Podcast
Questions and Answers
How many kilometers of vessels are present in the human body?
How many kilometers of vessels are present in the human body?
- 150,000 km
- 75,000 km
- 50,000 km
- 100,000 km (correct)
What is the estimated number of blood cells in the human body?
What is the estimated number of blood cells in the human body?
- 50 million
- 60 million
- 100 million
- 75 million (correct)
How many times does the heart beat in a person's lifetime of 80 years?
How many times does the heart beat in a person's lifetime of 80 years?
- 2 billion times
- 2.5 billion times
- 3.5 billion times (correct)
- 4 billion times
What is the direction of blood flow in the human body?
What is the direction of blood flow in the human body?
What type of circulatory system do humans have?
What type of circulatory system do humans have?
What is unique about the human heart?
What is unique about the human heart?
What is the purpose of the lymphatic system?
What is the purpose of the lymphatic system?
What is the term for the study of the circulatory system?
What is the term for the study of the circulatory system?
What type of cells in the heart generate an electrical signal to coordinate contraction?
What type of cells in the heart generate an electrical signal to coordinate contraction?
What is the volume of blood ejected from the heart during each contraction?
What is the volume of blood ejected from the heart during each contraction?
What is the formula to calculate cardiac output (CO)?
What is the formula to calculate cardiac output (CO)?
What system alters heart rate (HR) by changing the depolarization of the autorhythmic cells?
What system alters heart rate (HR) by changing the depolarization of the autorhythmic cells?
What is the heart rate (HR) in the example given in the text, where CO = 5.4 L/min?
What is the heart rate (HR) in the example given in the text, where CO = 5.4 L/min?
What is the amount of blood remaining in the heart after each beat, at rest?
What is the amount of blood remaining in the heart after each beat, at rest?
What percentage of the blood is made up of water?
What percentage of the blood is made up of water?
What is the main function of erythropoietin (EPO)?
What is the main function of erythropoietin (EPO)?
What is the purpose of blood doping in athletic performance?
What is the purpose of blood doping in athletic performance?
What is the main component of the cardiac muscle?
What is the main component of the cardiac muscle?
What is the trigger for erythropoietin (EPO) release?
What is the trigger for erythropoietin (EPO) release?
What is the function of the circulating portion of the blood?
What is the function of the circulating portion of the blood?
What is the percentage of protein in the blood composition?
What is the percentage of protein in the blood composition?
Where is erythropoietin (EPO) produced?
Where is erythropoietin (EPO) produced?
What is the direction of blood flow in the arterial system?
What is the direction of blood flow in the arterial system?
Why does blood pressure decrease as blood flows away from the heart?
Why does blood pressure decrease as blood flows away from the heart?
What is the significance of the two numbers in a blood pressure reading?
What is the significance of the two numbers in a blood pressure reading?
What is the relationship between blood pressure and the distance from the heart?
What is the relationship between blood pressure and the distance from the heart?
What is the main reason for the difference in pressure between the arterial and venous systems?
What is the main reason for the difference in pressure between the arterial and venous systems?
What is the direction of blood flow in the venous system?
What is the direction of blood flow in the venous system?
What is the systolic pressure in the arteries when the heart has contracted?
What is the systolic pressure in the arteries when the heart has contracted?
What is the term for the condition where the blood pressure drops when standing up?
What is the term for the condition where the blood pressure drops when standing up?
Why does blood 'pool' in the feet when standing?
Why does blood 'pool' in the feet when standing?
What is the function of the venous valve in the circulatory system?
What is the function of the venous valve in the circulatory system?
What is the term for the movement of fluid through the capillary walls?
What is the term for the movement of fluid through the capillary walls?
What is one of the key functions of the lymphatic system?
What is one of the key functions of the lymphatic system?
What is the term for the pressure in the arteries when the heart is fully relaxed?
What is the term for the pressure in the arteries when the heart is fully relaxed?
What happens when not enough blood is returning to the heart?
What happens when not enough blood is returning to the heart?
What is the purpose of the action of venous valves?
What is the purpose of the action of venous valves?
What is the term for the movement of fluid in both directions on squeezing a fluid-filled tube?
What is the term for the movement of fluid in both directions on squeezing a fluid-filled tube?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Human Circulatory System
- The human circulatory system is a closed system, physically separated from the rest of the body, consisting of vessels and a pump.
- The human heart is divided into right and left sides, making it a "double" circulatory system.
Blood Composition
- Blood is a connective tissue made up of cellular elements suspended in a fluid matrix called plasma.
- It makes up a quarter of the extracellular fluid (ECF) and acts as a buffer between cells and the external environment.
- Blood composition is 92% water, 7% protein, and 1% dissolved organic molecules.
Erythropoiesis
- Erythropoiesis is controlled by the glycoprotein erythropoietin (EPO) and cytokines produced by the kidneys.
- The trigger for EPO release is hypoxia, which relieves reduced oxygen-carrying capacity.
Blood Doping
- Blood doping is used to improve athletic performance by artificially improving the body's ability to transport oxygen to tissues/muscles.
- Three common types of blood doping are blood transfusion, injection of EPO, and injection of synthetic oxygen carriers.
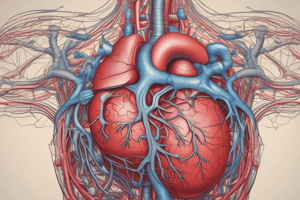
The Heart
- The heart is the "workhorse" of the body, generating pressure to force blood continuously around the body.
- It is composed predominantly of cardiac muscle.
Heart Contraction
- Specialized cells within the heart generate an electrical signal to coordinate contraction.
- This electrical signal depolarizes the membrane, spreading rapidly through the conducting pathway.
Mechanical Events of the Heart
- The heart's mechanical events are controlled by the electrical signal, leading to contraction and relaxation.
Heart Rate
- The heart rate is altered by the autonomic nervous system, changing the depolarization of the autorhythmic cells.
- Cardiac output (CO) is measured by the stroke volume (SV) x heart rate (HR).
Blood Flow
- Blood flows from an area of high to low pressure, driven by blood pressure.
- The arterial system is under high pressure, and the venous system is under low pressure.
Blood Pressure
- Blood pressure is recorded as two numbers: systolic pressure (120 mmHg) and diastolic pressure (80 mmHg).
- Systolic pressure is the pressure in the arteries when the heart has contracted, and diastolic pressure is the pressure in the arteries when the heart is fully relaxed.
Postural Hypotension
- Postural hypotension occurs when standing causes blood to "pool" in the feet, leading to a decrease in blood pressure.
- This can cause fainting, especially in cases where the person does not move their legs.
Capillary Transport
- There are three mechanisms of exchange in capillary transport: movement between endothelium, transcytosis, and bulk flow.
Lymphatic System
- The lymphatic system has three key functions: returning filtered fluid to the circulatory system, fat reabsorption from the gut into circulation, and destroying foreign pathogens.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.