Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which muscle is located in the superficial compartment of the anterior forearm?
Which muscle is located in the superficial compartment of the anterior forearm?
- Flexor digitorum superficialis
- Flexor carpi ulnaris
- Pronator teres (correct)
- Flexor policis longus
What is the origin of Pronator teres muscle?
What is the origin of Pronator teres muscle?
- Medial border of coronoid process (correct)
- Lateral epicondyle of humerus
- Radial tuberosity
- Medial epicondyle of humerus
Which muscle is NOT part of the superficial compartment of the anterior forearm?
Which muscle is NOT part of the superficial compartment of the anterior forearm?
- Flexor carpi radialis
- Palmaris longus
- Flexor digitorum profundus (correct)
- Flexor carpi ulnaris
What is the main function of the Flexor carpi radialis muscle?
What is the main function of the Flexor carpi radialis muscle?
Which muscle is located in the middle compartment of the anterior forearm?
Which muscle is located in the middle compartment of the anterior forearm?
Which vein is a superficial vein in the forearm?
Which vein is a superficial vein in the forearm?
Which structure forms the floor of the cubital fossa?
Which structure forms the floor of the cubital fossa?
Which muscle originates from the medial epicondyle, CFT, and antebrachial fascia and is responsible for flexion and abduction of the wrist?
Which muscle originates from the medial epicondyle, CFT, and antebrachial fascia and is responsible for flexion and abduction of the wrist?
What is the function of the pronator quadratus muscle?
What is the function of the pronator quadratus muscle?
Which muscle primarily flexes the distal phalanx of the thumb?
Which muscle primarily flexes the distal phalanx of the thumb?
What nerve innervates the Flexor carpi radialis muscle?
What nerve innervates the Flexor carpi radialis muscle?
The Cubital Fossa is bounded by which two muscles on its lateral and medial sides?
The Cubital Fossa is bounded by which two muscles on its lateral and medial sides?
What is the insertion site for Flexor carpi ulnaris?
What is the insertion site for Flexor carpi ulnaris?
Which muscle is responsible for flexing the proximal phalanx of the fingers?
Which muscle is responsible for flexing the proximal phalanx of the fingers?
What is the function of the Palmaris longus muscle?
What is the function of the Palmaris longus muscle?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
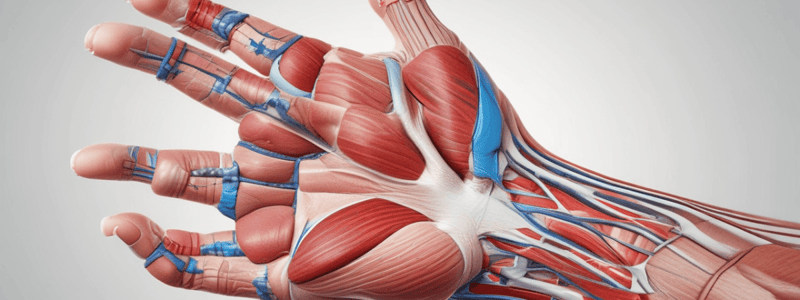
Muscles of the Anterior Forearm
- Pronator teres muscle: originates from ulnar head, medial border of coronoid process, and inserts into anterior surface of radius; functions in pronation and weak flexion of forearm; innervated by median nerve
- Flexor carpi radialis muscle: originates from medial epicondyle, CFT, and antebrachial fascia; inserts into base of 1st and 2nd metacarpal; functions in flexion and abduction of the wrist; innervated by median nerve
- Palmaris longus muscle: originates from medial epicondyle, CFT, and antebrachial fascia; inserts into flexor retinaculum and palmar aponeurosis; functions in flexion of the wrist and stretches the palmar aponeurosis; innervated by median nerve
- Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle: originates from humeral head, medial epicondyle, and inserts into pisiform and 5th metacarpal bone; functions in flexion and adduction of the wrist; innervated by ulnar nerve
Middle Compartment
- Flexor digitorum superficialis muscle: originates from humeroulnar head, medial epicondyle, CFT, and anterior surface of ulnar collateral ligament; inserts into sides of the medial 4 middle phalanx; functions in flexion of the proximal phalanx; innervated by median nerve
Deep Compartment
- Flexor digitorum profundus muscle: originates from anterior and medial surface of ulna, interosseus membrane; inserts into base of the medial 4 distal phalanx; functions in flexion of the distal phalanx; innervated by median nerve (lateral half) and ulnar nerve (medial half)
- Flexor policis longus muscle: originates from anterior surface of radius, interosseus membrane; inserts into base of the distal phalanx of thumb; functions in flexion of the distal phalanx of the thumb; innervated by median nerve
- Pronator quadratus muscle: originates from lower part of ulna; inserts into lower part of ulna; functions in pronation of the forearm; innervated by median nerve
Cubital Fossa
- Triangular fossa in front of the elbow joint: bounded medially by pronator teres, laterally by brachioradialis muscle, and based on a line passing through the epicondyle
- Contents of the cubital fossa: not specified
Superficial Veins of the Forearm
- Cephalic vein
- Basilic vein
- Median cubital vein
- Median vein of forearm
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.