Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following correctly represents sodium sulfide?
Which of the following correctly represents sodium sulfide?
- Na2O
- NaCl
- Na2S (correct)
- Na3P
What is the formula for iron(III) oxide?
What is the formula for iron(III) oxide?
- HgO
- Hg2O
- Fe2O3 (correct)
- FeO
Which element is a transition metal that can form more than one kind of ion?
Which element is a transition metal that can form more than one kind of ion?
- Al
- Na
- Cu (correct)
- Cs
What is the charge on the cation in the compound Fe2O3?
What is the charge on the cation in the compound Fe2O3?
Which of the following polyatomic ions is a cation?
Which of the following polyatomic ions is a cation?
What is the purpose of coefficients in a balanced chemical equation?
What is the purpose of coefficients in a balanced chemical equation?
In the reaction C2H6 + 7O2 → 4CO2 + 6H2O, how many total oxygen atoms are present on the product side?
In the reaction C2H6 + 7O2 → 4CO2 + 6H2O, how many total oxygen atoms are present on the product side?
What is a correct balanced equation for the reaction of ethane (C2H6) with oxygen (O2)?
What is a correct balanced equation for the reaction of ethane (C2H6) with oxygen (O2)?
When balancing the equation C2H6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O, which element must be balanced last?
When balancing the equation C2H6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O, which element must be balanced last?
Which one of the following statements best describes the application of stoichiometry in everyday life?
Which one of the following statements best describes the application of stoichiometry in everyday life?
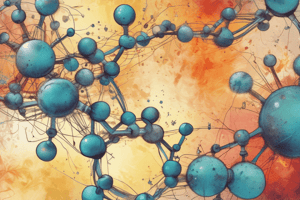
What type of mixture is represented by Image I?
What type of mixture is represented by Image I?
How is Image II best categorized?
How is Image II best categorized?
What does the composition of molecules in Image III indicate?
What does the composition of molecules in Image III indicate?
Which of the following best describes a physical property of matter?
Which of the following best describes a physical property of matter?
Which option represents a chemical property of matter?
Which option represents a chemical property of matter?
Image I is comprised of similar blue spheres. What can be inferred about its classification?
Image I is comprised of similar blue spheres. What can be inferred about its classification?
The organization of spheres in Image II suggests what about its purity?
The organization of spheres in Image II suggests what about its purity?
Which of the following statements about the properties of matter is true?
Which of the following statements about the properties of matter is true?
Which type of radiation was discovered by Ernest Rutherford?
Which type of radiation was discovered by Ernest Rutherford?
What does the atomic number (Z) represent?
What does the atomic number (Z) represent?
How are isotopes defined?
How are isotopes defined?
What is the atomic mass number based on?
What is the atomic mass number based on?
Which of the following is true about the mass of subatomic particles?
Which of the following is true about the mass of subatomic particles?
What percentage of carbon isotopes in a natural sample is typically C-12?
What percentage of carbon isotopes in a natural sample is typically C-12?
Which scientist coined the term 'proton'?
Which scientist coined the term 'proton'?
What is the balanced reaction for the formation of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen?
What is the balanced reaction for the formation of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen?
Which element does not have a stable isotope with mass number 14?
Which element does not have a stable isotope with mass number 14?
What is considered the theoretical yield in a chemical reaction?
What is considered the theoretical yield in a chemical reaction?
In the reaction of 2 Al(s) + 3 Cl2(g) → 2 AlCl3(s), if 1.50 mol of Al and 3.00 mol of Cl2 react, what is the limiting reactant?
In the reaction of 2 Al(s) + 3 Cl2(g) → 2 AlCl3(s), if 1.50 mol of Al and 3.00 mol of Cl2 react, what is the limiting reactant?
If 1.50 mol of Al yield 2.00 mol of AlCl3, how many moles of Cl2 remain at the end of the reaction that started with 3.00 mol?
If 1.50 mol of Al yield 2.00 mol of AlCl3, how many moles of Cl2 remain at the end of the reaction that started with 3.00 mol?
What is the oxidation state of sulfur in H2S?
What is the oxidation state of sulfur in H2S?
In potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7), what is the oxidation state of one chromium atom?
In potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7), what is the oxidation state of one chromium atom?
What characterizes a strong electrolyte?
What characterizes a strong electrolyte?
In the reaction FeO (s) + C (s) -> Fe (s) + CO (g), which substance is the reducing agent?
In the reaction FeO (s) + C (s) -> Fe (s) + CO (g), which substance is the reducing agent?
What is the oxidation state of sulfur in the polyatomic ion SO42-?
What is the oxidation state of sulfur in the polyatomic ion SO42-?
In a single-displacement reaction represented as A + MX -> M + AX, what happens to element A?
In a single-displacement reaction represented as A + MX -> M + AX, what happens to element A?
What is the oxidation number of sulfur in sodium sulfite (Na2SO3)?
What is the oxidation number of sulfur in sodium sulfite (Na2SO3)?
Flashcards
Element
Element
A substance made up of only one type of atom. An element cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
Compound
Compound
A substance made up of two or more different elements chemically combined in a fixed ratio. Compounds can be broken down into simpler substances (elements) by chemical means.
Homogeneous Mixture
Homogeneous Mixture
A mixture that has a uniform composition throughout. The different components are evenly distributed and not easily distinguishable.
Heterogeneous Mixture
Heterogeneous Mixture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Physical Property
Physical Property
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chemical Property
Chemical Property
Signup and view all the flashcards
Physical Change
Physical Change
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chemical Change
Chemical Change
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dalton's atomic theory
Dalton's atomic theory
Signup and view all the flashcards
J.J. Thomson's contribution to atomic structure
J.J. Thomson's contribution to atomic structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Millikan's oil drop experiment
Millikan's oil drop experiment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radioactivity
Radioactivity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rutherford's discovery of radioactive emissions
Rutherford's discovery of radioactive emissions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atomic nucleus
Atomic nucleus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neutrons
Neutrons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Isotopes
Isotopes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transition Metal Ions
Transition Metal Ions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Writing Ionic Compound Formulas
Writing Ionic Compound Formulas
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polyatomic Ions
Polyatomic Ions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common Cations
Common Cations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Which is the transition metal?
Which is the transition metal?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing Chemical Equations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stoichiometric Coefficients
Stoichiometric Coefficients
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry
Signup and view all the flashcards
Balanced Chemical Equation
Balanced Chemical Equation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subscript in Chemical Formula
Subscript in Chemical Formula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Limiting reactant
Limiting reactant
Signup and view all the flashcards
Excess reactant
Excess reactant
Signup and view all the flashcards
Theoretical yield
Theoretical yield
Signup and view all the flashcards
Actual yield
Actual yield
Signup and view all the flashcards
Percent yield
Percent yield
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxidation Number Rule for Polyatomic Ions
Oxidation Number Rule for Polyatomic Ions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxidation State of Elements
Oxidation State of Elements
Signup and view all the flashcards
Strong Electrolyte
Strong Electrolyte
Signup and view all the flashcards
Single-Displacement Reaction
Single-Displacement Reaction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxidizing Agent
Oxidizing Agent
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reducing Agent
Reducing Agent
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxidized Species
Oxidized Species
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reduced Species
Reduced Species
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Chapter 1: The Basics of Chemistry
- Chemistry is the study of matter, its properties, and the mechanisms involved in its changes.
- Matter is any substance that has mass and occupies space.
- The fundamental building blocks of matter are atoms, which cannot be chemically broken down into smaller components.
- Atoms combine to form larger molecules and compounds.
- Matter comes in three states: gas, solid, and liquid.
States of Matter
- Solids: Atoms are closely packed together, relatively stationary, slightly compressible, have a definite shape and volume.
- Liquids: Atoms are more spread out, have intermediate mobility, slightly compressible, no definite shape, but definite volume.
- Gases: Atoms are very far apart, high velocities, highly compressible, no definite shape or volume.
Classification of Matter
- Matter:
- Pure substance: Cannot be physically separated.
- Element: Cannot be decomposed chemically.
- Compound: Can be decomposed chemically.
- Mixture: Can be physically separated.
- Homogeneous mixture: Uniform composition (solution).
- Heterogeneous mixture: Non-uniform composition.
- Pure substance: Cannot be physically separated.
The Scientific Method
- Develop theories that are consistent with available data.
- Make observations about nature using experiences, thoughts, and readings.
- Ask interesting questions.
- Formulate hypotheses based on observations and questions.
- Develop testable predictions from hypotheses.
- Gather data to test predictions and verify results.
Units of Measurement
- Property | English units | SI units
- --|---|---
- Mass* | pounds (lbs) | kilogram (kg)
- Length* | yard (yd) | Meter (m)
- Volume* | gallon (gal) | Cubic Meter (m^3)
- Temperature* | Fahrenheit (°F) | Kelvins (K)
Temperature Scales
- Conversion formulas for temperature scales: °F = (°C) + 32 °C = (°F - 32)/9 9 * K =°C + 273.15
Significant Figures
- Report all measurements to one digit past the last digit of certainty.
- The number of digits in a measurement indicates the precision of the measurement.
- Zeros between non-zero digits are significant
- Leading zeros are not significant
- Trailing zeros after a decimal point are significant
Exact Quantities
- Quantities whose precision is considered infinite are known as exact numbers
- Equality statements or conversion factors
Dimensional Analysis
- Use conversion factors to express a given unit in a different unit
- The magnitude of the units in the conversion factor has to be the same as the given unit; therefore, the given unit has to be on the bottom and the new unit on the top
- The magnitude of the units on the top and bottom has to be the same
Density
- Density is the ratio of mass to volume.
- Density = mass/volume
- Density, is a physical property, unique to each substance, and is temperature dependent.
- Water Density at 20°C = 0.99823 g/mL
Chapter 2: Matter at the Atomic Level
- Atoms are extremely small, fundamental particles of matter.
- Atoms of the same element are identical to each other
- Atoms in chemical reactions are not changed into other elements; atoms are neither created or destroyed.
- Compounds are formed when atoms of more than one element combine in a fixed, whole-number ratio.
- Atomic theory
- J.J. Thomson and the electron
- Rutherford's gold-foil experiment and the nuclear model of the atom
- Atomic numbers
- lons
- Atomic mass and isotopes
- The periodic table
- The mole and Avogadro's number
- Radioactivity
- Subatomic particles
- Symbols of elements, and their relations to atomic numbers and mass numbers
- Isotopes and their percent natural abundance
- Average mass calculation
- Properties of metals, nonmetals and metalloids
- Using the Periodic Table to predict properties of elements and formations of ions
Important Concepts
- Atomic number (Z): The number of protons in an atom.
- Mass number (A): The sum of protons and neutrons in an atom.
- Isotopes: Atoms of the same element with different mass numbers (different numbers of neutrons).
- Isotopic abundance: The percentage of each isotope in a naturally occurring sample of an element.
- Atomic mass: The weighted average of the masses of all the naturally occurring isotopes of an element.
- Atom: The smallest unit of an element that retains the properties of that element.
- Mole: A unit that represents 6.022 x 10^23 particles (atoms or molecules).
- Molar mass: The mass of one mole of a substance in grams/mole
Chapter 3: Molecules, Compounds, and Their Composition
- Introduction: Importance of compound formulas and naming.
- Chemical formulas representing compounds.
- Differentiating ionic and covalent compounds
- Naming ionic and molecular compounds
- Molar mass calculation
- Mass percent calculation
- Calculating empirical formula
- Calculating molecular formulas
Chapter 4: Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometry
- Introduction: Defining chemical reactions and their relevance to understanding chemical systems.
- Chemical Equations provide a representation of reactants and products.
- Coefficents are used when balancing chemical equations for conservation of mass, showing the number of moles of each reactant and product in a chemical reaction.
- Stoichiometry: relates the amounts of compounds or elements involved in a reaction.
- Using chemical equations/coefficients to calculate the number of moles of reactants/products needed or formed in a reaction.
- Limiting reactants: The reactant that determines the amount of product that can be formed.
- Excess reactants: The reactant that is not completely consumed in the reaction.
- Calculating the percent yield of a chemical reaction and the relationship between theoretical and actual yields.
- Types of chemical reactions to be aware of: - double replacement (exchange/metathesis - precipitation - acid-base neutralization - gas -forming
- Reactions in aqueous solutions:
- solutions/solvents/solutes
- molarity calculations including using molarity in stoichiometric calculations
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry
- Introduction to Thermochemistry
- Energy Types (Kinetic and Potential)
- Law of Conservation of Energy
- System and Surrounding
- Heat and Work relationships
- Enthalpy of reaction
- Specific Heat measurement
- Calorimetry (Coffee cup and Bomb)
- Hess's Law
Chapter 6: Early Quantum Theory - The Nature of Light and Matter
- Introduction (Classical Mechanics vs Quantum theory)
- Electromagnetic Radiation
- Wavelength and Frequency
- The Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Atomic Spectroscopy
- Planck's constant
- Bohr Model
- De Broglie Wavelength
- The Uncertainty Principle
- Quantum Mechanics
- Quantum Numbers
- Using Quantum Mechanics to describe electron behavior in atoms
Chapter 8: Representing Valence Electrons: Lewis Structures of Atoms, Ions, and Molecules
- Introduction to Electron Configurations, Lewis Structures
- Lewis Structures of selected atoms
- Writing Lewis Structures
- Formal Charges
- Resonance
- Exceptions to the Octet Rule
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.