Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main characteristic that defines Cnidarians?
What is the main characteristic that defines Cnidarians?
- Asymmetry
- Spherical Symmetry
- Radial Symmetry (correct)
- Bilateral Symmetry
What is the function of nematocysts in Cnidarians?
What is the function of nematocysts in Cnidarians?
- Capturing Prey (correct)
- Respiration
- Temperature Regulation
- Reproduction
Which tissue layer in Cnidarians is responsible for capturing food and secreting mucus?
Which tissue layer in Cnidarians is responsible for capturing food and secreting mucus?
- Endoderm
- Mesoglea
- Gastrovascular Cavity
- Ectoderm (correct)
What separates the ectoderm and endoderm in Cnidarians' body structure?
What separates the ectoderm and endoderm in Cnidarians' body structure?
Which term describes sessile animals that form colonies in the world of Cnidarians?
Which term describes sessile animals that form colonies in the world of Cnidarians?
Which type of cnidarian tends to stay as polyps during their life cycle?
Which type of cnidarian tends to stay as polyps during their life cycle?
What important biological concept was first discovered using the cnidarian Hydra?
What important biological concept was first discovered using the cnidarian Hydra?
Why are cnidarians considered important in understanding the effects of climate change on marine life?
Why are cnidarians considered important in understanding the effects of climate change on marine life?
What is the purpose of the Cnidarian Model Systems Meeting, or Cnidofest, mentioned in the text?
What is the purpose of the Cnidarian Model Systems Meeting, or Cnidofest, mentioned in the text?
What aspect makes cnidarians well-suited for studying various biology aspects?
What aspect makes cnidarians well-suited for studying various biology aspects?
Study Notes
Cnidarians: Understanding the Diverse and Fascinating World of Stinging Animals
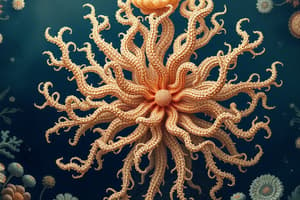
Cnidarians, also known as Coelenterates, are a diverse group of aquatic animals that include hydroids, jellyfish, sea anemones, and corals (Figure 1). These animals are characterized by their radial symmetry and the presence of stinging cells called nematocysts, which are used for capturing prey and defense mechanisms. The name Cnidaria is derived from the Greek word for "nettle," reflecting their stinging capabilities. Cnidarians are found in various aquatic environments, from cold arctic waters to the equator, and from shallow tide pools to the bottom of the deep ocean.
Body Structure and Symmetry
Cnidarians have a simple body plan, with radial symmetry, which allows for capturing food from all directions (Figure 2). The body is made up of two main tissue layers: the outer ectoderm and the inner endoderm. The ectoderm is responsible for capturing food and secreting mucus, while the endoderm produces digestive enzymes and breaks down food particles. The mesoglea, a jelly-like substance, separates the ectoderm and endoderm, and they both surround a central cavity called the gastrovascular cavity.
Diverse Life Cycles
Cnidarians display a broad variety of life cycles, with some species having only a polyp form (sessile animals that form colonies), while others have both a polyp and a medusa form (free-swimming animals with tentacles). Some cnidarians, such as jellyfish, take on a medusa form during their life cycle, while others, like sea anemones, remain as polyps. The life cycles of cnidarians are depicted in Figure 3, showing the solitary freshwater polyp Hydra, the marine jellyfish Clytia, and the anthozoan polyp Nematostella vectensis.
Importance in Biological Research
Cnidarians have played a significant role in biological research, providing insights into various aspects of biology, including regeneration, neurobiology, and development. For instance, the concept of a developmental organizer was first discovered using the cnidarian Hydra, and Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP), a widely used tool in molecular biology, is derived from jellyfish. Research on cnidarians has also contributed to understanding the role of muscle cells and their organization in cnidarians, which is distinct from bilaterians.
Conservation and Future Research
Cnidarians are an essential part of ocean ecosystems, with many species being threatened by climate change and other environmental factors. Understanding cnidarian biology can help us better understand and address the effects of climate change on these animals and their habitats. Additionally, cnidarians have the potential to provide insights into regenerative medicine and the development of epitheliomuscular/myoepithelial cells. The second annual Cnidarian Model Systems Meeting, or Cnidofest, was organized to bring together researchers working on cnidarians, aiming to foster communication and collaboration in the community.
In conclusion, cnidarians are unique and fascinating animals that play a significant role in the aquatic world. Their simple body structure, radial symmetry, and stinging capabilities make them well-suited for studying various biology aspects, while their role in the ecosystem highlights the importance of understanding their biology in the context of environmental changes and conservation efforts.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Test your knowledge on the diverse world of cnidarians, including their body structure, life cycles, importance in biological research, and conservation efforts. Explore facts about hydroids, jellyfish, sea anemones, and corals in this quiz.