Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of fibrocartilage?
What is the primary function of fibrocartilage?
- Acts as a shock absorber in joints (correct)
- Provides a smooth surface for joint movement
- Supports the respiratory system
- Facilitates nutrient absorption
Which type of growth occurs from the perichondrium in cartilage?
Which type of growth occurs from the perichondrium in cartilage?
- Appositional growth (correct)
- Endochondral growth
- Hypertrophic growth
- Interstitial growth
What is the primary role of osteoblasts in bone formation?
What is the primary role of osteoblasts in bone formation?
- Remove old bone tissue
- Maintain calcium balance in the blood
- Transport nutrients to bone cells
- Produce collagen and mineralized ground substance (correct)
Which component constitutes the highest percentage of bone's inorganic material?
Which component constitutes the highest percentage of bone's inorganic material?
What characterizes osteoclasts and their function in bone?
What characterizes osteoclasts and their function in bone?
What is the primary function of collagen fibers in connective tissue?
What is the primary function of collagen fibers in connective tissue?
Which type of lymphocyte is responsible for producing plasma cells that secrete antibodies?
Which type of lymphocyte is responsible for producing plasma cells that secrete antibodies?
What is the main component of the ground substance in connective tissue?
What is the main component of the ground substance in connective tissue?
Which type of fiber is known for providing flexibility and the ability to return to its original shape after stretching?
Which type of fiber is known for providing flexibility and the ability to return to its original shape after stretching?
What distinguishes reticular fibers from collagen fibers?
What distinguishes reticular fibers from collagen fibers?
What is the primary function of connective tissue in the body?
What is the primary function of connective tissue in the body?
Which type of connective tissue is primarily responsible for energy storage?
Which type of connective tissue is primarily responsible for energy storage?
Which fixed cell type is most common in connective tissue and is involved in the synthesis of fibers?
Which fixed cell type is most common in connective tissue and is involved in the synthesis of fibers?
What role do macrophages play in connective tissue?
What role do macrophages play in connective tissue?
Which of the following is NOT a function of connective tissue?
Which of the following is NOT a function of connective tissue?
What type of wandering cell in connective tissue serves as a defense mechanism against microorganisms?
What type of wandering cell in connective tissue serves as a defense mechanism against microorganisms?
Which component of the extracellular matrix provides structural support in connective tissues?
Which component of the extracellular matrix provides structural support in connective tissues?
What is the primary role of mast cells in connective tissue?
What is the primary role of mast cells in connective tissue?
What is the primary characteristic of mesenchyme tissue?
What is the primary characteristic of mesenchyme tissue?
Which type of connective tissue is primarily known for its insulation and energy storage?
Which type of connective tissue is primarily known for its insulation and energy storage?
How does brown adipose tissue primarily function in the body?
How does brown adipose tissue primarily function in the body?
Which of the following is considered a specialized connective tissue?
Which of the following is considered a specialized connective tissue?
What is a key feature of loose areolar connective tissue?
What is a key feature of loose areolar connective tissue?
What characteristic distinguishes yellow (white) adipose tissue from brown adipose tissue?
What characteristic distinguishes yellow (white) adipose tissue from brown adipose tissue?
In terms of development, what do the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm represent?
In terms of development, what do the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm represent?
What process modifies the ground substance in skeletal tissue?
What process modifies the ground substance in skeletal tissue?
What is the primary component of the bone matrix that provides strength?
What is the primary component of the bone matrix that provides strength?
Which type of bone is characterized by being densely packed with few gaps?
Which type of bone is characterized by being densely packed with few gaps?
What is the correct sequence of cell differentiation during intramembranous ossification?
What is the correct sequence of cell differentiation during intramembranous ossification?
Which component of blood is responsible for the transportation of oxygen?
Which component of blood is responsible for the transportation of oxygen?
What percentage of blood plasma is water?
What percentage of blood plasma is water?
What structural change occurs in tendons and ligaments with aging?
What structural change occurs in tendons and ligaments with aging?
What condition results from a deficiency of collagen type III?
What condition results from a deficiency of collagen type III?
What primary function does blood serve besides transportation?
What primary function does blood serve besides transportation?
What distinguishes dense regular connective tissue from dense irregular connective tissue?
What distinguishes dense regular connective tissue from dense irregular connective tissue?
What type of cartilage is most abundant and characterized as flexible yet tough?
What type of cartilage is most abundant and characterized as flexible yet tough?
Which of the following best describes the primary structure of cartilage?
Which of the following best describes the primary structure of cartilage?
What function does cartilage primarily serve in joints?
What function does cartilage primarily serve in joints?
Which type of dense connective tissue contains a greater need for oxygen due to its high capillary density?
Which type of dense connective tissue contains a greater need for oxygen due to its high capillary density?
Which tissue type is primarily found in regions providing protection, such as the dermis?
Which tissue type is primarily found in regions providing protection, such as the dermis?
Chondrocytes are located within cavities called what?
Chondrocytes are located within cavities called what?
What primarily makes up the extracellular matrix of cartilage?
What primarily makes up the extracellular matrix of cartilage?
Flashcards
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes
White blood cells that play a crucial role in the immune system. They are responsible for recognizing and destroying foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses.
Plasma Cells
Plasma Cells
Specialized B lymphocytes that produce and secrete antibodies, proteins that bind to and neutralize specific pathogens.
Collagen Fibers
Collagen Fibers
The most common type of protein fiber in connective tissue, providing strength and support. They are also important for tissue repair.
Reticular Fibers
Reticular Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elastic Fibers
Elastic Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elastic Cartilage
Elastic Cartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Appositional Growth
Appositional Growth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interstitial Growth
Interstitial Growth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bone Functions
Bone Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluid & Diffusion in Connective Tissue
Fluid & Diffusion in Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ground Substance: Solid, Semisolid, Liquid
Ground Substance: Solid, Semisolid, Liquid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Specialized Connective Tissue
Specialized Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Embryonic Connective Tissue: Mesenchyme
Embryonic Connective Tissue: Mesenchyme
Signup and view all the flashcards
Germ Layers: Endoderm
Germ Layers: Endoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Germ Layers: Mesoderm
Germ Layers: Mesoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Germ Layers: Ectoderm
Germ Layers: Ectoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adult Connective Tissue
Adult Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Osteoid?
What is Osteoid?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the main types of fibers found in bone matrix?
What are the main types of fibers found in bone matrix?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Compact bone
Compact bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spongy bone
Spongy bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intramembranous ossification
Intramembranous ossification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endochondrial ossification
Endochondrial ossification
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Blood?
What is Blood?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the main components of blood?
What are the main components of blood?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Connective Tissue Function
Connective Tissue Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Components of Connective Tissues
Components of Connective Tissues
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibroblast
Fibroblast
Signup and view all the flashcards
Macrophage
Macrophage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adipocytes
Adipocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mast Cell
Mast Cell
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fixed vs. Wandering Cells
Fixed vs. Wandering Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dense Connective Tissue
Dense Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cartilage
Cartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chondrocytes
Chondrocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extracellular Matrix of Cartilage
Extracellular Matrix of Cartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of Cartilage
Types of Cartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyaline Cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Connective Tissue Overview
- Connective tissue forms a framework for epithelial tissue.
- Connective tissues provide structural support, transport nutrients, and offer immunological defense.
- They also store energy, connect tissue types, facilitate movement, cushion and insulate, and protect delicate organs.
Connective Tissue Components
- Cells are embedded in extracellular matrix.
- The extracellular matrix is comprised of fibers and ground substance.
- Fibrous material includes collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers.
- Ground substance is fluid and chemical.
- Cell types include fixed cells (e.g., fibroblasts, macrophages, adipocytes, mast cells) and wandering cells (e.g., lymphocytes, plasma cells, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, monocytes).
Fixed Cells
- Fibroblasts: The most common cell type, synthesizing and excreting fibers.
- Macrophages: Ingest foreign matter like bacteria. They originate from monocytes.
- Adipocytes (Fat Cells): Store fats or lipids.
- Mast Cells: Release chemical signals in response to injury, triggering inflammation and immune responses.
Wandering Cells
- Lymphocytes (T and B): Part of the immune system, recognizing and binding to foreign substances. T cells are immunity cells; B cells produce plasma cells.
- Plasma Cells: Specialized lymphocytes that produce and secrete antibodies.
- Blood Cells: (Neutrophils, Eosinophils, Basophils): Part of the immune system, involved in responses to allergy, parasites, and infection. Monocytes enhance immune response.
Extracellular Matrix
- Protein fibers secreted by fibroblasts are:
- Collagen (most common, 25-30% of body's protein)
- Reticular
- Elastic
- Ground substance: Fluid and chemicals including proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans. This water-rich component makes up 60-80% of the substance.
Specialized Connective Tissue
-
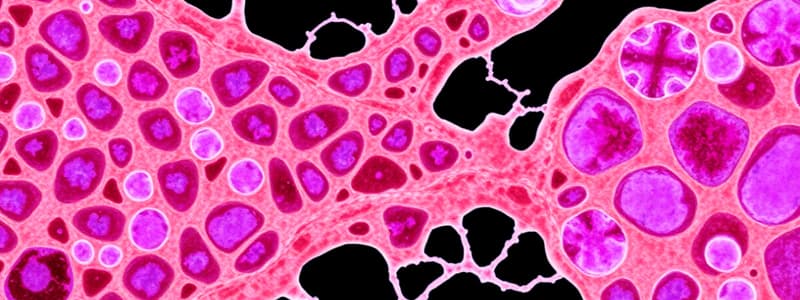
Cartilage: Supportive connective tissue found in joints, rib cage, ear, and nose. Special types are hyaline, fibrocartilage, and elastic.
-
Hyaline Cartilage: Most abundant, found in articular cartilage, embryonic skeleton, costal cartilages, trachea. Hyaline cartilage is bluish-white with a matrix of chondroitin sulfate.
-
Fibrocartilage: Toughest, with densely packed collagen fibers and no perichondrium, found in intervertebral discs, menisci, and symphysis.
-
Elastic Cartilage: Possesses many elastic fibers, found in the ears and epiglottis.
-
Bone: A rigid connective tissue that provides support and protection and is responsible for movement. Bone is composed of:
- Organic component (35%): Cells (osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts), collagen fibers.
- Inorganic component (65%): Calcium phosphate, with magnesium, carbonate, and fluoride ions. Bone has a specialized ground substance called osteoid. Fibers are collagen Types I and V.
-
Blood: A liquid connective tissue without fibers and with highly fluid ground substance and mobile cells. It transports oxygen, hormones, nutrients and helps prevent disease. Blood's components are cells (RBC, WBC, platelets) and plasma (water and proteins).
Bone Cell Types
- Osteoprogenitor cells: Give rise to osteoblasts.
- Osteoblasts: Bone-forming cells synthesizing and secreting collagen and mineralized ground substance (calcium).
- Osteocytes: Mature bone cells, smaller in appearance, maintaining calcium balance in the matrix.
- Osteoclasts: Large cells from monocytes/macrophages, involved in bone growth, healing, and remodeling by digesting bone tissue.
Bone Structure
- Bone structure includes Haversian canals.
Bone Ossification
- Intramembranous ossification: Forms flat bones (skull, face) from vascularized areas, beginning with osteoprogenitor cells, then osteoblasts, and finally osteocytes.
- Endochondral ossification: Forms long bones (like the humerus), starting as cartilage that transforms into bone.
Tissue and Aging
- Tissue healing is less efficient in the elderly.
- Cells divide more slowly.
- Arteries lose elasticity.
- Tendons and ligaments lose flexibility, becoming more fragile.
- Blood cell synthesis declines.
Clinical Anatomy Aspects of Connective Tissue
- Collagen type III deficiency can cause ruptures in arteries and intestines.
- Connective tissue degeneration can occur (e.g., scurvy, tumor).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.