Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which type of muscle is involuntary and found in the walls of internal organs?
Which type of muscle is involuntary and found in the walls of internal organs?
- Skeletal and cardiac muscle
- Smooth muscle (correct)
- Skeletal muscle
- Cardiac muscle
Which type of muscle forms the majority of the human muscular system?
Which type of muscle forms the majority of the human muscular system?
- Cardiac and smooth muscle
- Cardiac muscle
- Smooth muscle
- Skeletal muscle (correct)
What is the main structural difference between skeletal and cardiac muscles?
What is the main structural difference between skeletal and cardiac muscles?
- Presence of more nuclei in skeletal muscle fibers
- Higher abundance of myoglobin in skeletal muscle
- Presence of intercalated discs in cardiac muscle (correct)
- Greater density of mitochondria in cardiac muscle
In terms of cellular structure, what distinguishes skeletal muscle fibers from cardiac muscle fibers?
In terms of cellular structure, what distinguishes skeletal muscle fibers from cardiac muscle fibers?
What is the main difference between a myofibril and a sarcomere?
What is the main difference between a myofibril and a sarcomere?
What cellular process leads to the formation of a muscle fiber from multiple myoblasts?
What cellular process leads to the formation of a muscle fiber from multiple myoblasts?
What distinguishes the cellular structure of skeletal muscle fibers from cardiac muscle fibers?
What distinguishes the cellular structure of skeletal muscle fibers from cardiac muscle fibers?
Why do skeletal muscle fibers contain multiple nuclei?
Why do skeletal muscle fibers contain multiple nuclei?
What is the primary function of Transverse tubules (T tubules) in skeletal muscle fibers?
What is the primary function of Transverse tubules (T tubules) in skeletal muscle fibers?
What distinguishes the sarcoplasmic reticulum from the smooth endoplasmic reticulum found in other cells?
What distinguishes the sarcoplasmic reticulum from the smooth endoplasmic reticulum found in other cells?
Why do satellite cells only activate/differentiate if the muscle they're close to is strained or injured?
Why do satellite cells only activate/differentiate if the muscle they're close to is strained or injured?
How does muscle hypertrophy differ from the typical formation of new cells?
How does muscle hypertrophy differ from the typical formation of new cells?
Why can't mature muscle cells (muscle fibers) regenerate on their own?
Why can't mature muscle cells (muscle fibers) regenerate on their own?
What is the role of transverse tubules (T tubules) in skeletal muscle fibers?
What is the role of transverse tubules (T tubules) in skeletal muscle fibers?
What is the primary function of satellite cells in muscle tissue?
What is the primary function of satellite cells in muscle tissue?
How do sarcomeres contribute to muscle function?
How do sarcomeres contribute to muscle function?
What is the primary significance of tongue fasciculations in the context of muscle health?
What is the primary significance of tongue fasciculations in the context of muscle health?
In what situation would eye twitches (fasciculations) typically occur?
In what situation would eye twitches (fasciculations) typically occur?
What is the key characteristic of fasciculations in muscles?
What is the key characteristic of fasciculations in muscles?
What is the primary function of satellite cells in muscle tissue?
What is the primary function of satellite cells in muscle tissue?
What distinguishes the cellular structure of skeletal muscle fibers from cardiac muscle fibers?
What distinguishes the cellular structure of skeletal muscle fibers from cardiac muscle fibers?
What is the main difference between a myofibril and a sarcomere?
What is the main difference between a myofibril and a sarcomere?
In terms of muscle contraction, what distinguishes the cellular structure of fast twitch fibers from slow twitch fibers?
In terms of muscle contraction, what distinguishes the cellular structure of fast twitch fibers from slow twitch fibers?
What is the primary factor that contributes to the difference in muscle contraction speed between fast twitch and slow twitch fibers?
What is the primary factor that contributes to the difference in muscle contraction speed between fast twitch and slow twitch fibers?
Which type of muscle fibers have low blood supply, fatigue rapidly, and are anaerobic?
Which type of muscle fibers have low blood supply, fatigue rapidly, and are anaerobic?
What is the primary characteristic of slow twitch type 1 muscle fibers?
What is the primary characteristic of slow twitch type 1 muscle fibers?
Which type of muscle fibers are primarily used by sprinters?
Which type of muscle fibers are primarily used by sprinters?
What distinguishes the cellular structure of fast twitch type 2a and 2b fibers from slow twitch type 1 fibers?
What distinguishes the cellular structure of fast twitch type 2a and 2b fibers from slow twitch type 1 fibers?
What is the primary function of myoglobin in muscle fibers?
What is the primary function of myoglobin in muscle fibers?
Which type of neuron is associated with slow twitch muscle fibers?
Which type of neuron is associated with slow twitch muscle fibers?
What distinguishes myoglobin from hemoglobin in terms of location and function?
What distinguishes myoglobin from hemoglobin in terms of location and function?
How does the presence of myoglobin affect the appearance of muscle fibers?
How does the presence of myoglobin affect the appearance of muscle fibers?
What is the primary function of myoglobin in Fast Twitch Type II muscle fibers?
What is the primary function of myoglobin in Fast Twitch Type II muscle fibers?
What distinguishes the primary energy production process in Fast Twitch Type II muscle fibers from Slow Twitch muscle fibers?
What distinguishes the primary energy production process in Fast Twitch Type II muscle fibers from Slow Twitch muscle fibers?
Why are Fast Twitch Type II muscle fibers well-suited for sprinting activities?
Why are Fast Twitch Type II muscle fibers well-suited for sprinting activities?
What is the primary advantage of Fast Twitch Type II muscle fibers in extraocular muscles, speaking, and swallowing muscles?
What is the primary advantage of Fast Twitch Type II muscle fibers in extraocular muscles, speaking, and swallowing muscles?
What is the primary reason for slow twitch Type I muscle fibers to use aerobic respiration?
What is the primary reason for slow twitch Type I muscle fibers to use aerobic respiration?
Why are slow twitch Type I muscle fibers referred to as 'Red'?
Why are slow twitch Type I muscle fibers referred to as 'Red'?
What is the key characteristic that enables slow twitch Type I muscle fibers to stay energized for a long time?
What is the key characteristic that enables slow twitch Type I muscle fibers to stay energized for a long time?
How do slow twitch Type I muscle fibers differ from fast twitch Type II muscle fibers in terms of lactic acid production?
How do slow twitch Type I muscle fibers differ from fast twitch Type II muscle fibers in terms of lactic acid production?
What is the primary role of Golgi tendon organs in muscle physiology?
What is the primary role of Golgi tendon organs in muscle physiology?
What distinguishes the primary function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle fibers from other cellular structures?
What distinguishes the primary function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle fibers from other cellular structures?
In terms of energy production, what sets Fast Twitch Type II muscle fibers apart from Slow Twitch muscle fibers?
In terms of energy production, what sets Fast Twitch Type II muscle fibers apart from Slow Twitch muscle fibers?
What is the primary characteristic of slow twitch Type I muscle fibers in terms of endurance?
What is the primary characteristic of slow twitch Type I muscle fibers in terms of endurance?
What is the primary role of troponin in muscle contraction?
What is the primary role of troponin in muscle contraction?
What is primarily responsible for the sliding of actin and myosin filaments during muscle contraction?
What is primarily responsible for the sliding of actin and myosin filaments during muscle contraction?
Which structure prevents myosin from binding to actin during muscle relaxation?
Which structure prevents myosin from binding to actin during muscle relaxation?
What is happening in a muscle that is working but maintaining its length?
What is happening in a muscle that is working but maintaining its length?
What contributes to the maintenance of muscle length during contraction?
What contributes to the maintenance of muscle length during contraction?
What prevents the muscle from shortening during a contraction?
What prevents the muscle from shortening during a contraction?
What is the significance of maintaining cross-bridges between actin and myosin in a functioning muscle?
What is the significance of maintaining cross-bridges between actin and myosin in a functioning muscle?
Which term describes maintaining a constant tension while changing in length?
Which term describes maintaining a constant tension while changing in length?
What term refers to constant length, even if tension is changing?
What term refers to constant length, even if tension is changing?
How would you describe exercises that involve maintaining a constant speed of contraction?
How would you describe exercises that involve maintaining a constant speed of contraction?
What term is used to describe a hypothetical type of muscle contraction that maintains a constant temperature?
What term is used to describe a hypothetical type of muscle contraction that maintains a constant temperature?
What is the primary role of troponin in muscle contraction?
What is the primary role of troponin in muscle contraction?
What happens when there is very little calcium around in muscle cells?
What happens when there is very little calcium around in muscle cells?
What is the primary function of myosin in muscle contraction?
What is the primary function of myosin in muscle contraction?
What is the main role of tropomyosin in muscle contraction?
What is the main role of tropomyosin in muscle contraction?
What is the primary role of troponin in muscle contraction?
What is the primary role of troponin in muscle contraction?
What contributes to the maintenance of muscle length during contraction?
What contributes to the maintenance of muscle length during contraction?
What is the main structural difference between skeletal and cardiac muscles?
What is the main structural difference between skeletal and cardiac muscles?
Why can't mature muscle cells (muscle fibers) regenerate on their own?
Why can't mature muscle cells (muscle fibers) regenerate on their own?
What is the primary role of satellite cells in muscle tissue?
What is the primary role of satellite cells in muscle tissue?
What is the main advantage of Fast Twitch Type II muscle fibers in extraocular muscles, speaking, and swallowing muscles?
What is the main advantage of Fast Twitch Type II muscle fibers in extraocular muscles, speaking, and swallowing muscles?
What is the primary role of myosin in a single sarcomere during muscle contraction?
What is the primary role of myosin in a single sarcomere during muscle contraction?
What is the effect of insufficient calcium in a muscle cell during contraction?
What is the effect of insufficient calcium in a muscle cell during contraction?
Which statement best describes the interaction of myosin with actin in a single sarcomere during muscle contraction?
Which statement best describes the interaction of myosin with actin in a single sarcomere during muscle contraction?
In terms of muscle contraction, what is the primary function of troponin?
In terms of muscle contraction, what is the primary function of troponin?
What is the primary function of transverse tubules (T tubules) in skeletal muscle fibers?
What is the primary function of transverse tubules (T tubules) in skeletal muscle fibers?
What happens when there is very little calcium around in muscle cells?
What happens when there is very little calcium around in muscle cells?
What is the primary reason for slow twitch Type I muscle fibers to use aerobic respiration?
What is the primary reason for slow twitch Type I muscle fibers to use aerobic respiration?
What distinguishes the cellular structure of fast twitch fibers from slow twitch fibers in terms of lactic acid production?
What distinguishes the cellular structure of fast twitch fibers from slow twitch fibers in terms of lactic acid production?
What will happen if Ca++ remains and more ATP is available in the muscle?
What will happen if Ca++ remains and more ATP is available in the muscle?
If Ca++ disappears in the muscle, what will happen to myosin?
If Ca++ disappears in the muscle, what will happen to myosin?
What happens if Ca++ is present but no ATP is available in the muscle?
What happens if Ca++ is present but no ATP is available in the muscle?
What is the consequence of myosin remaining attached to its actin binding site in the muscle when there is no ATP available?
What is the consequence of myosin remaining attached to its actin binding site in the muscle when there is no ATP available?
During a muscle contraction, which statement best describes the stacking up of multiple muscle fiber membrane potentials?
During a muscle contraction, which statement best describes the stacking up of multiple muscle fiber membrane potentials?
What is the primary role of titin in muscle fibers?
What is the primary role of titin in muscle fibers?
In terms of muscle contraction, what distinguishes the cellular structure of fast-oxidative-glycolytic fibers from slow-oxidative fibers?
In terms of muscle contraction, what distinguishes the cellular structure of fast-oxidative-glycolytic fibers from slow-oxidative fibers?
What is the primary role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle physiology?
What is the primary role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle physiology?
What is the primary function of transverse (T) tubules in skeletal muscle fibers?
What is the primary function of transverse (T) tubules in skeletal muscle fibers?
What happens when there is an insufficient amount of calcium ions in muscle cells?
What happens when there is an insufficient amount of calcium ions in muscle cells?
What distinguishes the primary energy production process in Fast Twitch Type II muscle fibers from Slow Twitch muscle fibers?
What distinguishes the primary energy production process in Fast Twitch Type II muscle fibers from Slow Twitch muscle fibers?
What is the specialized role of endoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells?
What is the specialized role of endoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells?
How is the release of Ca++ from the endoplasmic reticulum characterized in muscle cells?
How is the release of Ca++ from the endoplasmic reticulum characterized in muscle cells?
What connects the endoplasmic reticulum to T Tubules in muscle cells?
What connects the endoplasmic reticulum to T Tubules in muscle cells?
What is the characteristic of the reuptake of Ca++ by the endoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells?
What is the characteristic of the reuptake of Ca++ by the endoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells?
What is responsible for rapidly transmitting the depolarization message to the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells?
What is responsible for rapidly transmitting the depolarization message to the sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells?
If there is a lack of calcium ions in muscle cells, what will be affected?
If there is a lack of calcium ions in muscle cells, what will be affected?
Which structure primarily prevents myosin from binding to actin during muscle relaxation?
Which structure primarily prevents myosin from binding to actin during muscle relaxation?
In terms of cellular structure, what distinguishes skeletal muscle fibers from cardiac muscle fibers?
In terms of cellular structure, what distinguishes skeletal muscle fibers from cardiac muscle fibers?
Qual es le characteristic principal que distingue le contraction muscular del fibra musculare?
Qual es le characteristic principal que distingue le contraction muscular del fibra musculare?
Qual es le resultato si le calcium non dispare in le musculo?
Qual es le resultato si le calcium non dispare in le musculo?
Qual es le principal function de myosina in un singule sarcomero durante le contraction muscular?
Qual es le principal function de myosina in un singule sarcomero durante le contraction muscular?
In relation al contraction muscular, qual distingue le structura cellular del fibra muscular de contraction rapida-oxidative-glicolitic de fibra muscular de contraction lente-oxidative?
In relation al contraction muscular, qual distingue le structura cellular del fibra muscular de contraction rapida-oxidative-glicolitic de fibra muscular de contraction lente-oxidative?
During a muscle contraction, what best describes the relationship between the action of myofibrils and the message conduction of the plasma membrane?
During a muscle contraction, what best describes the relationship between the action of myofibrils and the message conduction of the plasma membrane?
What distinguishes the primary role of satellite cells in muscle tissue?
What distinguishes the primary role of satellite cells in muscle tissue?
How are slow twitch Type I muscle fibers characterized in terms of blood supply, fatigue, and aerobic/anaerobic nature?
How are slow twitch Type I muscle fibers characterized in terms of blood supply, fatigue, and aerobic/anaerobic nature?
What is the consequence of myosin remaining attached to its actin binding site in the muscle when there is no ATP available?
What is the consequence of myosin remaining attached to its actin binding site in the muscle when there is no ATP available?
What is the consequence of myosin remaining attached to its actin binding site in the muscle when there is no ATP available?
What is the consequence of myosin remaining attached to its actin binding site in the muscle when there is no ATP available?
What contributes to the maintenance of muscle length during contraction?
What contributes to the maintenance of muscle length during contraction?
What is primarily responsible for the sliding of actin and myosin filaments during muscle contraction?
What is primarily responsible for the sliding of actin and myosin filaments during muscle contraction?
What is the primary role of troponin in muscle contraction?
What is the primary role of troponin in muscle contraction?
What is the primary factor contributing to the strength of muscle contraction?
What is the primary factor contributing to the strength of muscle contraction?
What distinguishes the primary role of satellite cells in muscle tissue?
What distinguishes the primary role of satellite cells in muscle tissue?
In terms of energy production, what sets Fast Twitch Type II muscle fibers apart from Slow Twitch muscle fibers?
In terms of energy production, what sets Fast Twitch Type II muscle fibers apart from Slow Twitch muscle fibers?
What is the primary function of titin in muscle fibers?
What is the primary function of titin in muscle fibers?
What is the primary factor contributing to the contraction of skeletal muscles?
What is the primary factor contributing to the contraction of skeletal muscles?
What distinguishes the primary role of motor neurons in stimulating skeletal muscle fibers?
What distinguishes the primary role of motor neurons in stimulating skeletal muscle fibers?
Which characteristic sets motor neurons apart from other nerves in the body?
Which characteristic sets motor neurons apart from other nerves in the body?
What is the essential requirement for skeletal muscle contraction?
What is the essential requirement for skeletal muscle contraction?
What is the primary reason that skeletal muscles have to be stimulated by a nerve in order to contract?
What is the primary reason that skeletal muscles have to be stimulated by a nerve in order to contract?
What is the primary function of the neuromuscular junction in muscle physiology?
What is the primary function of the neuromuscular junction in muscle physiology?
What distinguishes the structure of skeletal muscles from cardiac muscles in terms of electrical activity?
What distinguishes the structure of skeletal muscles from cardiac muscles in terms of electrical activity?
What is the primary role of myosin in muscle fibers during contraction?
What is the primary role of myosin in muscle fibers during contraction?
What is the final result of the process where ACh binds to receptors on the motor end plate?
What is the final result of the process where ACh binds to receptors on the motor end plate?
What is the primary role of tropomyosin in muscle contraction?
What is the primary role of tropomyosin in muscle contraction?
What is the consequence of calcium remaining bound to troponin in the muscle fiber?
What is the consequence of calcium remaining bound to troponin in the muscle fiber?
In the absence of ATP, what effect does myosin remaining attached to its actin binding site have on muscle contraction?
In the absence of ATP, what effect does myosin remaining attached to its actin binding site have on muscle contraction?
Which type of acetylcholine receptor is also responsive to nicotine?
Which type of acetylcholine receptor is also responsive to nicotine?
What type of acetylcholine receptor is found in skeletal muscle?
What type of acetylcholine receptor is found in skeletal muscle?
Which compound do muscarinic receptors also bind to?
Which compound do muscarinic receptors also bind to?
What classifies acetylcholine receptors based on their responsiveness to specific substances?
What classifies acetylcholine receptors based on their responsiveness to specific substances?
How is muscle contraction stopped?
How is muscle contraction stopped?
What is the primary method to get a muscle to stop doing what it's doing?
What is the primary method to get a muscle to stop doing what it's doing?
What is the role of IPSP for muscle in muscle contraction?
What is the role of IPSP for muscle in muscle contraction?
Why is it said that all neuromuscular junctions are excitatory?
Why is it said that all neuromuscular junctions are excitatory?
What is the consequence of a muscle where ACh binds to receptors but does not open their ion channels?
What is the consequence of a muscle where ACh binds to receptors but does not open their ion channels?
What is the primary target of destruction in Myasthenia Gravis?
What is the primary target of destruction in Myasthenia Gravis?
What is the approximate ratio of women to men affected by Myasthenia Gravis in the United States?
What is the approximate ratio of women to men affected by Myasthenia Gravis in the United States?
What percentage of nicotinic ACh receptors in skeletal muscle's motor end plate can be destroyed by Myasthenia Gravis?
What percentage of nicotinic ACh receptors in skeletal muscle's motor end plate can be destroyed by Myasthenia Gravis?
What is the primary target for treatment of Myasthenia Gravis?
What is the primary target for treatment of Myasthenia Gravis?
Which treatment approach aims to make acetylcholine (ACh) last longer in the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) for patients with Myasthenia Gravis?
Which treatment approach aims to make acetylcholine (ACh) last longer in the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) for patients with Myasthenia Gravis?
What is a treatment method that aims to remove circulating antibodies in Myasthenia Gravis?
What is a treatment method that aims to remove circulating antibodies in Myasthenia Gravis?
What type of receptors are skeletal muscle acetylcholine receptors?
What type of receptors are skeletal muscle acetylcholine receptors?
What is the primary neurotransmitter that binds to skeletal muscle acetylcholine receptors?
What is the primary neurotransmitter that binds to skeletal muscle acetylcholine receptors?
What is the specific responsiveness of skeletal muscle acetylcholine receptors to external substances?
What is the specific responsiveness of skeletal muscle acetylcholine receptors to external substances?
During which phase of a twitch contraction is tension developing due to the cross-bridge cycling?
During which phase of a twitch contraction is tension developing due to the cross-bridge cycling?
Why is the relaxation phase longer than the contraction phase in a twitch contraction?
Why is the relaxation phase longer than the contraction phase in a twitch contraction?
What is the primary reason for the time delay from the action potential to the onset of contraction during the latent period of a twitch contraction?
What is the primary reason for the time delay from the action potential to the onset of contraction during the latent period of a twitch contraction?
What is the primary difference between isometric and isotonic twitches?
What is the primary difference between isometric and isotonic twitches?
What happens when isotonic twitches occur in a muscle?
What happens when isotonic twitches occur in a muscle?
In terms of muscle contraction, what distinguishes the role of myosin during isometric and isotonic twitches?
In terms of muscle contraction, what distinguishes the role of myosin during isometric and isotonic twitches?
What is the term for the increase in muscle tension from successive action potentials during the phase of mechanical activity?
What is the term for the increase in muscle tension from successive action potentials during the phase of mechanical activity?
What is the term for the phenomenon where a muscle fiber is stimulated again before it has fully relaxed from its last twitch?
What is the term for the phenomenon where a muscle fiber is stimulated again before it has fully relaxed from its last twitch?
What is the term used for the increase in muscle fiber's tension due to multiple stimuli arriving before the muscle fiber has relaxed from its last twitch?
What is the term used for the increase in muscle fiber's tension due to multiple stimuli arriving before the muscle fiber has relaxed from its last twitch?
In the context of muscle contraction, what does tetany refer to?
In the context of muscle contraction, what does tetany refer to?
What is the primary effect of too much summation on muscle contraction?
What is the primary effect of too much summation on muscle contraction?
How does tetanic contraction differ from a single twitch contraction?
How does tetanic contraction differ from a single twitch contraction?
What contributes to the rate of onset of muscle fatigue?
What contributes to the rate of onset of muscle fatigue?
What is a characteristic of fatigued muscle in terms of shortening velocity?
What is a characteristic of fatigued muscle in terms of shortening velocity?
Which factor determines the type of muscle fiber that will be affected by fatigue?
Which factor determines the type of muscle fiber that will be affected by fatigue?
What happens to relaxation time when squeeze intensity decreases?
What happens to relaxation time when squeeze intensity decreases?
What is the primary role of the stretch reflex in muscle physiology?
What is the primary role of the stretch reflex in muscle physiology?
What is the main function of reciprocal innervation in muscle physiology?
What is the main function of reciprocal innervation in muscle physiology?
In terms of muscle physiology, what does the ascending information sent to the brain primarily serve for?
In terms of muscle physiology, what does the ascending information sent to the brain primarily serve for?
What is the result of painful stimulation of the skin on the ipsilateral limb?
What is the result of painful stimulation of the skin on the ipsilateral limb?
What is the response of the contralateral limb to painful stimulation of the skin?
What is the response of the contralateral limb to painful stimulation of the skin?
What effect does painful stimulation of the skin have on both the ipsilateral and contralateral limbs?
What effect does painful stimulation of the skin have on both the ipsilateral and contralateral limbs?
Which type of pathways are considered sensory and afferent?
Which type of pathways are considered sensory and afferent?
What type of information do ascending pathways primarily carry?
What type of information do ascending pathways primarily carry?
Which of the following types of pathways are associated with autonomic functions?
Which of the following types of pathways are associated with autonomic functions?
Which part of the cerebral cortex is responsible for the ongoing control of voluntary movements?
Which part of the cerebral cortex is responsible for the ongoing control of voluntary movements?
What is the primary function of the neurons in the primary motor cortex and premotor cortex?
What is the primary function of the neurons in the primary motor cortex and premotor cortex?
Which area of the cerebral cortex is primarily made up of neurons that give rise to descending pathways for motor control?
Which area of the cerebral cortex is primarily made up of neurons that give rise to descending pathways for motor control?
What is the primary source of input to the cerebellum from the sensorimotor cortex?
What is the primary source of input to the cerebellum from the sensorimotor cortex?
Which structure receives input from the vestibular system, eyes, skin, muscles, joints, and tendons?
Which structure receives input from the vestibular system, eyes, skin, muscles, joints, and tendons?
Where does the cerebellum send input to, ultimately impacting smooth motion and balance?
Where does the cerebellum send input to, ultimately impacting smooth motion and balance?
Flashcards
Smooth Muscle
Smooth Muscle
Involuntary muscle found in internal organs.
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal Muscle
Voluntary muscle attached to bones.
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Involuntary, striated muscle found in the heart.
Sarcomeres
Sarcomeres
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sarcomere
Sarcomere
Signup and view all the flashcards
Troponin
Troponin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tropomyosin
Tropomyosin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myosin
Myosin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Actin
Actin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fast Twitch (Type II) Fibers
Fast Twitch (Type II) Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Slow Twitch (Type I) Fibers
Slow Twitch (Type I) Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Satellite Cells
Satellite Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Signup and view all the flashcards
T-Tubules
T-Tubules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myoglobin
Myoglobin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Golgi Tendon Organs
Golgi Tendon Organs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calcium Ions
Calcium Ions
Signup and view all the flashcards
ATP
ATP
Signup and view all the flashcards
Titin
Titin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Contraction
Muscle Contraction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Fatigue
Muscle Fatigue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscle Endurance
Muscle Endurance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
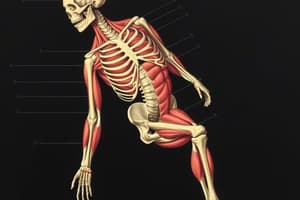
Muscle Types and Characteristics
- Smooth muscle: involuntary, found in internal organs
- Skeletal muscle: majority of human muscular system, voluntary, attached to bones
- Cardiac muscle: involuntary, found in heart, striated
Muscle Fiber Structure
- Skeletal muscle fibers: multinucleated, voluntary
- Cardiac muscle fibers: single nucleus, involuntary
- Myofibrils: composed of sarcomeres, contractile units of muscle fibers
- Sarcomere: functional unit of muscle contraction, consists of actin and myosin filaments
Muscle Contraction
- Myofibril: composed of sarcomeres, contractile units of muscle fibers
- Sarcomere: functional unit of muscle contraction, consists of actin and myosin filaments
- Troponin: regulates muscle contraction, binds to calcium ions
- Tropomyosin: blocks myosin binding to actin, prevents muscle contraction
- Myosin: motor protein, responsible for muscle contraction
- Actin: protein filament, interacts with myosin during muscle contraction
Muscle Fiber Types
- Fast twitch (Type II) fibers: rapid contraction, high force, low endurance, anaerobic, low blood supply
- Slow twitch (Type I) fibers: slow contraction, low force, high endurance, aerobic, high blood supply
- Fast twitch Type II fibers: high power, short duration, low endurance
- Slow twitch Type I fibers: low power, long duration, high endurance
Muscle Physiology
- Satellite cells: precursor cells, differentiate into muscle fibers, repair damaged muscle tissue
- Sarcoplasmic reticulum: stores and releases calcium ions, regulates muscle contraction
- Transverse tubules (T-tubules): rapid transmission of depolarization message to sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Myoglobin: stores oxygen, facilitates muscle contraction
- Golgi tendon organs: sense muscle tension, regulate muscle contraction
Muscle Contraction Regulation
- Calcium ions: regulate muscle contraction, bind to troponin
- ATP: energy source for muscle contraction, needed for myosin to release from actin
- Titin: responsible for muscle elasticity, returns muscle to resting state
Muscle Function and Performance
- Muscle length: maintained during contraction, due to cross-bridges between actin and myosin
- Muscle contraction: sliding of actin and myosin filaments, regulated by calcium ions and ATP
- Muscle fatigue: results from decreased ATP and calcium ions, leads to muscle relaxation
- Muscle endurance: ability to sustain muscle contraction over time, dependent on muscle fiber type and energy production
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.