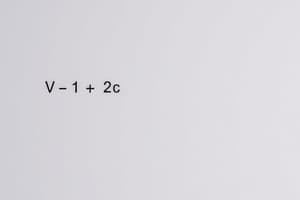Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the compressibility factor (Z) for ideal gases?
What is the compressibility factor (Z) for ideal gases?
- 2
- Variable
- 0
- 1 (correct)
At low pressure and high temperature, real gases behave like ideal gases.
At low pressure and high temperature, real gases behave like ideal gases.
True (A)
What is Van Der Waals' equation used for?
What is Van Der Waals' equation used for?
Describing the behavior of real gases.
In real gases, the attractive force between molecules ___ exist.
In real gases, the attractive force between molecules ___ exist.
Which of the following correctly describes ion-dipole forces?
Which of the following correctly describes ion-dipole forces?
Match the types of intermolecular forces with their descriptions:
Match the types of intermolecular forces with their descriptions:
What is an unsaturated solution?
What is an unsaturated solution?
All solutions are mixtures, but not all mixtures are solutions.
All solutions are mixtures, but not all mixtures are solutions.
A ___ solution contains the maximum possible amount of dissolved solute at equilibrium.
A ___ solution contains the maximum possible amount of dissolved solute at equilibrium.
Which of the following characteristics apply to ideal gases?
Which of the following characteristics apply to ideal gases?
At low pressure and high temperature, real gases behave similarly to ideal gases.
At low pressure and high temperature, real gases behave similarly to ideal gases.
What is the compressibility factor (Z) for ideal gases?
What is the compressibility factor (Z) for ideal gases?
The formula for the compressibility factor is Z = (P * Vm)/(R * T). Here, P stands for _______.
The formula for the compressibility factor is Z = (P * Vm)/(R * T). Here, P stands for _______.
Match the following intermolecular forces with their characteristics:
Match the following intermolecular forces with their characteristics:
An unsaturated solution can _______ more solute at a given temperature.
An unsaturated solution can _______ more solute at a given temperature.
What is the difference between a saturated and a supersaturated solution?
What is the difference between a saturated and a supersaturated solution?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Ideal Gases vs. Real Gases
- Ideal gases have negligible volume, no intermolecular forces, and perfectly elastic collisions.
- Real gases have appreciable volume, intermolecular forces, and non-elastic collisions.
- Real gases behave more like ideal gases at low pressure and high temperature.
Compressibility Factor (Z)
- Compressibility factor (Z) is a measure of how much a real gas deviates from ideal gas behavior.
- For ideal gases, Z = 1.
- Z = (P * Vm)/(R * T) where P is pressure, Vm is molar volume, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is temperature.
Van Der Waal's Equation
- Van Der Waal's equation accounts for the non-ideal behavior of real gases by introducing correction factors for pressure and volume.
- (P + n²a/V²)(V-nb)=nRT.
- The pressure of a real gas is lower than that of an ideal gas.
Intermolecular Forces
- Intermolecular forces are attractive forces between molecules.
- Ion-dipole force: Attractive force between an ion and a polar molecule.
- Ion-ion interaction: Strong attractive force between oppositely charged ions, often found in solid salts.
- Dipole-dipole interaction: Attractive force between polar molecules.
- The strength of intermolecular forces influences the state of matter: strongest in solids, weakest in gases.
Solutions
- A binary solution is a homogeneous mixture of two components.
- Classification of solutions:
- According to the amount of solute:
- Unsaturated solution: Can dissolve more solute.
- Saturated solution: Contains the maximum possible amount of dissolved solute at equilibrium.
- Supersaturated solution: Contains more dissolved solute than the equilibrium amount.
- According to the nature of the solute:
- Electrical conductivity: Solutions can be classified based on their ability to conduct electricity.
- According to the amount of solute:
- All solutions are mixtures, but not all mixtures are solutions.
Ideal Gases vs. Real Gases
- Ideal gases are theoretical and do not have intermolecular forces
- Real gases have intermolecular forces and take up space
- Real gases behave more like ideal gases at low pressures and high temperatures
Compressibility Factor (Z)
- The compressibility factor is a measure of how much a real gas deviates from ideal gas behavior
- The compressibility factor is equal to 1 for ideal gases
- The compressibility factor is calculated by dividing the product of pressure and molar volume by the product of the ideal gas constant and temperature
Van Der Waal's Equation
- The van der Waal's equation is a modification of the ideal gas law to account for the intermolecular forces and volume of real gas molecules
- The 'a' value represents attraction between gas molecules, the 'b' value represents the actual volume of the molecules themselves
- The van der Waals equation predicts that the pressure of a real gas is lower than that of an ideal gas at the same temperature and volume
Intermolecular Forces
- Intermolecular forces exist between molecules and are weaker than intramolecular forces that hold atoms together within a molecule
- Ion-dipole forces involve an interaction between an ion and a polar molecule
- Ion-ion attractions are strong and occur in solid states
- Dipole-dipole interactions occur between polar molecules
- The stronger the intermolecular force, the more difficult it is to separate the molecules. The stronger the force, the higher the melting and boiling points of that molecule.
Solutions
- A binary solution has two components and is a homogeneous mixture
- An unsaturated solution can dissolve more solute
- A saturated solution contains the maximum possible amount of dissolved solute at a given temperature
- A supersaturated solution contains more dissolved solute than the saturated solution
- The electrical conductivity of a solution depends on the nature of the solute
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.