in some individuals?
Which of the following muscles is located in the intermediate layer of the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which of the following muscles is located in the intermediate layer of the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which of the listed muscles is responsible for flexing the middle phalanges of the digits?
Which of the listed muscles is responsible for flexing the middle phalanges of the digits?
What is the nerve supply for the flexor digitorum superficialis?
What is the nerve supply for the flexor digitorum superficialis?
Which of the following muscles is located in the deep layer of the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which of the following muscles is located in the deep layer of the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which of the following actions is caused by flexor digitorum profundus?
Which of the following actions is caused by flexor digitorum profundus?
The flexor digitorum profundus is unique in that it's innervated by two different nerves; which two?
The flexor digitorum profundus is unique in that it's innervated by two different nerves; which two?
What is the primary action of the pronator quadratus muscle?
What is the primary action of the pronator quadratus muscle?
Which nerve innervates the pronator quadratus muscle?
Which nerve innervates the pronator quadratus muscle?
Which artery gives rise to the anterior and posterior interosseous arteries?
Which artery gives rise to the anterior and posterior interosseous arteries?
Which artery is the larger of the two terminal branches of the brachial artery?
Which artery is the larger of the two terminal branches of the brachial artery?
The ulnar artery forms which structure in the hand?
The ulnar artery forms which structure in the hand?
Which of the following best describes the path of the radial artery in the forearm?
Which of the following best describes the path of the radial artery in the forearm?
The radial artery is smaller than the ulnar artery and begins in the cabital fossa at the level of the...
The radial artery is smaller than the ulnar artery and begins in the cabital fossa at the level of the...
Which of the following statements accurately describes the innervation pattern of the muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the innervation pattern of the muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm?
What is the key functional difference in the actions of the flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) and flexor digitorum profundus (FDP)?
What is the key functional difference in the actions of the flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) and flexor digitorum profundus (FDP)?
Which of the following lists ONLY deep flexor muscles of the forearm?
Which of the following lists ONLY deep flexor muscles of the forearm?
A patient presents with an inability to flex the distal interphalangeal joints of their 4th and 5th fingers, which nerve is MOST likely injured?
A patient presents with an inability to flex the distal interphalangeal joints of their 4th and 5th fingers, which nerve is MOST likely injured?
After a stab wound to the anterior forearm, a patient has weakness in wrist flexion and adduction. Which muscle is MOST likely affected?
After a stab wound to the anterior forearm, a patient has weakness in wrist flexion and adduction. Which muscle is MOST likely affected?
In a procedure, a surgeon needs to identify the structure that constitutes the lateral border of the cubital fossa. Which of the following is the correct anatomical landmark?
In a procedure, a surgeon needs to identify the structure that constitutes the lateral border of the cubital fossa. Which of the following is the correct anatomical landmark?
A weightlifter strains his forearm. He can still flex his wrist, but has difficulty flexing his thumb at the interphalangeal joint. Which muscle is MOST likely injured?
A weightlifter strains his forearm. He can still flex his wrist, but has difficulty flexing his thumb at the interphalangeal joint. Which muscle is MOST likely injured?
A surgeon is repairing a lacerated brachial artery in the cubital fossa. Which structure is MOST at risk of iatrogenic injury during this procedure?
A surgeon is repairing a lacerated brachial artery in the cubital fossa. Which structure is MOST at risk of iatrogenic injury during this procedure?
A medical student is studying the anterior compartment of the forearm. Which statement accurately describes the arrangement of the superficial muscles from lateral to medial?
A medical student is studying the anterior compartment of the forearm. Which statement accurately describes the arrangement of the superficial muscles from lateral to medial?
After a motorcycle accident, a patient is diagnosed with damage to the anterior interosseous nerve. Which specific function would be MOST affected in this patient?
After a motorcycle accident, a patient is diagnosed with damage to the anterior interosseous nerve. Which specific function would be MOST affected in this patient?
A patient reports numbness and tingling affecting the palmar aspect of the first three digits. The symptoms worsen with repetitive wrist flexion. What anatomical structure is MOST likely compressing the median nerve in this scenario?
A patient reports numbness and tingling affecting the palmar aspect of the first three digits. The symptoms worsen with repetitive wrist flexion. What anatomical structure is MOST likely compressing the median nerve in this scenario?
During a surgical approach to the distal radius, a surgeon must carefully retract the tendons of the wrist flexors. What is the MOST medial tendon that the surgeon MUST identify and protect to avoid functional deficits?
During a surgical approach to the distal radius, a surgeon must carefully retract the tendons of the wrist flexors. What is the MOST medial tendon that the surgeon MUST identify and protect to avoid functional deficits?
A competitive arm wrestler experiences a sudden, sharp pain in their cubital fossa during a match. They are now unable to strongly supinate their forearm, and they also have difficulty flexing their elbow when the forearm is supinated. Which structure is MOST likely injured?
A competitive arm wrestler experiences a sudden, sharp pain in their cubital fossa during a match. They are now unable to strongly supinate their forearm, and they also have difficulty flexing their elbow when the forearm is supinated. Which structure is MOST likely injured?
Flashcards
Cubital Fossa Definition
Cubital Fossa Definition
A triangular space in front of the elbow joint.
Cubital Fossa Base
Cubital Fossa Base
Imaginary line between the epicondyles of the humerus
Cubital Fossa Lateral Border
Cubital Fossa Lateral Border
Medial border of the brachioradialis muscle
Cubital Fossa Medial Border
Cubital Fossa Medial Border
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cubital Fossa Apex
Cubital Fossa Apex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cubital Fossa Roof
Cubital Fossa Roof
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cubital Fossa Floor
Cubital Fossa Floor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cubital Fossa Contents (lateral to medial)
Cubital Fossa Contents (lateral to medial)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anterior Compartment of Forearm Contents
Anterior Compartment of Forearm Contents
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscles in Anterior Forearm
Muscles in Anterior Forearm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vessels in Anterior Forearm
Vessels in Anterior Forearm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nerves in Anterior Forearm
Nerves in Anterior Forearm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pronator Teres -
Pronator Teres -
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flexor Carpi Radialis
Flexor Carpi Radialis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Palmaris Longus
Palmaris Longus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pronator Teres Action
Pronator Teres Action
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flexor Pollicis Longus
Flexor Pollicis Longus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Flexor Digitorum Profundus
Flexor Digitorum Profundus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pronator Quadratus
Pronator Quadratus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pronator Quadratus function
Pronator Quadratus function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ulnar Artery Definition
Ulnar Artery Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ulnar Artery Branches
Ulnar Artery Branches
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radial Artery Definition
Radial Artery Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Median Nerve Supply.
Median Nerve Supply.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Objectives
- By the end of this lecture, students should be able to describe the cubital fossa (definition, boundaries, and contents).
- Students should be able to list the names of the Flexors Group of Forearm (superficial and deep muscles).
- Students should be able to identify the common flexor origin of flexor muscles and their innervation and movements.
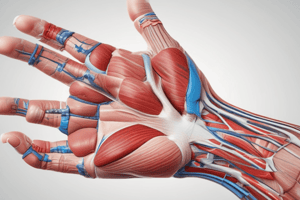
Cubital Fossa
- Description: A triangular space in front of the elbow joint.
Cubital Fossa Boundaries
- Base: An imaginary line between the 2 epicondyles of the humerus.
- Lateral Boundary: Medial border of brachioradialis.
- Medial Boundary: Lateral border of pronator teres.
- Apex: Where the brachioradialis overlaps the pronator teres.
Cubital Fossa (Roof)
- Skin
- Superficial fascia contains the cephalic vein, lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm, basilic vein, medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm and medial cubital vein.
- Deep fascia
- Bicipital aponeurosis
Cubital Fossa (Floor)
- Brachialis (medially)
- Supinator (laterally)
Cubital Fossa Contents (From lateral to medial)
- Radial nerve and its deep branch.
- Tendon of biceps brachii.
- Termination of the brachial artery and the beginning of the radial and ulnar arteries.
- Median nerve.
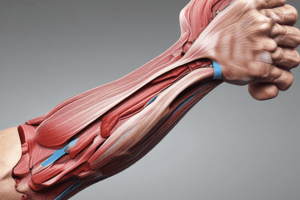
Components of the Anterior Compartment of the Forearm
- Muscles
- Nerves
- Vessels
Contents of the Anterior Compartment of the Forearm
- There are 8 muscles arranged in two groups: superficial (5) and deep (3)
- The vessels are the radial and ulnar.
- The nerves are the median and ulnar nerves, including the anterior interosseous branch of the median nerve.
Pronator Teres Muscle
- Origin: Two heads, humeral and ulnar.
- Insertion: Pronator tuberosity on the middle lateral surface of the radius.
- Nerve supply: Median nerve.
- Action: Pronation of the forearm and helps in flexion of the forearm.
- The lateral border forms the medial boundary of the cubital fossa.
- The median nerve passes between the two heads, and the ulnar artery passes deep to the ulnar head.
Flexor Carpi Radialis
- Origin: Medial epicondyle and adjoining deep fascia.
- Course: Forms a fusiform belly and a tendon in the middle of the forearm.
- Located at the wrist and accompanied by the tendon of the brachioradialis laterally.
- At this location the radial artery intervenes between two tendons.
- Insertion: Palmer surface of the base of the second and third metacarpal bones.
- Nerve Supply: Median nerve.
- Action: Flexion of the wrist and abduction of the wrist along with the ECRL (Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus) & ECRB (Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis).
Palmaris Longus
- Origin: Medial epicondyle of the humerus.
- Course: Long tendon passing in front of the flexor retinaculum.
- Insertion: Continues as the central part of the palmar aponeurosis.
- Nerve Supply: Median nerve.
- Action: Weak flexor of the wrist.
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
- Origin: Two heads, humeral head, which originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus, and ulnar head, which originates from the medial margin of the olecranon process, and 2/3rd of the posterior border of the ulna.
- Course: The two heads form a tendinous arch, where the ulnar nerve and posterior ulnar recurrent artery passes below it.
- Insertion: Pisiform bone.
- Nerve Supply: Ulnar nerve.
- Action: Flexor of the wrist, along with ECU- Adduction.
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
- Origin, 2 heads
- Humeroulnar:
- Medial epicondyle of humerus
- Medial margin of coronoid process
- Radial head:
- Whole length of anterior oblique line of radius
- Course: Forms four tendons above the wrist, arranged in superficial (mostly radial) and deep groups of two each.
- Passes below the flexor retinaculum and diverges in the palm; superficial for the middle and ring fingers, and deep for the index and ring fingers
- Nerve supply: Median nerve.
Distal attachments of flexor digitorum superficialis (cont.):
- Insertion: At the base of the proximal phalanx, each digit tendon splits into two allowing for the passage of the tendon of F digitorum profundus
- The slips reunite again, and split again to be attached to the side of the shaft of the middle phalanx.
- Action: Flexion of the middle phalanx at the proximal interphalangeal joint.
- Action: Prolonged contraction leads to flexion of the metacarpophalangeal joint and the wrist joint
Deep Flexors
- Flexor Pollicis Longus
- Flexor Digitorum Profundus
- Pronator Quadratus
Flexor Pollicis Longus
- Origin: The anterior surface of the shaft of the radius below the anterior oblique line.
- Origin: Adjoining interosseous membrane.
- Course: Passes below the flexor retinaculum.
- Insertion: Palmar surface of the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb.
- Nerve Supply: Anterior interosseous branch of the median nerve.
- Action: Flexor of the thumb.
Flexor Digitorum Profundus
- Origin: Anterior and medial surface of the upper three-fourths of the shaft of the ulna, including the medial surface of coronoid and olecranon process.
- Origin: Adjoining interosseous membrane and the upper three-fourths of the posterior border of the ulna.
- Course: Forms four tendons.
- Course: Remains united except for the tendon for the index finger.
- Passes deep to the flexor retinaculum.
- Course: Diverges in the palm.
- Passes in between slips of superficialis.
- Course: Give origin to four lumbricals.
- Insertion: Palmar surface of the base of terminal (distal) phalanx of medial four fingers.
- Nerve Supply: Medial part- Ulnar nerve, Lateral part - Anterior Interosseous branch of median nerve
- Action: Flexes the terminal phalanx.
Pronator Quadratus
- Description: Quadrilateral muscle extends anteriorly in front of the interosseous membrane to both bones of the forearm.
- Origin: The bony ridge on the antero-medial surface of the lower 1/4th of the ulna.
- Insertion: The anterior surface of the lower 1/4th of the radius and adjoining anterior border of radius, triangular area just above the ulnar notch.
- Nerve Supply: Anterior interosseous branch of the median nerve.
Functional Classification of Flexor Muscles
- Flexors of the Wrist: FI. Carpi Radialis, FI. Carpi Ulnaris
- Flexors of Middle Phalanges: FI. Digitorum Superficialis
- Flexors of Distal Phalanges: FI. Digitorum Profundus, FI. Pollicis Longus
- Pronators of the Forearm: Pronator Teres, Pronator Quadratus
Ulnar Artery
- The larger of the two terminal branches of the brachial artery.
- Begins in the cubital fossa at the level of the neck of the radius.
- Descends through the anterior compartment of the forearm.
- Enters the palm in front of the flexor retinaculum with the ulnar nerve.
- Ends by forming the superficial palmar arch by anastomosing with the superficial palmar branch of the radial artery.
Ulnar Artery Branches
- Muscular branches.
- A recurrent branch for anastomosis around the elbow joint.
- A common interosseous artery, which gives anterior and posterior interosseous arteries.
- Branches to anastomoses around the wrist joint.
Radial Artery
- Smaller terminal branch of the brachial artery.
- Begins in the cubital fossa at the level of the neck of the radius.
- Descends downward and laterally.
- Leaves the forearm by winding around the lateral aspect of the wrist to reach the dorsum of the hand.
Radial Artery Branches
- Muscular
- Recurrent branch for anastomosis around the elbow joint.
- Superficial palmar branch, joins the ulnar artery to form the superficial palmar arch.
Nerve Supply
- All muscles on the front of the forearm are supplied by the median nerve except the flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) and the medial half of the flexor digitorum profundus (FDP), which are supplied by the ulnar nerve.
Superficial Muscles
- The superficial group of muscles on the front of the forearm consists of five muscles arranged from lateral to medial:
- Pronator teres
- Flexor carpi radialis
- Palmaris longus (15% are absent)
- Flexor digitorum superficialis (lies in a deeper plane)
- Flexor carpi ulnaris
- General Info:
- Some have an additional origin from other bones.
- The pronator teres is inserted in the radius, & the remaining 4 muscles are inserted in the hand.
- All are supplied by the median nerve except the flexor carpi ulnaris supplied by the ulnar nerve.
- All help in flexion of the elbow joint and have specific actions indicated by the name of the muscles.
- The nerve that innervates the flexor carpi radialis is the median nerve.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.