Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the term 'common integument' referring to?
What is the term 'common integument' referring to?
- The internal organs of the body
- The skin with its covering of hair, skin glands, and specialized parts like claws, hoofs, and horns (correct)
- The skin with its covering of feathers and beaks
- The structure of plant leaves
What is the main role of the skin in animals?
What is the main role of the skin in animals?
- Maintaining bone health
- Transporting oxygen in the body
- Protecting against injury and aiding in temperature regulation (correct)
- Producing insulin
Which layer of the skin contains blood vessels and nerves?
Which layer of the skin contains blood vessels and nerves?
- Subcutis
- Epidermis
- Sebaceous gland
- Dermis (correct)
What is the importance of footpads in animals?
What is the importance of footpads in animals?
How do nails, claws, and hoofs differ among species?
How do nails, claws, and hoofs differ among species?
What is the significance of horns in animals?
What is the significance of horns in animals?
What is the function of the nails, claws, and hoofs mentioned in the text?
What is the function of the nails, claws, and hoofs mentioned in the text?
Which part of the equine hoof is described as having a strongly curved wall?
Which part of the equine hoof is described as having a strongly curved wall?
In equine anatomy, what fills the ground surface between the wall and frog?
In equine anatomy, what fills the ground surface between the wall and frog?
What is the function of the digital pads in horses?
What is the function of the digital pads in horses?
What is the main purpose of the thick epidermal covering mentioned in the text?
What is the main purpose of the thick epidermal covering mentioned in the text?
Which animals have only digital pads called bulbs located in their hooves according to the text?
Which animals have only digital pads called bulbs located in their hooves according to the text?
What is the function of the arrector pili muscle?
What is the function of the arrector pili muscle?
Which structure is responsible for the production of sebum?
Which structure is responsible for the production of sebum?
What is the role of primitive hair follicles?
What is the role of primitive hair follicles?
Which component of the hair follicle has a restricted life and is eventually discarded?
Which component of the hair follicle has a restricted life and is eventually discarded?
In what way do many adult glands open, according to the text?
In what way do many adult glands open, according to the text?
Which structure helps in causing goosebumps?
Which structure helps in causing goosebumps?
What is the clinical importance of the cornual process of the frontal bone when dehorning an adult animal?
What is the clinical importance of the cornual process of the frontal bone when dehorning an adult animal?
According to the image, which structure is numbered as 4?
According to the image, which structure is numbered as 4?
Which one of the following statements is correct regarding wavy wool hairs?
Which one of the following statements is correct regarding wavy wool hairs?
The frontal sinus in cattle extends into the $__$.
The frontal sinus in cattle extends into the $__$.
Which of the following is a characteristic of the guard hair?
Which of the following is a characteristic of the guard hair?
What is the function of the periople in the equine hoof?
What is the function of the periople in the equine hoof?
How does the claw structure in carnivores differ from a nail?
How does the claw structure in carnivores differ from a nail?
What is a characteristic feature of horns in domestic ruminants?
What is a characteristic feature of horns in domestic ruminants?
Which statement about claws in carnivores is true?
Which statement about claws in carnivores is true?
What is a characteristic feature of horns in domestic ruminants?
What is a characteristic feature of horns in domestic ruminants?
What structure is labeled as '1' in the image?
What structure is labeled as '1' in the image?
What is the term used to describe the loose connective tissue beneath the skin?
What is the term used to describe the loose connective tissue beneath the skin?
Which type of hair provides a 'topcoat' in animals?
Which type of hair provides a 'topcoat' in animals?
What substance, responsible for coloration, is produced in specialized cells called melanocytes?
What substance, responsible for coloration, is produced in specialized cells called melanocytes?
What is the primary function of the fine, wavy wool hairs in animals?
What is the primary function of the fine, wavy wool hairs in animals?
Which type of hair is associated with touch receptors and has a restricted distribution in the body?
Which type of hair is associated with touch receptors and has a restricted distribution in the body?
Where is melanin produced in animals, contributing to their coloration?
Where is melanin produced in animals, contributing to their coloration?
What is the function of the digital pads in horses?
What is the function of the digital pads in horses?
What is the primary function of nails, claws, and hoofs across different species?
What is the primary function of nails, claws, and hoofs across different species?
In equine anatomy, what fills the space between the bars and the frog in the hoof?
In equine anatomy, what fills the space between the bars and the frog in the hoof?
What is a characteristic feature of the equine hoof wall?
What is a characteristic feature of the equine hoof wall?
How do the structures enclosing the distal phalanx differ despite having similar functions?
How do the structures enclosing the distal phalanx differ despite having similar functions?
What structure corresponds with the digital bulb of primates and the digital pad of carnivores in equine anatomy?
What structure corresponds with the digital bulb of primates and the digital pad of carnivores in equine anatomy?
What is the primary function of guard hairs in animals?
What is the primary function of guard hairs in animals?
What is the initial step in the development of hair follicles?
What is the initial step in the development of hair follicles?
What is the primary cause of albinism in animals?
What is the primary cause of albinism in animals?
What is a potential consequence of a disturbed coat pattern in animals?
What is a potential consequence of a disturbed coat pattern in animals?
What is the primary function of the arrector pili muscle in animals?
What is the primary function of the arrector pili muscle in animals?
What is the primary purpose of the thick epidermal covering (nails, claws, hoofs) in animals?
What is the primary purpose of the thick epidermal covering (nails, claws, hoofs) in animals?
What is the primary function of tactile hairs?
What is the primary function of tactile hairs?
Where are tactile hairs typically located on animals?
Where are tactile hairs typically located on animals?
What is the significance of the venous sinus found within the dermal sheath of tactile hairs?
What is the significance of the venous sinus found within the dermal sheath of tactile hairs?
How do tactile hair follicles differ from those of regular coat hairs in their development?
How do tactile hair follicles differ from those of regular coat hairs in their development?
What is the meaning of the term 'torus' in the context of the common integument?
What is the meaning of the term 'torus' in the context of the common integument?
What is the primary function of the periople in the equine hoof?
What is the primary function of the periople in the equine hoof?
In carnivores, how does the structure of claws differ from nails?
In carnivores, how does the structure of claws differ from nails?
Which structure in domestic ruminants has an osseous base provided by the cornual processes of the frontal bones?
Which structure in domestic ruminants has an osseous base provided by the cornual processes of the frontal bones?
What is the significance of the caudal frontal sinus extending into the horn in ruminants?
What is the significance of the caudal frontal sinus extending into the horn in ruminants?
What is the primary role of the frog in the equine hoof?
What is the primary role of the frog in the equine hoof?
Which of the following statements about horns in domestic ruminants is correct?
Which of the following statements about horns in domestic ruminants is correct?
What is the primary function of guard hairs in animals?
What is the primary function of guard hairs in animals?
Which structure is responsible for the development of the bulb (hair matrix) of hair?
Which structure is responsible for the development of the bulb (hair matrix) of hair?
What is a characteristic feature of the guard hairs seen in cattle?
What is a characteristic feature of the guard hairs seen in cattle?
Where do many glands open in the adult body, as mentioned in the text?
Where do many glands open in the adult body, as mentioned in the text?
What is the main function of arrector pili muscles in animals?
What is the main function of arrector pili muscles in animals?
Why do hairs have restricted lives and are eventually discarded?
Why do hairs have restricted lives and are eventually discarded?
What is the term used to describe the loose connective tissue beneath the skin?
What is the term used to describe the loose connective tissue beneath the skin?
Which type of hair is associated with touch receptors and has a restricted distribution in the body?
Which type of hair is associated with touch receptors and has a restricted distribution in the body?
What substance, responsible for coloration, is produced in specialized cells called melanocytes?
What substance, responsible for coloration, is produced in specialized cells called melanocytes?
Which type of hair provides a 'topcoat' in animals?
Which type of hair provides a 'topcoat' in animals?
What is the primary function of the fine, wavy wool hairs in animals?
What is the primary function of the fine, wavy wool hairs in animals?
What is the main role of the skin in animals?
What is the main role of the skin in animals?
Which of the following best describes the shedding process in domesticated animals?
Which of the following best describes the shedding process in domesticated animals?
What is the primary difference between the 'primary' and 'secondary' hairs described in the text?
What is the primary difference between the 'primary' and 'secondary' hairs described in the text?
According to the information provided, what is the main function of the 'wool hairs' described in the text?
According to the information provided, what is the main function of the 'wool hairs' described in the text?
What is the significance of the 'guard hairs' mentioned in the text?
What is the significance of the 'guard hairs' mentioned in the text?
How do the hair follicles in mature dogs and cats differ from the simple follicles found shortly after birth?
How do the hair follicles in mature dogs and cats differ from the simple follicles found shortly after birth?
What is the primary function of the 'spring shedding' process described in the text?
What is the primary function of the 'spring shedding' process described in the text?
What is the primary function of the periople in the equine hoof?
What is the primary function of the periople in the equine hoof?
How does the claw structure in carnivores differ from a nail?
How does the claw structure in carnivores differ from a nail?
What is a characteristic feature of horns in domestic ruminants?
What is a characteristic feature of horns in domestic ruminants?
What is the significance of the caudal frontal sinus extending into the horn in ruminants?
What is the significance of the caudal frontal sinus extending into the horn in ruminants?
What is the primary role of the frog in the equine hoof?
What is the primary role of the frog in the equine hoof?
What is the primary function of guard hairs in animals?
What is the primary function of guard hairs in animals?
What is the initial step in the development of hair follicles?
What is the initial step in the development of hair follicles?
What is a potential consequence of a disturbed coat pattern in animals?
What is a potential consequence of a disturbed coat pattern in animals?
What is the primary cause of albinism in animals?
What is the primary cause of albinism in animals?
What is the role of primitive hair follicles?
What is the role of primitive hair follicles?
Which one of the following statements is correct regarding wavy wool hairs?
Which one of the following statements is correct regarding wavy wool hairs?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
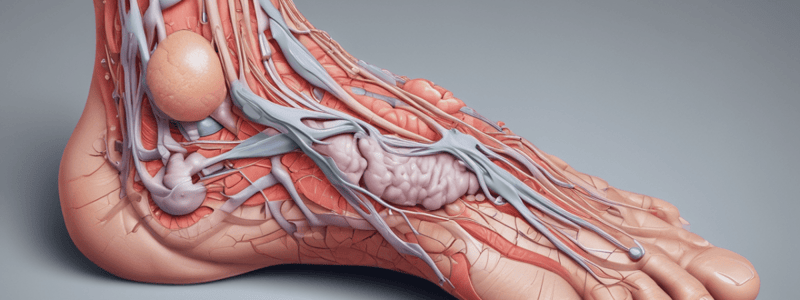
Common Integument
- Definition: ordinary skin with its covering of hair and variety of skin glands, as well as more specialized parts such as claws, hoofs, and horns
- Role: covers the body and protects it against injury, temperature control, and enables the animal to respond to various external stimuli
- Layers: epidermis (out), dermis (in), and subcutaneous cushion (or Pulvinus)
Hair
- Thick haircoat is spread over the body (most species) except about the mouth and other openings and on the surfaces of the feet
- Three types of hair:
- Straight, rather stiff guard hairs provide a “topcoat”
- Fine, wavy wool hairs provide an “undercoat”
- Stout tactile hairs of restricted distribution are associated with touch receptors
- Hair follicles develop from an ectodermal bud, with the distal end forming a bulbous enlargement
Footpads
- Digital cushions on which animals walk
- Ruminants and pigs: digital pads called bulb located in the hoof
- Horse: digital pads called frog located in the hoof
- Functional and in contact with the ground
Nails, Claws, and Hoofs
- Similar structures enclosing the distal phalanx appear strikingly different
- Local modifications of skin
- Serve primarily to protect the underlying tissues
- Used for: scratching, digging, weapon, and grabbing food
Equine Hoof
- Reduces concussion on foot impact
- Presents three parts: wall, sole, and associated pad (horny structure)
- Wall: strongly curved, with sides sharply inflected to form the so-called bars
- Sole: fills the ground surface between wall and frog, meeting the wall at a junction known as the white line
- Frog: part of the footpad that makes contact with the ground
Horns
- Horns of domestic ruminants: have osseous bases provided by the cornual processes of the frontal bones
- Permanent and grow continuously after their first appearance soon after birth
- Caudal frontal sinus extending into horn
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.