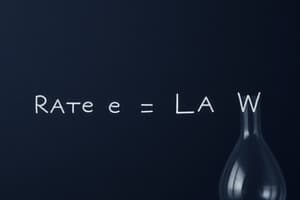Podcast
Questions and Answers
Why is refining experiments a crucial step in the scientific method?
Why is refining experiments a crucial step in the scientific method?
- To ensure the initial hypothesis is always proven correct.
- To identify potential sources of error and improve the accuracy of results. (correct)
- To discourage criticism from other scientists.
- To reduce the time and resources spent on experimentation.
What key factor differentiates diffusion in liquids from diffusion in gases?
What key factor differentiates diffusion in liquids from diffusion in gases?
- Diffusion in liquids requires an external force, while gases diffuse spontaneously.
- Diffusion only occurs in liquids at high temperatures, whereas gases diffuse at any temperature.
- Gases only diffuse in closed containers, while liquids can diffuse in open spaces.
- The rate of diffusion is generally slower in liquids due to stronger intermolecular forces. (correct)
Brownian motion provides evidence for which fundamental scientific theory?
Brownian motion provides evidence for which fundamental scientific theory?
- The theory of general equilibrium.
- The theory of relativity.
- The wave theory of light.
- The particle theory of matter. (correct)
How does the increased kinetic energy of particles influence the behavior of matter?
How does the increased kinetic energy of particles influence the behavior of matter?
What is the crucial role of air particles in explaining the random movement of smoke particles?
What is the crucial role of air particles in explaining the random movement of smoke particles?
Which statement accurately describes the process of sublimation?
Which statement accurately describes the process of sublimation?
How do changes in temperature influence the state of matter?
How do changes in temperature influence the state of matter?
Why are changes of state considered physical changes?
Why are changes of state considered physical changes?
Why do water droplets form on a bathroom mirror during a hot shower?
Why do water droplets form on a bathroom mirror during a hot shower?
In an experimental setup involving iodine sublimation with an ice-cooled watch glass, what is the primary purpose of the ice?
In an experimental setup involving iodine sublimation with an ice-cooled watch glass, what is the primary purpose of the ice?
Flashcards
What is a change of state?
What is a change of state?
Changes of state are physical changes, meaning no chemical changes are taking place.
Kinetic Energy
Kinetic Energy
The amount of motion of these particles depends on the kinetic energy particles with more kinetic energy move further apart.
Energy in State Changes
Energy in State Changes
Energy is always involved in changes of state. Matter either absorbs or releases energy when it changes from one state to another.
Sublimation
Sublimation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brownian Motion
Brownian Motion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diffusion in Liquids
Diffusion in Liquids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Observation
Observation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Making a Hypothesis
Making a Hypothesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Making a Prediction
Making a Prediction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Planning the experiment(s)
Planning the experiment(s)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Chemical kinetics studies reaction rates and factors that influence them.
Reaction Rate
- Defined as the change in reactant or product concentration over time.
- For $aA + bB \rightarrow cC + dD$, Rate $= -\frac{1}{a} \frac{\Delta[A]}{\Delta t} = -\frac{1}{b} \frac{\Delta[B]}{\Delta t} = \frac{1}{c} \frac{\Delta[C]}{\Delta t} = \frac{1}{d} \frac{\Delta[D]}{\Delta t}$
Rate Law
- An equation relating reaction rate to reactant concentrations raised to certain powers.
- General form: Rate $= k[A]^m[B]^n$, $k$ is the rate constant, $m$ and $n$ are reaction orders.
- Overall reaction order is the sum of individual orders ($m + n$).
- Determined experimentally, not from reaction stoichiometry.
Common Rate Laws
- Zero-Order: Rate $= k$; rate is independent of reactant concentration.
- First-Order: Rate $= k[A]$; rate is directly proportional to reactant concentration.
- Second-Order: Rate $= k[A]^2$ or Rate $= k[A][B]$; rate is proportional to the square of one reactant or the product of two.
Temperature Dependence
- Arrhenius Equation: $k = Ae^{-\frac{E_a}{RT}}$; relates rate constant to temperature.
- $A$ is pre-exponential factor, $E_a$ is activation energy, $R$ is gas constant (8.314 J/(mol⋅K)), $T$ is absolute temperature in Kelvin.
- Activation Energy ($E_a$): Minimum energy for a reaction to occur; higher $E_a$ results in slower rate.
Catalysis
- A catalyst speeds up a reaction without being consumed.
- Homogeneous catalysis: Catalyst and reactants are in the same phase.
- Heterogeneous catalysis: Catalyst and reactants are in different phases.
Reaction Mechanisms
- A reaction mechanism is a series of elementary steps from reactants to products.
- An elementary step is a single step where rate law can be derived from stoichiometry.
- The rate-determining step is the slowest step, governing overall reaction rate.
Floyd-Warshall Algorithm
- Used to find the shortest paths between all pairs of vertices in a graph.
- Input is a graph $G = (V, E)$ with edge weights $w: E \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ and adjacency matrix $D$. $D$ is initialized such that:
- $d_{ij} = w(i, j)$ if edge $(i, j) \in E$
- $d_{ij} = \infty$ if edge $(i, j) \notin E$
- $d_{ij} = 0$ if $i = j$
- Output is a distance matrix $D^* = (d_{ij}^)$, where $d_{ij}^$ is the length of the shortest path from $i$ to $j$.
- Algorithm:
- for $k$ from 1 to $|V|$:
- for $i$ from 1 to $|V|$:
-
for $j$ from 1 to $|V|$: -
$D[i][j] := \min(D[i][j], D[i][k] + D[k][j])$
- The algorithm guarantees shortest paths when there are no negative cycles.
- Time Complexity: $\Theta(|V|^3)$
- Space Complexity: $\Theta(|V|^2)$
- The algorithm works with negative edge weights, but not negative cycles.
- The presence of negative cycles are indicated with negative values on the diagonal ($D[i][i] < 0$).
Lecture 24: Photodiodes
- Photodiodes convert light into electrical current.
- Light can be a source of energy.
- Photovoltaic effect: Light shines on a semiconductor, generating electron-hole pairs.
- Electron-hole pairs will recombine without a potential field.
- Separation of electron-hole pairs by a potential barrier creates a voltage.
- Photodiodes efficiently collect light-generated carriers.
- Light-generated carriers are collected to produce current under reverse bias.
- Current increases linearly with light intensity.
- Photodiodes typically operate in reverse bias.
- Structure
- Basic structure: P-N junction.
- Light shone on the intrinsic region to create electron-hole pairs.
- Improved structure: p-i-n photodiode
- Intrinsic (i) region between p and n regions to increase absorption volume.
- Responsivity ($\Re$): Ratio of photocurrent ($I_{ph}$) to incident optical power ($P_{opt}$).
- Represents effectiveness: $\qquad \Re = \frac{I_{ph}}{P_{opt}}$
- Quantum efficiency ($\eta$): Number of electron-hole pairs generated per incident photon $\qquad \eta = \frac{I_{ph}/q}{P_{opt}/hv} = \frac{\text{Number of electron-hole pairs}}{\text{Number of incident photons}}$
- Avalanche Gain (M): $\qquad M = \frac{I_M}{I_{ph}}$
- Key performance parameters:
- Responsivity: Sensitivity measure.
- Speed: Limited by transit time.
- Dark Current: Current when there is no light.
- Noise: Random current fluctuations.
- Capacitance: Can limit speed.
- Advantages
- High sensitivity, fast response, low noise, small size, low cost
- Disadvantages
- Temperature dependence, dark current, capacitance, fragility
- Photodiodes can be used;
- Detect presence/absence of light.
- Light measurement.
- Medical imaging, etc.
Markdown Quickstart
- Markdown simplifies text formatting for the web.
Markdown Syntax
Headers
## Heading Level 1
## Heading Level 2
### Heading Level 3
Emphasis
- Italic text*
- *Bold text**
- **Bold italic text***
Lists
- Ordered lists use numbers:
1. First item
2. Second item
- Unordered lists use asterisks or hyphens:
- First item
- Second item
Links
[Link text](URL)
Images

Code
- Inline code is enclosed in backticks:
printf() - Code blocks are enclosed in triple backticks:
\`\`\`python
print("Hello, world!")
\`\`\`
Block Quotes
> This is a block quote.
Horizontal Rule
- --
Tables
- Tables require defined headers and separator lines:
| Header 1 | Header 2 |
| -------- | -------- |
| Cell 1 | Cell 2 |
Mathematical Formulas
- Mathematical formulas use LaTeX.
Inline: \(x = y + 2\)
Block: \[ f(x) = \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \hat{f}(\xi) e^{2 \pi i \xi x} \, d\xi \]
Chemical Kinetics: Rate Details
Rate $= -\frac{1}{a} \frac{d[A]}{dt} = -\frac{1}{b} \frac{d[B]}{dt} = \frac{1}{c} \frac{d[C]}{dt} = \frac{1}{d} \frac{d[D]}{dt}$ where:
- $a, b, c, d$ are stoichiometric coefficients. Reaction Rate Law:
- Rate $= k[A]^x [B]^y$
- Where $k =$ rate constant
- $x =$ reaction order w.r.t $A$
- $y =$ reaction order w.r.t $B$
- $x + y =$ overall reaction order Zero Order Reaction:
- Rate $= k[A]^0 = k$
- $A \rightarrow Products$
- $-\frac{d[A]}{dt} = k$
- $[A] = [A]_0 - kt$
- $t_{1/2} = \frac{[A]_0}{2k}$ First Order Reaction:
- Rate $= k[A]^1 = k[A]$
- $A \rightarrow Products$
- $-\frac{d[A]}{dt} = k[A]$
- $\ln[A] = \ln[A]_0 - kt$
- $t_{1/2} = \frac{0.693}{k}$ Second Order Reaction:
- Rate $= k[A]^2$
- $A \rightarrow Products$
- $-\frac{d[A]}{dt} = k[A]^2$
- $\frac{1}{[A]} = \frac{1}{[A]_0} + kt$
- $t_{1/2} = \frac{1}{k[A]_0}$
Arrhenius Equation
- $k = A e^{-E_a/RT}$
- $E_a$ = activation energy.
- $R$ = gas constant (8.314 J/mol·K)
- $A$ = frequency factor.
- $\ln(\frac{k_2}{k_1}) = \frac{E_a}{R} (\frac{1}{T_1} - \frac{1}{T_2})$
### Notable Products
-
Binomial Square:
- $(a + b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab + b^2$
- $(a - b)^2 = a^2 - 2ab + b^2$
-
Conjugate Binomials:
-
$(a + b)(a - b) = a^2 - b^2$
-
Binomial with Common Term:
-
$(x + a)(x + b) = x^2 + (a + b)x + ab$
-
Binomial Cube:
-
$(a + b)^3 = a^3 + 3a^2b + 3ab^2 + b^3$
-
$(a - b)^3 = a^3 - 3a^2b + 3ab^2 - b^3$
{## Factorization
- Common Factor:
- $ab + ac = a(b + c)$
- Difference of Squares:
- $a^2 - b^2 = (a + b)(a - b)$
- Perfect Square Trinomial:
- $a^2 + 2ab + b^2 = (a + b)^2$
- $a^2 - 2ab + b^2 = (a - b)^2$
- Trinomial of the form $x^2 + bx + c$:
- $x^2 + bx + c = (x + p)(x + q)$, where $p + q = b$ and $pq = c$
- Sum or Difference of Cubes:
- $a^3 + b^3 = (a + b)(a^2 - ab + b^2)$
- $a^3 - b^3 = (a - b)(a^2 + ab + b^2)$ Basic Markdown Syntax: Markdown is a straightforward way to format text on the web. Headers:
# Heading 1,## Heading 2, etc., create headers of different sizes. Emphasis:*italic*or_italic_for italic text.**bold**or__bold__for bold text. Lists:- Ordered:
1. First item,2. Second item - Unordered:
- Item,* ItemLinks: - Link text creates a hyperlink. Images:
embeds an image. Code:- Inline code:
printf()is an example. Block code are enclosed in triple backticks. Blockquotes: - Use
>to create blockquotes. Horizontal Rules: ---creates a horizontal line. Tables: | Header 1 | Header 2 | | -------- | -------- | | Cell 1 | Cell 2 |
Static Equilibrium
Static equilibrium means an object is at rest and remains at rest.
- The object has zero translational and rotational acceleration. For translational equilibrium: $\sum \overrightarrow{F} = 0$
- In component form: $\sum F_x = 0$ and $\sum F_y = 0$ For rotational equilibrium: $\sum \tau = 0$ (sum of the torques acting on the body must be equal to zero) Torque Formula: $\tau = rF\sin\theta$ where:
- $r$ is the distance from the axis of rotation to the point where the force is applied.
- $F$ is the magnitude of the force.
- $\theta$ is the angle between the force vector and the vector
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.