Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the two basic requirements for all living organisms to survive?
What are the two basic requirements for all living organisms to survive?
- Sunlight and carbon dioxide
- Minerals and vitamins
- Food and oxygen (correct)
- Water and shelter
Which system in the human body transports substances from one part to another?
Which system in the human body transports substances from one part to another?
- Digestive system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Circulatory system (correct)
Approximately how many liters of blood are in an adult human body?
Approximately how many liters of blood are in an adult human body?
- 8.5
- 10.5
- 5.5 (correct)
- 2.5
Which of the following is NOT a major component of the circulatory system?
Which of the following is NOT a major component of the circulatory system?
What is the double-layered membrane surrounding the heart called?
What is the double-layered membrane surrounding the heart called?
What are the upper chambers of the heart called?
What are the upper chambers of the heart called?
What is the function of the atrioventricular valves?
What is the function of the atrioventricular valves?
Which type of blood vessel carries blood away from the heart?
Which type of blood vessel carries blood away from the heart?
Which blood vessels have very thin walls, only one cell thick?
Which blood vessels have very thin walls, only one cell thick?
Which part of the blood is mostly water?
Which part of the blood is mostly water?
What is the main function of red blood cells?
What is the main function of red blood cells?
Which component of blood helps in clotting?
Which component of blood helps in clotting?
What is the major vein that empties blood into the right auricle?
What is the major vein that empties blood into the right auricle?
Which artery carries blood to the lungs?
Which artery carries blood to the lungs?
What is the circulation of blood between the heart and the lungs called?
What is the circulation of blood between the heart and the lungs called?
What is the name of the instrument used to amplify the sound of a heartbeat?
What is the name of the instrument used to amplify the sound of a heartbeat?
What is measured using a sphygmomanometer?
What is measured using a sphygmomanometer?
Which blood type is known as the universal donor?
Which blood type is known as the universal donor?
Which blood type is known as the universal recipient?
Which blood type is known as the universal recipient?
What is a voluntary act of donating blood called?
What is a voluntary act of donating blood called?
Why is the circulatory system essential for survival in larger organisms?
Why is the circulatory system essential for survival in larger organisms?
What is the functional significance of the septum in the human heart?
What is the functional significance of the septum in the human heart?
Which characteristic distinguishes arteries from veins in terms of blood flow dynamics?
Which characteristic distinguishes arteries from veins in terms of blood flow dynamics?
How do red blood cells facilitate oxygen transport throughout the body?
How do red blood cells facilitate oxygen transport throughout the body?
Why is the double circulation system in humans considered more efficient than a single circulation system?
Why is the double circulation system in humans considered more efficient than a single circulation system?
What role do white blood cells play in maintaining overall health?
What role do white blood cells play in maintaining overall health?
How does the structure of capillaries facilitate their function in nutrient and waste exchange?
How does the structure of capillaries facilitate their function in nutrient and waste exchange?
What is the underlying mechanism for the sound produced during a heartbeat?
What is the underlying mechanism for the sound produced during a heartbeat?
How does regular exercise contribute to heart health?
How does regular exercise contribute to heart health?
What is the significance of knowing one's blood group for blood transfusions?
What is the significance of knowing one's blood group for blood transfusions?
Which blood vessel is responsible for carrying deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs?
Which blood vessel is responsible for carrying deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs?
What is the role of platelets in the blood?
What is the role of platelets in the blood?
Which of the following is a key difference between pulmonary and systemic circulation?
Which of the following is a key difference between pulmonary and systemic circulation?
What is the primary risk associated with prolonged high blood pressure?
What is the primary risk associated with prolonged high blood pressure?
If a person has blood type A, which antibodies are present in their plasma?
If a person has blood type A, which antibodies are present in their plasma?
What is the correct sequence of blood flow in pulmonary circulation?
What is the correct sequence of blood flow in pulmonary circulation?
Why is blood donation considered a voluntary act?
Why is blood donation considered a voluntary act?
Which of the following dietary habits is most beneficial for maintaining a healthy heart?
Which of the following dietary habits is most beneficial for maintaining a healthy heart?
What is the primary function of the vena cava?
What is the primary function of the vena cava?
How does a stethoscope amplify the sound of a heartbeat?
How does a stethoscope amplify the sound of a heartbeat?
If a patient with blood type B requires a blood transfusion but only blood types AB and O are available, what is the primary reason blood type AB would be a less suitable choice than blood type O?
If a patient with blood type B requires a blood transfusion but only blood types AB and O are available, what is the primary reason blood type AB would be a less suitable choice than blood type O?
In a scenario where a patient's blood pressure consistently reads 160/100 mmHg, despite lifestyle modifications, what is the most critical physiological consequence to monitor?
In a scenario where a patient's blood pressure consistently reads 160/100 mmHg, despite lifestyle modifications, what is the most critical physiological consequence to monitor?
During intense physical activity, the body's demand for oxygen increases. What physiological mechanism ensures that the heart meets this increased demand?
During intense physical activity, the body's demand for oxygen increases. What physiological mechanism ensures that the heart meets this increased demand?
A researcher is investigating the factors influencing blood flow velocity in different types of blood vessels. Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between vessel type and blood flow velocity?
A researcher is investigating the factors influencing blood flow velocity in different types of blood vessels. Which of the following statements accurately describes the relationship between vessel type and blood flow velocity?
A patient with a history of atherosclerosis experiences a sudden blockage in a coronary artery. What is the most immediate and life-threatening consequence of this blockage?
A patient with a history of atherosclerosis experiences a sudden blockage in a coronary artery. What is the most immediate and life-threatening consequence of this blockage?
How does the structure of capillaries—being only one cell layer thick—optimize their function in the circulatory system?
How does the structure of capillaries—being only one cell layer thick—optimize their function in the circulatory system?
What is the physiological basis for the 'lub-dub' sound produced by the heart, and what do these sounds signify in terms of heart valve function?
What is the physiological basis for the 'lub-dub' sound produced by the heart, and what do these sounds signify in terms of heart valve function?
Individuals with blood type O are considered universal donors because their red blood cells lack A and B antigens. However, in specific circumstances, why might transfusing type O blood to a recipient with a different blood type still pose a risk?
Individuals with blood type O are considered universal donors because their red blood cells lack A and B antigens. However, in specific circumstances, why might transfusing type O blood to a recipient with a different blood type still pose a risk?
A scientist is studying the effect of a new drug on blood pressure. The drug selectively blocks the action of Angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor. What is the expected outcome of administering this drug to a hypertensive patient?
A scientist is studying the effect of a new drug on blood pressure. The drug selectively blocks the action of Angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor. What is the expected outcome of administering this drug to a hypertensive patient?
Following a severe injury, a patient experiences significant blood loss and requires a blood transfusion. However, due to an administrative error, the patient receives blood that is not compatible with their blood type, leading to an acute hemolytic transfusion reaction. What is the underlying mechanism causing the primary life-threatening consequence in this scenario?
Following a severe injury, a patient experiences significant blood loss and requires a blood transfusion. However, due to an administrative error, the patient receives blood that is not compatible with their blood type, leading to an acute hemolytic transfusion reaction. What is the underlying mechanism causing the primary life-threatening consequence in this scenario?
The circulatory system transports substances throughout the body using blood.
The circulatory system transports substances throughout the body using blood.
The heart is located in the abdominal cavity.
The heart is located in the abdominal cavity.
Arteries carry blood away from the heart.
Arteries carry blood away from the heart.
Veins typically carry oxygen-rich blood.
Veins typically carry oxygen-rich blood.
Capillaries have thick walls to withstand high blood pressure.
Capillaries have thick walls to withstand high blood pressure.
Plasma is the liquid part of the blood.
Plasma is the liquid part of the blood.
Red blood cells (RBCs) are responsible for fighting infections.
Red blood cells (RBCs) are responsible for fighting infections.
Platelets help in the clotting of blood.
Platelets help in the clotting of blood.
The aorta carries blood from the right ventricle to all parts of the body.
The aorta carries blood from the right ventricle to all parts of the body.
Pulmonary circulation involves blood flow between the heart and the lungs.
Pulmonary circulation involves blood flow between the heart and the lungs.
Systemic circulation involves blood flow between the heart and all body organs including the lungs.
Systemic circulation involves blood flow between the heart and all body organs including the lungs.
A heart beat is the sound produced when blood passes through the arteries.
A heart beat is the sound produced when blood passes through the arteries.
A sphygmomanometer is used to measure pulse rate.
A sphygmomanometer is used to measure pulse rate.
People with blood group O are called universal recipients.
People with blood group O are called universal recipients.
Blood group is determined by the presence of antibodies on red blood cells.
Blood group is determined by the presence of antibodies on red blood cells.
The circulatory system relies solely on diffusion to transport substances throughout the body.
The circulatory system relies solely on diffusion to transport substances throughout the body.
The human heart is located centrally in the chest cavity.
The human heart is located centrally in the chest cavity.
Atrioventricular valves allow blood to flow both from the auricles to the ventricles and from the ventricles back to the auricles.
Atrioventricular valves allow blood to flow both from the auricles to the ventricles and from the ventricles back to the auricles.
The pulmonary artery carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the lungs.
The pulmonary artery carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the lungs.
Arteries have valves to prevent the backflow of blood.
Arteries have valves to prevent the backflow of blood.
Plasma constitutes approximately 50% of the total blood volume.
Plasma constitutes approximately 50% of the total blood volume.
Erythrocytes, or red blood cells, are responsible for fighting infections in the body.
Erythrocytes, or red blood cells, are responsible for fighting infections in the body.
Platelets facilitate blood clotting by releasing haemoglobin at the site of injury.
Platelets facilitate blood clotting by releasing haemoglobin at the site of injury.
The vena cava carries oxygenated blood from the body organs to the left auricle of the heart.
The vena cava carries oxygenated blood from the body organs to the left auricle of the heart.
During pulmonary circulation, blood flows from the right ventricle to the left auricle via the aorta.
During pulmonary circulation, blood flows from the right ventricle to the left auricle via the aorta.
The sound of a heartbeat is produced by the contraction of the heart muscles.
The sound of a heartbeat is produced by the contraction of the heart muscles.
A sphygmomanometer measures the pulse rate by amplifying the sound of the heartbeat.
A sphygmomanometer measures the pulse rate by amplifying the sound of the heartbeat.
Individuals with blood group O have both A and B antigens on their red blood cells.
Individuals with blood group O have both A and B antigens on their red blood cells.
A person with blood type AB can donate blood to individuals with blood types A, B, and O.
A person with blood type AB can donate blood to individuals with blood types A, B, and O.
Consuming a diet high in oily and fried foods is beneficial for maintaining heart health.
Consuming a diet high in oily and fried foods is beneficial for maintaining heart health.
All living organisms need food and ______ to survive.
All living organisms need food and ______ to survive.
The human transport system carries substances from one part of the ______ to another.
The human transport system carries substances from one part of the ______ to another.
The three major parts of the circulatory system are the heart, blood vessels and ______.
The three major parts of the circulatory system are the heart, blood vessels and ______.
The heart is protected by the rib ______.
The heart is protected by the rib ______.
The upper chambers of the heart are called ______ or atria.
The upper chambers of the heart are called ______ or atria.
The blood is carried to different parts of the body through blood ______.
The blood is carried to different parts of the body through blood ______.
[Blank] carry blood away from the heart.
[Blank] carry blood away from the heart.
[Blank] help to carry the blood towards the heart.
[Blank] help to carry the blood towards the heart.
The liquid part of blood is called ______.
The liquid part of blood is called ______.
Red blood cells are red due to the presence of ______.
Red blood cells are red due to the presence of ______.
[Blank] help in the clotting of blood.
[Blank] help in the clotting of blood.
The circulation of blood through the heart twice is called ______ circulation.
The circulation of blood through the heart twice is called ______ circulation.
The circulation of blood between the heart and lungs is called ______ circulation.
The circulation of blood between the heart and lungs is called ______ circulation.
The instrument to measure heartbeat is called a ______.
The instrument to measure heartbeat is called a ______.
Blood group O is called universal ______.
Blood group O is called universal ______.
The circulatory system transports substances throughout the body with the help of ______.
The circulatory system transports substances throughout the body with the help of ______.
The human heart has four chambers: two upper small chambers called ______ and two lower large chambers called ventricles.
The human heart has four chambers: two upper small chambers called ______ and two lower large chambers called ventricles.
[Blank] are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body.
[Blank] are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body.
The liquid part of the blood, called ______, is yellowish in color and consists of 90% water.
The liquid part of the blood, called ______, is yellowish in color and consists of 90% water.
[Blank], also known as erythrocytes, contain hemoglobin, a red-colored pigment responsible for carrying oxygen.
[Blank], also known as erythrocytes, contain hemoglobin, a red-colored pigment responsible for carrying oxygen.
[Blank], or leukocytes, play a vital role in the body's defense by destroying germs and fighting infection.
[Blank], or leukocytes, play a vital role in the body's defense by destroying germs and fighting infection.
The ______, also called thrombocytes, are responsible for the clotting of blood to prevent excessive blood loss after an injury.
The ______, also called thrombocytes, are responsible for the clotting of blood to prevent excessive blood loss after an injury.
The impure blood from the body enters the right auricle through two major veins called ______.
The impure blood from the body enters the right auricle through two major veins called ______.
Exchange of gases takes place in the ______, where carbon dioxide is removed from the blood and oxygen is absorbed.
Exchange of gases takes place in the ______, where carbon dioxide is removed from the blood and oxygen is absorbed.
Blood circulates through the heart twice in one complete round, which is known as ______.
Blood circulates through the heart twice in one complete round, which is known as ______.
Contraction of the heart causes blood to flow through the arteries, producing a force or pressure, and the closing of valves creates a sound called ______.
Contraction of the heart causes blood to flow through the arteries, producing a force or pressure, and the closing of valves creates a sound called ______.
The throbbing sound felt in arteries due to the expansion of their walls when blood is forced into the aorta is called ______.
The throbbing sound felt in arteries due to the expansion of their walls when blood is forced into the aorta is called ______.
The instrument used to measure blood pressure is called ______.
The instrument used to measure blood pressure is called ______.
People with blood group ______ are called universal donors because their red blood cells have no antigens.
People with blood group ______ are called universal donors because their red blood cells have no antigens.
What is the human body's transport system called?
What is the human body's transport system called?
Name the three major components of the circulatory system.
Name the three major components of the circulatory system.
Name the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart.
Name the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart.
Which blood vessels carry blood towards the heart?
Which blood vessels carry blood towards the heart?
What is the fluid part of the blood called?
What is the fluid part of the blood called?
Name the red-colored pigment present in RBCs.
Name the red-colored pigment present in RBCs.
Which type of blood cells help in fighting infection?
Which type of blood cells help in fighting infection?
What instrument is used to measure heartbeat?
What instrument is used to measure heartbeat?
What instrument is used to measure blood pressure?
What instrument is used to measure blood pressure?
People with which blood group are called universal donors?
People with which blood group are called universal donors?
Explain why the circulatory system is essential for multicellular organisms, especially when considering the limitations of diffusion.
Explain why the circulatory system is essential for multicellular organisms, especially when considering the limitations of diffusion.
Describe the structural adaptation of capillaries that facilitates the exchange of substances between blood and body tissues.
Describe the structural adaptation of capillaries that facilitates the exchange of substances between blood and body tissues.
How does the structure of arteries differ from that of veins, and how do these differences relate to their respective functions in the circulatory system?
How does the structure of arteries differ from that of veins, and how do these differences relate to their respective functions in the circulatory system?
Explain the importance of the septum in the human heart. What would be the consequence if this were absent?
Explain the importance of the septum in the human heart. What would be the consequence if this were absent?
Describe how the pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein are exceptions to the general rule that arteries carry oxygenated blood and veins carry deoxygenated blood.
Describe how the pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein are exceptions to the general rule that arteries carry oxygenated blood and veins carry deoxygenated blood.
Explain the role of hemoglobin in red blood cells and its significance for oxygen transport in the body.
Explain the role of hemoglobin in red blood cells and its significance for oxygen transport in the body.
How do white blood cells protect the body from infection, and what is the importance of this function?
How do white blood cells protect the body from infection, and what is the importance of this function?
Describe the role of platelets in blood clotting and explain why this process is essential for maintaining homeostasis.
Describe the role of platelets in blood clotting and explain why this process is essential for maintaining homeostasis.
Distinguish between pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation, highlighting the specific pathways each circuit takes.
Distinguish between pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation, highlighting the specific pathways each circuit takes.
Explain the connection between heart rate, pulse, and blood pressure, and how these parameters reflect the overall function of the cardiovascular system.
Explain the connection between heart rate, pulse, and blood pressure, and how these parameters reflect the overall function of the cardiovascular system.
Describe how a stethoscope is used to measure heartbeat and what the different components of this instrument do.
Describe how a stethoscope is used to measure heartbeat and what the different components of this instrument do.
A person has blood type AB. Explain what antigens and antibodies are present in their blood, and why they are considered universal recipients.
A person has blood type AB. Explain what antigens and antibodies are present in their blood, and why they are considered universal recipients.
Why are individuals with blood type O considered universal donors, and what limitations do they face when receiving blood transfusions?
Why are individuals with blood type O considered universal donors, and what limitations do they face when receiving blood transfusions?
Explain how regular exercise can reduce the risk of heart disease, referencing specific benefits mentioned in the text.
Explain how regular exercise can reduce the risk of heart disease, referencing specific benefits mentioned in the text.
Describe three specific dietary recommendations from the text that contribute to maintaining a healthy heart and circulatory system.
Describe three specific dietary recommendations from the text that contribute to maintaining a healthy heart and circulatory system.
Explain why the structure of capillaries, being only one cell thick, is essential for their function in the circulatory system.
Explain why the structure of capillaries, being only one cell thick, is essential for their function in the circulatory system.
How does the double circulatory system in humans contribute to a more efficient delivery of oxygen to the body compared to a single circulatory system?
How does the double circulatory system in humans contribute to a more efficient delivery of oxygen to the body compared to a single circulatory system?
Describe the implications of having a reduced number of platelets in the blood, such as in the case of dengue fever, and explain why this condition can be life-threatening.
Describe the implications of having a reduced number of platelets in the blood, such as in the case of dengue fever, and explain why this condition can be life-threatening.
Explain how the structure of the heart, specifically the presence of valves and the septum, ensures unidirectional blood flow and prevents the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Explain how the structure of the heart, specifically the presence of valves and the septum, ensures unidirectional blood flow and prevents the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Discuss how lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise play a critical role in maintaining healthy blood pressure and preventing hypertension.
Discuss how lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise play a critical role in maintaining healthy blood pressure and preventing hypertension.
Explain how the 'universal donor' and 'universal recipient' blood type designations are determined and why these classifications are critical in blood transfusions.
Explain how the 'universal donor' and 'universal recipient' blood type designations are determined and why these classifications are critical in blood transfusions.
Describe the functions of the three types of blood cells and explain how a deficiency in any one type can lead to specific health problems.
Describe the functions of the three types of blood cells and explain how a deficiency in any one type can lead to specific health problems.
Contrast the structural and functional differences between arteries and veins, and explain how these differences support their respective roles in blood circulation.
Contrast the structural and functional differences between arteries and veins, and explain how these differences support their respective roles in blood circulation.
Describe the role of haemoglobin in red blood cells and explain how its structure allows it to efficiently transport oxygen throughout the body.
Describe the role of haemoglobin in red blood cells and explain how its structure allows it to efficiently transport oxygen throughout the body.
Explain what the systolic and diastolic pressure measurements represent in blood pressure readings, and how these values provide insight into cardiovascular health.
Explain what the systolic and diastolic pressure measurements represent in blood pressure readings, and how these values provide insight into cardiovascular health.
Flashcards
Circulatory System
Circulatory System
A transport system for moving substances throughout our body with the help of blood.
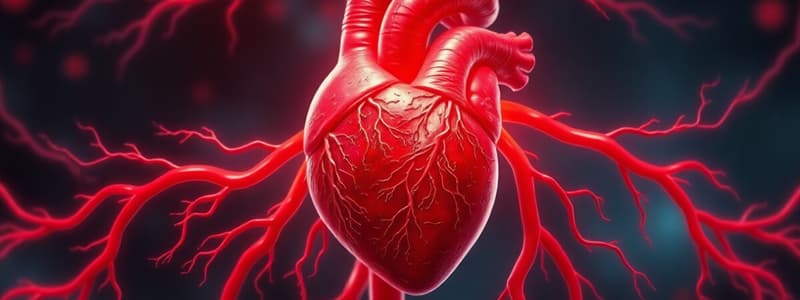
Heart
Heart
Muscular, pear-shaped organ in the chest cavity that pumps blood.
Pericardium
Pericardium
Double-layered membrane surrounding the heart.
Auricles (Atria)
Auricles (Atria)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventricles
Ventricles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atrioventricular Valves
Atrioventricular Valves
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Vessels
Blood Vessels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arteries
Arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Veins
Veins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Capillaries
Capillaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plasma
Plasma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
White Blood Cells (WBCs)
White Blood Cells (WBCs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Platelets (Thrombocytes)
Platelets (Thrombocytes)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Double Circulation
Double Circulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Circulation
Pulmonary Circulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systemic Circulation
Systemic Circulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulse
Pulse
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Pressure
Blood Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Transfusion
Blood Transfusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arteries Function
Arteries Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Veins Function
Veins Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stethoscope
Stethoscope
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sphygmomanometer
Sphygmomanometer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Groups (A, B, AB, O)
Blood Groups (A, B, AB, O)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Antigens
Antigens
Signup and view all the flashcards
Antibodies
Antibodies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Malnutrition
Malnutrition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Starvation
Starvation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Donation
Blood Donation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Donor
Blood Donor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Bank
Blood Bank
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Veins
Pulmonary Veins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Artery
Pulmonary Artery
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Group O
Blood Group O
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood group AB
Blood group AB
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stroke
Stroke
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heartbeat
Heartbeat
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vena Cava
Vena Cava
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aorta
Aorta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stethoscope parts
Stethoscope parts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Group A antibody
Blood Group A antibody
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Group B antibody
Blood Group B antibody
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood
Blood
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functions of Blood
Functions of Blood
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Circulation
Blood Circulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heartbeat Mechanism
Heartbeat Mechanism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benefits of Exercise
Benefits of Exercise
Signup and view all the flashcards
Good Food Habits
Good Food Habits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Normal Adult Heartbeat
Normal Adult Heartbeat
Signup and view all the flashcards
Harmful Effect of Hypertension
Harmful Effect of Hypertension
Signup and view all the flashcards
Antigens A and B
Antigens A and B
Signup and view all the flashcards
Matching Blood Groups
Matching Blood Groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benefits of Walking
Benefits of Walking
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sufficient Food
Sufficient Food
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Antibodies?
What are Antibodies?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Malnutrition?
What is Malnutrition?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Starvation?
What is Starvation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Flow Right Side
Blood Flow Right Side
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Flow Left Side
Blood Flow Left Side
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Transfusion Risks
Blood Transfusion Risks
Signup and view all the flashcards
Healthy Heart habits
Healthy Heart habits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Red Blood Cells
Red Blood Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
White Blood Cells
White Blood Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Platelets
Platelets
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Circulation Flow
Pulmonary Circulation Flow
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systemic Circulation Flow
Systemic Circulation Flow
Signup and view all the flashcards
Human Blood groups
Human Blood groups
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Group A transfusion
Blood Group A transfusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Group B transfusion
Blood Group B transfusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Group AB transfusion
Blood Group AB transfusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Group O transfusion
Blood Group O transfusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Septum (Heart)
Septum (Heart)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Plasma Composition
Blood Plasma Composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why walking is good for the heart?
Why walking is good for the heart?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Living organisms require food and oxygen to survive.
- Metabolic activities produce waste materials that need to be transported out of the body.
- The circulatory system transports necessary substances and waste throughout the body.
- Diffusion alone isn't efficient for transport and waste removal over long distances.
Circulatory System Components
- The circulatory system uses blood to transport substances throughout the body.
- An adult human body contains about 5.5 liters of blood.
- The circulatory system ensures blood reaches every cell.
- The three major components are the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
Heart Structure
- The heart is a muscular, pear-shaped organ in the chest cavity, slightly favoring the left side.
- An adult human heart is about the size of a clenched fist.
- It is protected by the rib cage.
- The heart is surrounded by a double-layered membrane called the pericardium.
- It has four chambers: two upper atria (or auricles) and two lower ventricles.
- Atria receive blood, while ventricles pump blood out of the heart.
- Atrioventricular valves between the atria and ventricles ensure one-way blood flow.
- There are no valves between the two auricles or between the two ventricles.
- A septum separates the right and left sides of the heart.
Blood Vessels
- Blood vessels are tubular channels that carry blood throughout the body.
- There are three types of blood vessels: arteries, veins, and capillaries.
- Arteries carry blood away from the heart to all parts of the body.
- Veins carry blood towards the heart.
- Arteries typically carry oxygen-rich blood, while veins carry carbon dioxide-rich blood, but pulmonary vessels are exceptions.
- A network of capillaries connects arteries and veins.
- Capillary walls are very thin, being only one cell thick.
- Arteries lie deep in tissues, except at the wrist and along the side of the neck, where the pulse can be felt.
- Veins lie closer to the skin's surface and can be seen as greenish-blue lines.
Arteries vs. Veins
- Arteries carry blood away from the heart; veins bring blood to the heart.
- Arteries carry oxygenated blood (except the pulmonary artery); veins carry deoxygenated blood (except the pulmonary vein).
- Arteries are deep-seated while veins are closer to the skin surface.
- Blood flow in arteries is jerky and under high pressure, while in veins it is smooth and under low pressure.
- Arteries lack valves, while veins have valves.
- Arteries have thick, elastic walls, while vein walls are thinner.
Blood Composition
- Blood is a red fluid inside blood vessels, comprising plasma and cells (corpuscles).
- Plasma is the yellowish, liquid part, 90% water, containing nutrients, waste, and hormones.
- The three types of blood cells are red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets.
- RBCs (erythrocytes) are red due to hemoglobin, which carries oxygen.
- WBCs (leukocytes) destroy germs and fight infection.
- Platelets (thrombocytes) aid in blood clotting.
- Reduced platelets due to dengue fever can lead to symptoms like bleeding gums or nose, bruising, and blood in urine and stool.
Blood Functions
- Blood carries food and oxygen to body cells.
- It transports waste products to excretory organs.
- Blood defends against infection by destroying germs.
- It facilitates blood clotting, preventing excessive blood loss.
- Blood assists in regulating body temperature.
Blood Circulation Process
- Blood circulates via the heart's pumping action.
- Deoxygenated blood from body organs enters the right atrium through the vena cava.
- Blood flows from the right atrium to the right ventricle.
- Blood is then pumped to the pulmonary artery through to the lungs.
- Gas exchange occurs in the lungs.
- Oxygenated blood is carried by the pulmonary vein to the left atrium.
- Blood flows from the left atrium to the left ventricle and then through the aorta to body parts.
Double Circulation
- Blood passes through the heart twice in one complete cycle.
- Pulmonary circulation occurs between the heart and lungs: right ventricle → pulmonary artery → lungs → pulmonary vein → left atrium.
- Systemic circulation occurs between the heart and body organs: left ventricle → aorta → body organs → vena cava → right atrium.
Heartbeat and Pulse
- Cardiac muscles contract and relax to pump blood.
- The contraction of the heart causes blood to flow through the arteries with pressure.
- Valve closure produces the sound known as heartbeat.
- A child's heartbeat is 90-100 times per minute, while an adult's is 70-80.
- Heartbeat increases during exercise, excitement, or stress.
- A stethoscope amplifies heartbeat sounds.
- A stethoscope consists of a chest piece, two earpieces, and a tube joining them.
- Pulse is the throbbing felt in arteries due to blood being forced into the aorta.
Blood Pressure
- The pumping heart creates pressure in arteries, known as blood pressure.
- A sphygmomanometer measures blood pressure.
- Physical activity raises blood pressure by increasing heart rate or narrowing arteries.
- Constant high blood pressure can damage the heart and arteries, potentially causing a stroke or death.
Blood Groups
- Human blood is categorized into four groups: A, B, AB, and O.
- Blood group is determined by the antigens present on red blood cells, either A or B.
- Blood group A has A antigens only.
- Blood group B has B antigens only.
- Blood group AB has both A and B antigens.
- Blood group O has neither A nor B antigens.
- Plasma contains antibodies, anti-A and anti-B, which do not attack antigens on their own RBCs.
Antigens and Antibodies in Blood Groups
- Blood group A has A antigens and anti-B antibodies.
- Blood group B has B antigens and anti-A antibodies.
- Blood group AB has both A and B antigens but no antibodies.
- Blood group O has no antigens but both anti-A and anti-B antibodies.
Blood Transfusion
- Blood transfusion is transferring blood from one person to another.
- It is performed when people are ill or injured.
- Blood is matched between donor and recipient to prevent clumping of red blood cells.
Blood Group Transfusion Compatibility
- Blood group A can donate to A and AB, and receive from A and O.
- Blood group B can donate to B and AB, and receive from B and O.
- Blood group AB can donate to AB only and receive from all groups (universal recipient).
- Blood group O can donate to all groups (universal donor) and receive from O only.
Keeping the Heart Healthy
- Regular exercise and good food habits are important for heart health.
- Regular exercise increases heart fitness, reduces heart disease risk, reduces body fat, controls weight, and lowers blood pressure.
- Walking is an effective exercise for overall fitness and weight control.
Good Food Habits
- Eating a balanced diet is essential for maintaining good health.
- Balanced diets vary by age, health, and occupation.
- Balanced diets help avoid malnutrition.
- Eating habits include eating slowly, keeping meals small and frequent, chewing food properly, and developing regular food habits.
- Food should be clean, protected from contaminants, and properly cooked.
- Avoid oily and fried foods.
- Use clean utensils.
- Include green salad, vegetables, and fruits in the diet.
- Drink plenty of clean, filtered water.
Extra Information
- The human heart weighs 225-340 grams and pumps about 16,360 liters of blood in 24 hours.
- A stroke is caused by an interruption of blood flow to the brain.
- Antigens are foreign substances that stimulate antibody production.
- Antibodies are chemicals that destroy antigens.
- Blood donation is voluntary and helps in emergencies.
- A blood donor provides about 420 mL of blood per donation.
- A blood bank collects, tests, and stores donated blood.
- Malnutrition is the lack of a balanced diet.
- Starvation is not having enough food for energy.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.