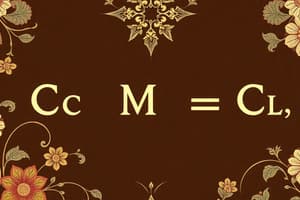Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the mass of oxygen in the given compound sample?
What is the mass of oxygen in the given compound sample?
- 10.15 g
- 4.433 g
- 15.6 g
- 5.717 g (correct)
What does the empirical formula (EF) represent?
What does the empirical formula (EF) represent?
- The actual number of atoms in a molecule
- The product of a chemical reaction
- The simplest whole number ratio of atoms in a compound (correct)
- The molecular weight of a compound
Given that the empirical formula of nicotine is C5H7N and its molar mass is 162 g/mol, what is a key characteristic of its molecular formula?
Given that the empirical formula of nicotine is C5H7N and its molar mass is 162 g/mol, what is a key characteristic of its molecular formula?
- It gives the exact number of atoms in a molecule
- It can be a whole number multiple of the empirical formula (correct)
- It must always be the same as the empirical formula
- It cannot be derived from the empirical formula
Which component is NOT involved in a chemical reaction?
Which component is NOT involved in a chemical reaction?
In the context of chemical equations, what do the symbols and formulas represent?
In the context of chemical equations, what do the symbols and formulas represent?
What is the correct chemical formula for Dinitrogen Tetroxide?
What is the correct chemical formula for Dinitrogen Tetroxide?
Which of the following compounds has the chemical formula H2SO4?
Which of the following compounds has the chemical formula H2SO4?
What is the definition of an empirical formula?
What is the definition of an empirical formula?
Which compound is correctly represented by the formula C12H22O11?
Which compound is correctly represented by the formula C12H22O11?
What does the term molar mass refer to?
What does the term molar mass refer to?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Chemical Compounds
- Dinitrogen Monoxide: N₂O
- Carbon Dioxide: CO₂
- Sulfur Trichloride: SCl₃
- Dinitrogen Tetroxide: N₄O₄
- Phosphorous Pentachloride: PCl₅
- Disulfur Dihydride: S₂H₂
Common Chemical Formulas and Acids
- Hydrochloric Acid: HCl
- Sulfuric Acid: H₂SO₄
- Nitric Acid: HNO₃
- Carbonic Acid: H₂CO₃
- Calcium Hydroxide: Ca(OH)₂
- Methane: CH₄
- Aluminum Oxide: Al₂O₃
- Sucrose: C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁
- Ethanol: C₂H₅OH
Molar Mass
- Defined as the mass of one mole of a substance (g/mol).
- Numerically equivalent to the atomic mass of the element expressed in atomic mass units.
Percentage Composition
- Represents the mass percentage of each element in a compound.
Empirical Formula
- Simplest ratio of atoms in a compound, expressed with the smallest whole number subscripts.
- Example Calculation:
- Mass of Phosphorous = 4.433 g
- Mass of Oxygen calculated from total sample = 5.717 g
Molecular Formula
- Actual formula of a molecular compound, showing the true number of each atom type.
- Relationship with the empirical formula determined through molar mass comparisons:
- ( X = \frac{\text{experimental formula mass}}{\text{empirical formula mass}} )
Chemical Reactions
- Involve substances (reactants) transforming into different substances (products).
- Represented with chemical equations, e.g., AgNO₃ + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO₃.
Stoichiometry
- Mole To Mole Calculation: Used to find moles of reactants/products based on known quantities.
- Mass To Mole Relationship: Converts mass of a substance to moles for calculations.
- Mole To Mass Relationship: Determines mass of products from moles of reactants.
- Mass To Mass Relationship: Calculates amounts of reactants and products based on initial masses.
Theoretical Yield
- Maximum possible quantity of product from given reactants.
- Actual Yield: Measured amount of product from a reaction.
- Percentage Yield: Ratio of actual yield to theoretical yield.
Limiting and Excess Reagents
- Limiting Reactant: Substance that limits the amount of product formed.
- Excess Reactant: Substance not entirely used in the reaction.
Gas Laws
- Boyle's Law: Volume inversely proportional to pressure at constant temperature (P₁V₁ = P₂V₂).
- Charles' Law: Volume directly proportional to absolute temperature at constant pressure (V₁/T₁ = V₂/T₂).
- Gay-Lussac's Law: Pressure directly proportional to temperature at constant volume (P₁/T₁ = P₂/T₂).
- Combined Gas Law: Integrates the three laws above, expressing pressure, volume, and temperature relationships for a fixed gas mass.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.