Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the two types of pericardium?
What are the two types of pericardium?
Fibrous and serous pericardium.
What shape is the heart?
What shape is the heart?
Cone-shaped.
What forms the apex of the heart?
What forms the apex of the heart?
The left ventricle.
What forms the base of the heart?
What forms the base of the heart?
Which structures receive venous blood in the heart?
Which structures receive venous blood in the heart?
What valve guards the right atrioventricular orifice?
What valve guards the right atrioventricular orifice?
Which valve guards the left atrioventricular orifice?
Which valve guards the left atrioventricular orifice?
What prevents backflow of blood into the ventricles during contraction?
What prevents backflow of blood into the ventricles during contraction?
Match the heart structures with their functions:
Match the heart structures with their functions:
What are the walls of the left atrium primarily like?
What are the walls of the left atrium primarily like?
What does the right ventricle contract to pump blood to?
What does the right ventricle contract to pump blood to?
What is the function of the coronary artery?
What is the function of the coronary artery?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Circulatory System Overview
- The heart consists of two muscular pumps (right and left heart) for pulmonary and systemic circulations, forming a continuous loop.
- Systemic circulation comprises many parallel circuits serving various organs and body regions.
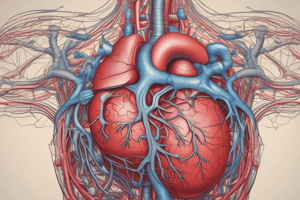
Heart Anatomy
- The heart is cone-shaped with:
- Apex: Directed downward, forward, and left; formed by the left ventricle; located 9 cm from midline, opposite the 5th intercostal space.
- Base: Directed upward, backward, and right; formed mainly by the left atrium; positioned in front of the middle four thoracic vertebrae.
Heart Surfaces and Borders
- Sterno-costal surface: Not specified in detail, but relevant for external anatomy.
- Heart borders include:
- Upper: formed by both atria
- Lower: formed by the right ventricle and part of the left ventricle
- Right: formed by the right atrium
- Left: formed by the left ventricle and left auricle
Blood Flow in the Heart
- Right Atrium: Receives non-oxygenated blood from the body via:
- Superior vena cava
- Inferior vena cava
- Coronary sinus
- Blood flows to the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve (right atrioventricular orifice).
- Right Ventricle: Pumps blood to lungs via pulmonary trunk; valves prevent backflow during contraction.
- Left Atrium: Receives oxygenated blood from lungs through four pulmonary veins; blood moves to left ventricle via mitral valve (left atrioventricular orifice).
- Left Ventricle: Pumps oxygenated blood to the body through the aorta; mitral valve closes to prevent backflow during contraction.
Valves of the Heart
- Tricuspid Valve: Between right atrium and right ventricle.
- Mitral Valve: Between left atrium and left ventricle.
- Pulmonary Valve: Between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk.
- Aortic Valve: Between left ventricle and aorta.
- Atrioventricular valves open during atrial contractions and close during ventricular contractions to prevent backflow.
- Semilunar valves open during ventricular contractions and close post-contraction.
Interior Structure of the Heart
- Right Atrium:
- Smooth posterior wall with openings for SVC, IVC, and coronary sinus; features a rough anterior wall and a “crista terminalis.”
- Septal wall has a depression called “fossa ovalis.”
- Left Atrium: Smooth walls, receiving four pulmonary veins.
- Right Ventricle: Thin-walled and large lumen; contains muscular projections (trabeculae carneae) and 3 papillary muscles; smooth outflowing part leads to pulmonary trunk.
- Left Ventricle: Thick-walled and smaller, circular lumen; includes trabeculae carneae and 2 papillary muscles; smooth outflowing part leads to aorta.
Blood Supply of the Heart
- Right Coronary Artery: Originates from the ascending aorta and runs in the coronary groove.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.