Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the normal systolic pressure measured in mmHg?
What is the normal systolic pressure measured in mmHg?
- 130 mmHg
- 110 mmHg
- 100 mmHg
- 120 mmHg (correct)
The diastolic pressure is always higher than the systolic pressure.
The diastolic pressure is always higher than the systolic pressure.
False (B)
What device is used to measure blood pressure?
What device is used to measure blood pressure?
Sphygmomanometer
The _____ circuit brings deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
The _____ circuit brings deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
Which of the following arteries supplies the liver with oxygenated blood?
Which of the following arteries supplies the liver with oxygenated blood?
Match the following body parts with their corresponding arteries:
Match the following body parts with their corresponding arteries:
The last sound heard during blood pressure measurement indicates systolic pressure.
The last sound heard during blood pressure measurement indicates systolic pressure.
What is the role of the pulmonary veins in the circulatory system?
What is the role of the pulmonary veins in the circulatory system?
Which of the following is NOT a function of blood?
Which of the following is NOT a function of blood?
Veins hold up to 70% of the total blood supply in the body.
Veins hold up to 70% of the total blood supply in the body.
What is the primary function of the heart in the circulatory system?
What is the primary function of the heart in the circulatory system?
The _____ arteries contain a higher percentage of elastic fibers than muscular arteries.
The _____ arteries contain a higher percentage of elastic fibers than muscular arteries.
Match the following blood components to their primary functions:
Match the following blood components to their primary functions:
What happens during vasodilation?
What happens during vasodilation?
The tunica media is typically thicker in veins than in arteries.
The tunica media is typically thicker in veins than in arteries.
What mechanism helps prevent backflow of blood in veins?
What mechanism helps prevent backflow of blood in veins?
Hemodynamics refers to the physiology of blood _____ .
Hemodynamics refers to the physiology of blood _____ .
Which of the following is NOT a factor affecting blood pressure?
Which of the following is NOT a factor affecting blood pressure?
Systolic pressure is the ______ of a blood pressure measurement.
Systolic pressure is the ______ of a blood pressure measurement.
During ______, the heart contracts and sends a wave of pressure through the bloodstream.
During ______, the heart contracts and sends a wave of pressure through the bloodstream.
During ______, the heart relaxes and pressure remains throughout the system.
During ______, the heart relaxes and pressure remains throughout the system.
The ______ circuit transports deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for gas exchange.
The ______ circuit transports deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for gas exchange.
Blood collected from the body returns to the heart via the superior and inferior ______.
Blood collected from the body returns to the heart via the superior and inferior ______.
The ______ circuit pumps oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
The ______ circuit pumps oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
The first sound heard during blood pressure measurement indicates ______ pressure.
The first sound heard during blood pressure measurement indicates ______ pressure.
The heart is essentially a _____ that drives the blood through the body.
The heart is essentially a _____ that drives the blood through the body.
Arteries are vessels leaving the heart that can carry _____ blood or not to the capillaries.
Arteries are vessels leaving the heart that can carry _____ blood or not to the capillaries.
Veins contain up to _____% of the total blood supply in the body.
Veins contain up to _____% of the total blood supply in the body.
Smooth muscle _____ leads to an increase in the diameter of the lumen.
Smooth muscle _____ leads to an increase in the diameter of the lumen.
The _____ is a single layer of endothelium lining the lumen of the blood vessel.
The _____ is a single layer of endothelium lining the lumen of the blood vessel.
Peripheral _____ refers to anything that impedes blood flow in the circulatory system.
Peripheral _____ refers to anything that impedes blood flow in the circulatory system.
The diameter of the blood vessel can be altered by contracting or relaxing the _____ media.
The diameter of the blood vessel can be altered by contracting or relaxing the _____ media.
Capillary beds allow for gas, nutrient, and waste _____ between cells and capillary lumen.
Capillary beds allow for gas, nutrient, and waste _____ between cells and capillary lumen.
Blood pressure is measured in _____.
Blood pressure is measured in _____.
The _____ valves in veins are essential to prevent backflow of blood.
The _____ valves in veins are essential to prevent backflow of blood.
Match the following factors with their effect on blood pressure:
Match the following factors with their effect on blood pressure:
Match the following vessels with their blood types:
Match the following vessels with their blood types:
What sound indicates the onset of systolic pressure during blood pressure measurement?
What sound indicates the onset of systolic pressure during blood pressure measurement?
Describe the pathway of deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
Describe the pathway of deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
What happens to the cuff pressure during blood pressure measurement as it approaches the diastolic pressure?
What happens to the cuff pressure during blood pressure measurement as it approaches the diastolic pressure?
Which blood vessels collect oxygenated blood from the lungs to return it to the heart?
Which blood vessels collect oxygenated blood from the lungs to return it to the heart?
How does the systemic circuit differ from the pulmonary circuit in terms of blood flow?
How does the systemic circuit differ from the pulmonary circuit in terms of blood flow?
What role does the cuff serve in the measurement of blood pressure using a sphygmomanometer?
What role does the cuff serve in the measurement of blood pressure using a sphygmomanometer?
Identify two functions of the celiac and renal arteries in relation to the organs they supply.
Identify two functions of the celiac and renal arteries in relation to the organs they supply.
What physiological change occurs during systole?
What physiological change occurs during systole?
What is the primary difference between arteries and veins regarding blood pressure and blood volume?
What is the primary difference between arteries and veins regarding blood pressure and blood volume?
Explain the significance of the tunica media in the structure of blood vessels.
Explain the significance of the tunica media in the structure of blood vessels.
What role do venous valves play in the circulatory system?
What role do venous valves play in the circulatory system?
Describe how vasodilation affects blood flow and blood pressure.
Describe how vasodilation affects blood flow and blood pressure.
What distinguishes elastic arteries from muscular arteries?
What distinguishes elastic arteries from muscular arteries?
How does blood viscosity contribute to blood pressure?
How does blood viscosity contribute to blood pressure?
Explain the function of capillary beds in the circulatory system.
Explain the function of capillary beds in the circulatory system.
In terms of hemodynamics, what does a pressure gradient indicate?
In terms of hemodynamics, what does a pressure gradient indicate?
Describe how blood vessel length affects blood pressure.
Describe how blood vessel length affects blood pressure.
Flashcards
Systolic pressure
Systolic pressure
The pressure in the arteries when the heart contracts.
Diastolic pressure
Diastolic pressure
The pressure in the arteries when the heart rests between beats.
Pulmonary circulation
Pulmonary circulation
The flow of blood through the heart & lungs to pick up oxygen.
Systemic circulation
Systemic circulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sphygmomanometer
Sphygmomanometer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brachial artery
Brachial artery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Celiac artery
Celiac artery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal artery
Renal artery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood function
Blood function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood vessel function
Blood vessel function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heart function
Heart function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Closed circulatory system
Closed circulatory system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Artery function
Artery function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elastic arteries
Elastic arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Capillary function
Capillary function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood pressure
Blood pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peripheral resistance
Peripheral resistance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood vessel radius
Blood vessel radius
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is systolic pressure?
What is systolic pressure?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is diastolic pressure?
What is diastolic pressure?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the pulmonary circuit?
What is the function of the pulmonary circuit?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the systemic circuit?
What is the function of the systemic circuit?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is blood pressure measured using a sphygmomanometer?
How is blood pressure measured using a sphygmomanometer?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the celiac artery?
What is the celiac artery?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the renal artery?
What is the renal artery?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the four pulmonary veins?
What are the four pulmonary veins?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the primary function of blood?
What is the primary function of blood?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the three main components of the circulatory system?
What are the three main components of the circulatory system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What type of circulatory system do humans have?
What type of circulatory system do humans have?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the key features of arteries?
What are the key features of arteries?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are elastic arteries and how do they function?
What are elastic arteries and how do they function?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are arterioles and their role?
What are arterioles and their role?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the importance of capillary beds?
What is the importance of capillary beds?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the main function of veins?
What is the main function of veins?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are venous valves and why are they important?
What are venous valves and why are they important?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the difference between vasodilation and vasoconstriction?
What is the difference between vasodilation and vasoconstriction?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary circuit
Pulmonary circuit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systemic circuit
Systemic circuit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arteries vs. Veins
Arteries vs. Veins
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Elastic Arteries?
What are Elastic Arteries?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Capillary Exchange
Capillary Exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Veins: Blood Reservoirs
Veins: Blood Reservoirs
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Venous Valves?
What are Venous Valves?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vasodilation vs. Vasoconstriction
Vasodilation vs. Vasoconstriction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Importance of Tunica Media
Importance of Tunica Media
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Pressure Basics
Blood Pressure Basics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systole
Systole
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diastole
Diastole
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of the pulmonary circuit?
What is the purpose of the pulmonary circuit?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of the systemic circuit?
What is the role of the systemic circuit?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the sounds heard during blood pressure measurement?
What are the sounds heard during blood pressure measurement?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the circulatory system do?
What does the circulatory system do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Venous Valves
Venous Valves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tunica Media
Tunica Media
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is blood pressure?
What is blood pressure?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why does the heart pump?
Why does the heart pump?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Blood
- Transports nutrients, wastes, maintains homeostasis, and protects the body
- Blood travels through vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries)
- Heart pumps blood throughout the body
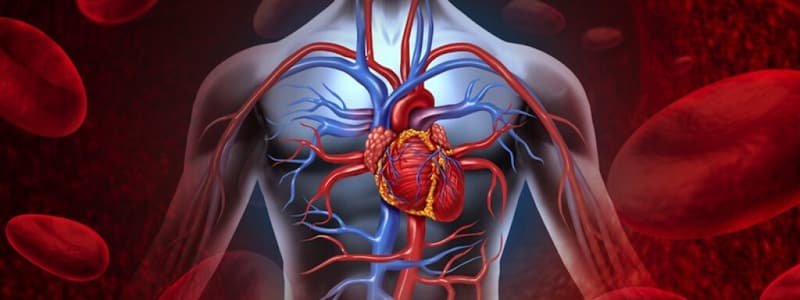
Circulatory System
- Closed system: blood always remains within vessels
- Arteries carry blood away from the heart (may carry oxygenated or deoxygenated blood)
- Arterioles are smaller vessels branching off arteries
- Capillary beds are sites of gas, nutrient, and waste exchange
- Venules collect blood from capillaries
- Veins carry blood back to the heart (under less pressure than arteries)
Blood Vessel Structure
- Tunics: layers surrounding the lumen (central blood-filled space)
- Tunica Interna: inner layer (endothelium)
- Tunica Media: middle layer (smooth muscle and elastic fibers, thicker in arteries)
- Tunica Externa: outer layer (connective tissue)
- Internal elastic lamina: band of connective tissue in arteries, between endothelium and tunica media
- Arteries and arterioles play a role in blood pressure regulation
- Vasodilation: widening of blood vessels (relaxation of smooth muscle)
- Vasoconstriction: narrowing of blood vessels (contraction of smooth muscle)
Blood Pressure
- Force exerted by blood on vessel walls (mmHg)
- Pressure gradient: higher pressure near the heart, lower in veins
- Blood pressure is influenced by several factors, including vessel radius, vessel length, blood viscosity, blood volume, and vessel compliance
- Blood pressure is measured using a sphygmomanometer and stethoscope
- Systolic pressure: pressure during ventricular contraction
- Diastolic pressure: pressure during ventricular relaxation
Pulmonary and Systemic Circulation
- Pulmonary circulation: right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs for gas exchange, and returns oxygenated blood to the heart
- Systemic circulation: left side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the body, and returns deoxygenated blood to the heart
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.