Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary way cholesterol interacts with lipid tails in a cell membrane?
What is the primary way cholesterol interacts with lipid tails in a cell membrane?
- It binds lipid tails firmly. (correct)
- It dissolves lipid tails.
- It repels lipid tails.
- It binds lipid tails loosely.
Which of the following best describes cholesterol's role in maintaining membrane fluidity?
Which of the following best describes cholesterol's role in maintaining membrane fluidity?
- It completely prevents fluidity.
- It acts as a regulator, preventing extreme fluidity or rigidity. (correct)
- It controls fluidity by reducing it at all temperatures.
- It increases fluidity regardless of temperature.
During cold weather, what is the critical function of cholesterol in cell membranes?
During cold weather, what is the critical function of cholesterol in cell membranes?
- It increases membrane rigidity.
- It causes membrane collapse.
- It prevents the membrane from freezing solid. (correct)
- It promotes the formation of ice crystals.
What effect does cholesterol have on cell membranes in hot weather?
What effect does cholesterol have on cell membranes in hot weather?
Which of these is NOT a function of cholesterol in a cell membrane?
Which of these is NOT a function of cholesterol in a cell membrane?
Flashcards
Cholesterol
Cholesterol
A type of fat-like molecule found in cell membranes.
Membrane Fluidity Control (1)
Membrane Fluidity Control (1)
Cholesterol helps prevent the lipid tails in cell membranes from packing too tightly.
Membrane Fluidity Control (2)
Membrane Fluidity Control (2)
Cholesterol helps ensure that cell membranes don't become too fluid in hot conditions.
Preventing Membrane Freezing
Preventing Membrane Freezing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cholesterol's Role in Membrane Fluidity
Cholesterol's Role in Membrane Fluidity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Cholesterol's Role in Maintaining Membrane Fluidity
- Cholesterol is a lipid molecule that plays a crucial role in maintaining the fluidity of cell membranes.
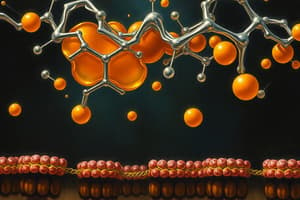
- It directly interacts with the hydrophobic lipid tails of the phospholipids in the membrane. This interaction is characterized by a strong binding between the cholesterol's rigid structure and the fatty acid tails.
- Cholesterol's presence in the membrane regulates membrane fluidity under varying temperatures.
- In cold temperatures, cholesterol prevents the phospholipids from packing too tightly together, which would lead to membrane solidification and a loss of membrane fluidity. It maintains the appropriate spacing between phospholipid molecules, thus preventing freezing.
- In contrast, in hot temperatures, cholesterol hinders excessive movement of phospholipid molecules. It reduces their movement, preventing the membrane from becoming overly fluid and maintaining optimal membrane structure.
- These effects on fluidity are crucial for the proper functioning of cellular processes. Maintaining the right balance is essential for optimal cell function.
- Cholesterol is distributed within the membrane, playing a role in varying membrane properties based on local needs.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.