Podcast
Questions and Answers
What happens to the diaphragm during inhalation?
What happens to the diaphragm during inhalation?
- It contracts and moves down. (correct)
- It remains stationary.
- It relaxes and moves up.
- It contracts and moves up.
Which structure carries deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart?
Which structure carries deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart?
- Pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary vein
- Superior vena cava (correct)
- Aorta
Which of the following adaptations might allow diving mammals like Cuvier's beaked whale to remain submerged for extended periods?
Which of the following adaptations might allow diving mammals like Cuvier's beaked whale to remain submerged for extended periods?
- High metabolic rate
- Higher oxygen consumption
- A slower heart rate (correct)
- Increased lung capacity (correct)
What occurs to the diaphragm during exhalation?
What occurs to the diaphragm during exhalation?
What is the primary function of the pulmonary arteries?
What is the primary function of the pulmonary arteries?
What distinguishes the heart structure of most amphibians compared to mammals?
What distinguishes the heart structure of most amphibians compared to mammals?
What is the function of the pulmonary circuit in a tetrapod?
What is the function of the pulmonary circuit in a tetrapod?
What characterizes double circulation in tetrapods?
What characterizes double circulation in tetrapods?
Which statement describes the pulmonary vs. systemic circuits in amphibians?
Which statement describes the pulmonary vs. systemic circuits in amphibians?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of a three-chambered heart?
Which of the following structures is NOT part of a three-chambered heart?
What evolutionary significance is shown in the heart structure of birds and mammals?
What evolutionary significance is shown in the heart structure of birds and mammals?
Why is the two-ventricle design advantageous for mammals?
Why is the two-ventricle design advantageous for mammals?
Which aspect of amphibians' circulatory system contributes to inefficiency in re-oxygenation?
Which aspect of amphibians' circulatory system contributes to inefficiency in re-oxygenation?
What is the primary function of a circulatory system?
What is the primary function of a circulatory system?
Which of the following is NOT a component of a closed circulatory system?
Which of the following is NOT a component of a closed circulatory system?
What are the benefits of double circulation compared to single circulation?
What are the benefits of double circulation compared to single circulation?
In which type of circulatory system does the circulatory fluid directly bathe the organs?
In which type of circulatory system does the circulatory fluid directly bathe the organs?
What are capillaries primarily responsible for?
What are capillaries primarily responsible for?
What is the significance of diastole in the cardiac cycle?
What is the significance of diastole in the cardiac cycle?
Which structure is responsible for carrying oxygen-poor blood toward the heart?
Which structure is responsible for carrying oxygen-poor blood toward the heart?
In non-tetrapod vertebrates, what type of heart do they possess?
In non-tetrapod vertebrates, what type of heart do they possess?
During countercurrent gas exchange in fish, what is the primary advantage?
During countercurrent gas exchange in fish, what is the primary advantage?
What is a significant disadvantage of single circulation in fish?
What is a significant disadvantage of single circulation in fish?
Which of the following statements about the function of the circulatory system is false?
Which of the following statements about the function of the circulatory system is false?
What role does the heart play in a closed circulatory system?
What role does the heart play in a closed circulatory system?
What structural feature sets veins apart from arteries?
What structural feature sets veins apart from arteries?
How does diffusion facilitate the exchange of nutrients and waste in multicellular organisms?
How does diffusion facilitate the exchange of nutrients and waste in multicellular organisms?
What is the main role of the circulatory and respiratory systems working together?
What is the main role of the circulatory and respiratory systems working together?
During which phase of the cardiac cycle does blood leave the heart?
During which phase of the cardiac cycle does blood leave the heart?
How does blood pressure in the arteries fluctuate during the cardiac cycle?
How does blood pressure in the arteries fluctuate during the cardiac cycle?
What is the significance of the countercurrent exchange system in fish gills?
What is the significance of the countercurrent exchange system in fish gills?
What type of breathing do mammals utilize to ventilate their lungs?
What type of breathing do mammals utilize to ventilate their lungs?
Which system directly delivers oxygen to body cells in insects?
Which system directly delivers oxygen to body cells in insects?
Which of the following best describes the function of alveoli in mammalian lungs?
Which of the following best describes the function of alveoli in mammalian lungs?
What is one disadvantage of obtaining oxygen from water compared to air?
What is one disadvantage of obtaining oxygen from water compared to air?
How do amphibians ventilate their lungs?
How do amphibians ventilate their lungs?
Which option describes the movement of air in bird lungs?
Which option describes the movement of air in bird lungs?
What type of blood is delivered from the lungs to the heart via the pulmonary veins?
What type of blood is delivered from the lungs to the heart via the pulmonary veins?
In which type of organism is a buccal pump used for ventilation?
In which type of organism is a buccal pump used for ventilation?
What is the rhythmic bulging of artery walls associated with each heartbeat called?
What is the rhythmic bulging of artery walls associated with each heartbeat called?
Which mechanism best describes how fish extract oxygen from water?
Which mechanism best describes how fish extract oxygen from water?
Flashcards
Double Circulation
Double Circulation
In double circulation, blood flows through the heart twice in one complete circuit. It ensures efficient oxygen delivery and high blood pressure in the systemic circuit, which carries oxygenated blood to the body.
Pulmocutaneous Circuit
Pulmocutaneous Circuit
The pulmocutaneous circuit in amphibians is responsible for transporting deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs and skin for gas exchange.
Amphibian Heart
Amphibian Heart
Amphibians have a three-chambered heart with two atria and one ventricle. The incomplete septum within the ventricle partially separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, leading to some mixing.
Reptile Heart
Reptile Heart
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mammalian and Avian Hearts
Mammalian and Avian Hearts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systemic Circuit
Systemic Circuit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Circuit
Pulmonary Circuit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Convergent Evolution (4-chambered Heart)
Convergent Evolution (4-chambered Heart)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of a circulatory system?
What is the function of a circulatory system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Open circulatory system
Open circulatory system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Closed circulatory system
Closed circulatory system
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the benefit of a closed circulatory system?
What is the benefit of a closed circulatory system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arteries
Arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Veins
Veins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Capillaries
Capillaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Single circulation
Single circulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diastole
Diastole
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systole
Systole
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory media
Respiratory media
Signup and view all the flashcards
Countercurrent gas exchange
Countercurrent gas exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventilation in mammals
Ventilation in mammals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventilation in birds
Ventilation in birds
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiac Cycle
Cardiac Cycle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Pressure
Blood Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systolic Pressure
Systolic Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diastolic Pressure
Diastolic Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulse
Pulse
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventilation
Ventilation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gills
Gills
Signup and view all the flashcards
Countercurrent Exchange
Countercurrent Exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tracheal System
Tracheal System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lungs
Lungs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveoli
Alveoli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Positive Pressure Breathing
Positive Pressure Breathing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Negative Pressure Breathing
Negative Pressure Breathing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diaphragm
Diaphragm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inhalation
Inhalation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exhalation
Exhalation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diving Respiration
Diving Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diving Mammals
Diving Mammals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Circulation and Gas Exchange
- A circulatory system connects the fluid surrounding cells with organs exchanging gases, absorbing nutrients, and disposing of wastes.
- Circulatory systems are composed of interconnecting vessels, a muscular pump (the heart), and a circulatory fluid (e.g., hemolymph or blood).
- Open circulatory systems have a circulatory fluid (hemolymph) that bathes the organs directly.
- Closed circulatory systems have a circulatory fluid (blood) confined to vessels, apart from interstitial fluid.
- Closed circulatory systems are more efficient because of higher blood pressure, enabling effective delivery of oxygen and nutrients in larger, more active animals.
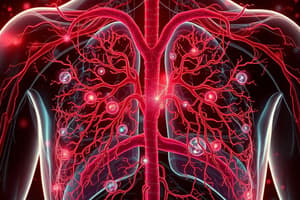
- Vertebrates have a closed circulatory system called the cardiovascular system, where blood travels through one-way vessels.
- Arteries carry blood away from the heart, veins carry blood to the heart, and capillaries connect arteries to veins.
- Non-tetrapod vertebrates (e.g., fish) have a two-chambered heart with single circulation. Blood leaves the heart and passes through two capillary beds before returning.
- Single circulation's disadvantage is lower blood pressure, which is less efficient.
- Tetrapods (e.g., amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals) have a three or four-chambered heart with double circulation.
- Double circulation involves two circuits: -Pulmonary/pulmocutaneous circuit picks up O2 from heart/skin; has lower blood pressure -Systemic circuit delivers O2 to body cells; has high blood pressure
- Amphibians, reptiles have 3-chambered hearts with two atria and one ventricle, with a ridge or partial septum.
- Birds and mammals have 4-chambered hearts with completely divided ventricles (convergent evolution).
- The heart contracts and relaxes in a rhythmic cycle called the cardiac cycle.
- The contraction phase is called systole, where blood is sent from the heart.
- The relaxation phase is called diastole, where blood is pumped into chambers.
- Blood pressure is the strain on artery walls, measured as systolic (during ventricular systole)/diastolic (during diastole) pressure and a pulse is the rhythmic bulging of artery walls with each heartbeat.
- Circulatory and respiratory systems work together to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Exchange with Environment
- Nutrients, gases, and wastes must pass through cell membranes through diffusion.
- Multicellular, simple body plans (e.g., gastrovascular cavity) participate in both digestion and material exchange.
- Complex animals have a respiratory and circulatory system to aid in diffusion to cells.
Gas Exchange
- Gas exchange supplies oxygen (O2) for cellular respiration and disposes of carbon dioxide (CO2) waste.
- Animals can use air or water as the oxygen source (respiratory medium). Ventilation moves the respiratory medium over the respiratory surface.
- In a given volume, there is less oxygen available in water than in air. Obtaining oxygen from water requires greater efficiency than air breathing.
- Animals require large, moist respiratory surfaces for gas exchange.
- Gills are a specialized gas exchange system in aquatic animals; oxygen diffuses from water into blood vessels, and carbon dioxide diffuses from blood into water.
- Fish gills use countercurrent exchange, where blood flows in the opposite direction of water flow over the gills, efficiently extracting oxygen. More than 80% of the dissolved oxygen in water is removed as water passes over the respiratory surface in fish gills.
- The tracheal system of insects consists of a network of branching tubes that supply oxygen directly to body cells, separate from the circulatory system.
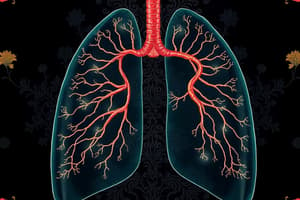
- Lungs are an infolding of the body surface that improves surface area for gas exchange. The circulatory system transports gases from lungs to the rest of the body. Gas exchange takes place in specialized air sacs called alveoli.
- Amphibians ventilate lungs through positive pressure breathing using a buccal pump.
- Birds have unidirectional airflow through lungs (increases efficiency) with multiple sacs that keep air flowing through lungs, requiring two cycles of inhalation and exhalation.
- Mammals ventilate their lungs by negative pressure breathing, where air is pulled into lungs as lung volume increases due to rib muscle and diaphragm contractions.
Respiratory Adaptations of Diving Mammals and Birds
- Diving mammals (e.g., Cuvier's beaked whale) store a lot of oxygen (high blood volume, high myoglobin), conserve oxygen (dive passively, lower metabolic needs, decrease heart rate, blood shunted to vital areas, exhale before diving), and have lungs that can collapse in high-pressure environments.
- Diving birds (e.g., Emperor penguin) have adaptations for respiration during dives, but specific details are not available in this summary.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.