Podcast
Questions and Answers
How many pairs of cranial nerves are there that originate from the brain?
How many pairs of cranial nerves are there that originate from the brain?
- 8 pairs
- 14 pairs
- 12 pairs (correct)
- 10 pairs
Which cranial nerve is unique in its origin as it arises from both the brain and the spinal cord?
Which cranial nerve is unique in its origin as it arises from both the brain and the spinal cord?
- 10th cranial nerve
- 12th cranial nerve
- 9th cranial nerve
- 11th cranial nerve (correct)
What is the total number of spinal nerves present in the human body?
What is the total number of spinal nerves present in the human body?
- 35 pairs
- 30 pairs
- 24 pairs
- 31 pairs (correct)
Where do all cranial nerves exit from the cranial cavity?
Where do all cranial nerves exit from the cranial cavity?
What is the primary exit pathway for spinal nerves?
What is the primary exit pathway for spinal nerves?
What is the neurotransmitter used by the first motor axon from the CNS to the autonomic ganglion?
What is the neurotransmitter used by the first motor axon from the CNS to the autonomic ganglion?
Which motor axon is associated with the autonomic ganglion?
Which motor axon is associated with the autonomic ganglion?
After the autonomic ganglion, which neurotransmitters can potentially be released by the second motor axon?
After the autonomic ganglion, which neurotransmitters can potentially be released by the second motor axon?
How many motor axons are involved in the autonomic pathway described?
How many motor axons are involved in the autonomic pathway described?
What is the primary function of the preganglionic nerve in the autonomic nervous system?
What is the primary function of the preganglionic nerve in the autonomic nervous system?
What response does the sympathetic nervous system trigger?
What response does the sympathetic nervous system trigger?
Where are the cell bodies of preganglionic neurons in the sympathetic nervous system located?
Where are the cell bodies of preganglionic neurons in the sympathetic nervous system located?
Which of the following functions is associated with the parasympathetic nervous system?
Which of the following functions is associated with the parasympathetic nervous system?
What is the structural term for the sympathetic nervous system?
What is the structural term for the sympathetic nervous system?
What type of fibers are the preganglionic fibers in the sympathetic nervous system?
What type of fibers are the preganglionic fibers in the sympathetic nervous system?
How do the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems operate with respect to one another?
How do the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems operate with respect to one another?
What is characteristic of postganglionic fibers in the sympathetic nervous system?
What is characteristic of postganglionic fibers in the sympathetic nervous system?
What are the locations of the postganglionic neurons in the sympathetic nervous system?
What are the locations of the postganglionic neurons in the sympathetic nervous system?
What are the three possible courses of preganglionic fibers in the sympathetic nervous system?
What are the three possible courses of preganglionic fibers in the sympathetic nervous system?
Which structure is an exception in the sympathetic nervous system regarding preganglionic sympathetic fibers?
Which structure is an exception in the sympathetic nervous system regarding preganglionic sympathetic fibers?
How do postganglionic axons reach the abdominal pelvic organs?
How do postganglionic axons reach the abdominal pelvic organs?
What do modified postganglionic neurons in the adrenal medulla release into the blood vessels?
What do modified postganglionic neurons in the adrenal medulla release into the blood vessels?
Which statement about splanchnic nerves is correct?
Which statement about splanchnic nerves is correct?
What is the primary function of the cells in the adrenal medulla?
What is the primary function of the cells in the adrenal medulla?
What happens during an 'adrenaline surge' in emergency situations?
What happens during an 'adrenaline surge' in emergency situations?
Which of the following accurately describes the sympathetic trunk?
Which of the following accurately describes the sympathetic trunk?
What is the primary neurotransmitter released by preganglionic neurons in the autonomic nervous system?
What is the primary neurotransmitter released by preganglionic neurons in the autonomic nervous system?
Where are the cell bodies of postganglionic neurons located?
Where are the cell bodies of postganglionic neurons located?
Which part of the nervous system is responsible for the involuntary control of heart rate?
Which part of the nervous system is responsible for the involuntary control of heart rate?
Which type of neuron in the autonomic nervous system is always myelinated?
Which type of neuron in the autonomic nervous system is always myelinated?
What type of muscle is primarily influenced by the autonomic nervous system?
What type of muscle is primarily influenced by the autonomic nervous system?
How does the control of motor neurons differ between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems?
How does the control of motor neurons differ between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems?
What is the main function of the autonomic nervous system?
What is the main function of the autonomic nervous system?
Which of the following statements is true about the autonomic nervous system?
Which of the following statements is true about the autonomic nervous system?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
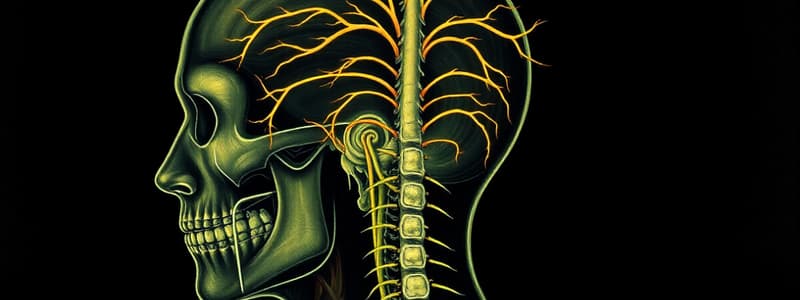
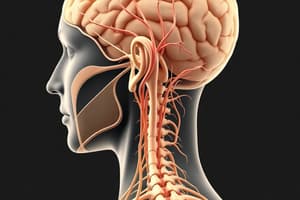
Cranial Nerves
- All 12 pairs of cranial nerves arise from the brain except the 11th cranial nerve which arises from the brain and spinal cord.
- All cranial nerves exit the cranial cavity through foramina in the cranium.
Spinal Nerves
- 31 pairs of spinal nerves (8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, 1 coccygeal nerves).
- All exit the vertebral column through intervertebral foramina.
Autonomic Nervous System
- Part of the Peripheral Nervous System that controls involuntary actions.
- Contains two nerve cells:
- Preganglionic: with cell body located in the brain stem or spinal cord, always myelinated, neurotransmitter is acetylcholine
- Postganglionic: with cell body located in an autonomic ganglion, non-myelinated, neurotransmitter is acetylcholine, epinephrine, or norepinephrine
Somatic vs. Autonomic Nervous System
- Somatic Nervous System:
- Sensory neuron (afferent pathway): Somatic senses & special senses
- Effector: Skeletal muscle
- Control of motor neuron and effect: Voluntary control, excitatory effect
- Motor Neuron (efferent pathway) and neurotransmitter: One motor axon from CNS to effector. NT is Acetylcholine
- Autonomic Nervous System:
- Sensory neuron (afferent pathway): Located in blood vessel & visceral organ
- Effector: Smooth muscles, cardiac muscles and glands
- Control of motor neuron and effect: Involuntary control, excitatory or inhibitory effect
- Motor Neuron (efferent pathway) and neurotransmitter: First motor axon from CNS to autonomic ganglion (preganglionic nerve). Second motor axon from autonomic ganglion to effector (postganglionic nerve). NT can be acetylcholine or norepinephrine
Subdivision of Autonomic Nervous System
- Sympathetic Nervous System:
- Prepares the body to function under stress (exercise, excitement, emergencies).
- Triggers fight or flight response.
- Prepares the body for intense muscle activity.
- Cell bodies of preganglionic neurons are in lateral horn of gray matter of spinal cord from T1-L2 (L3).
- Cell bodies of postganglionic neurons occur in two locations:
- Paravertebral ganglia: either side of the vertebral column, form sympathetic trunks (chains).
- Prevertebral ganglia: located in plexus that surround the origins of main branches of abdominal aorta.
- Preganglionic fibers are short and myelinated.
- Postganglionic fibers are long and non-myelinated.
- Parasympathetic Nervous System:
- Maintenance functions.
- Triggers "Rest-and-digest" response.
- Counterbalances sympathetic function.
Sympathetic Nervous System (Continued)
- Course of preganglionic fibres:
- Remain at same level: Synapse with postganglionic neuron of paravertebral ganglia.
- Ascend or descend within sympathetic trunk: Synapse with a paravertebral postganglionic neuron.
- No synapse: Pass through paravertebral ganglion without synapse, form splanchnic nerve. Synapse in prevertebral ganglion.
- Adrenal gland exception:
- Preganglionic sympathetic fibres do not synapse in prevertebral ganglia and terminate directly in the cells of adrenal medulla.
- These cells act as modified postganglionic neurons and release the NT (epinephrine/norepinephrine) directly into the blood vessels. This causes a widespread sympathetic response (adrenaline "surge" in emergency).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.