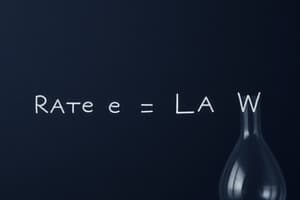Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the minimum energy required for a reaction to proceed called?
What is the minimum energy required for a reaction to proceed called?
- Kinetic energy
- Potential energy
- Activation energy (correct)
- Thermal energy
How do factors like temperature and concentration influence reaction rates?
How do factors like temperature and concentration influence reaction rates?
- They only affect gaseous reactions
- They have no impact on the reaction rate
- They generally enhance the reaction rate (correct)
- They slow down the reaction rate
Which analogy is used in the text to explain the concept of activation energy?
Which analogy is used in the text to explain the concept of activation energy?
- Flying a plane
- Hiking up a mountain (correct)
- Driving a car
- Cooking a meal
What effect does the presence of catalysts have on reaction rates?
What effect does the presence of catalysts have on reaction rates?
How can one optimize reaction conditions to achieve faster results?
How can one optimize reaction conditions to achieve faster results?
In chemical kinetics, what role do fundamental principles play?
In chemical kinetics, what role do fundamental principles play?
What does the rate law in chemical kinetics express?
What does the rate law in chemical kinetics express?
In the rate law equation v = k * c^n, what does 'n' represent?
In the rate law equation v = k * c^n, what does 'n' represent?
How does a second-order reaction with respect to a reactant behave?
How does a second-order reaction with respect to a reactant behave?
What is necessary for a successful chemical reaction according to collision theory?
What is necessary for a successful chemical reaction according to collision theory?
How is the activation energy related to the collision theory of chemical reactions?
How is the activation energy related to the collision theory of chemical reactions?
What does the rate constant 'k' in the rate law equation represent?
What does the rate constant 'k' in the rate law equation represent?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Chemical Kinetics in Class 12 Chemistry
As you move into your final years of high school chemistry, you'll find yourself delving deeper into various aspects of the subject, including chemical kinetics. This subfield deals with how fast and under which conditions reactions occur—a question vital to comprehending many natural processes and applications. Let's take this opportunity to explore some key concepts related to chemical kinetics within the context of Class 12 chemistry.
Rate Law and Reaction Order
The rate law is a mathematical expression depicting the relationship between the reaction rate (v) and reactant concentrations (c). It takes the form v = k * c^n, where (k) represents the rate constant, and (n) indicates the reaction order. A reaction may have different orders for distinct reactants, titled their individual reaction orders. For example, a second-order reaction with respect to hydrogen would mean that its rate doubles upon twice increasing its concentration while other variables remain unchanged.
Collision Theory and Activation Energy
Collision theory helps explain why reactions don't always happen instantly when molecules come closer. According to collision theory, three elements must coincide for a successful reaction to occur: a suitable orientation of colliding particles, sufficient energy to overcome the activation barrier, and enough frequency. Not all collisions lead to products; only those with adequate energy (activation energy) proceed as planned.
To better understand this concept, think of it like a hike up a mountain. Without enough energy, you won't reach the top, even if you attempt repeatedly. Similarly, molecules need a specific amount of energy called the activation energy to cross over the potential energy barrier and yield products.
Factors Influencing Reaction Rates
Several factors impact the speed of chemical reactions. Some significant ones include temperature, concentration of reactants, surface area of solids, presence of catalysts, and pressure changes. Increasing any of these factors generally enhances the reaction rate. Conversely, decreasing such parameters tends to slow down the process.
Understanding the relationships among these factors can help develop strategies in real-life scenarios. Suppose you want to increase the production rates of fertilizers or remove impurities from water using a chemical method. By controlling relevant factors – temperature, concentration, etc., you could optimize reaction conditions, leading to faster results.
Class 12 chemistry presents exciting challenges and opportunities to deepen your understanding of chemical phenomena. As you study chemical kinetics, remember that these fundamental principles will serve as building blocks in further studies and career paths. Happy studying!
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.