Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the function of the glomerulus in the nephron?
What is the function of the glomerulus in the nephron?
- Create filtrate (correct)
- Regulate specific gravity
- Control urine color
- Produce urine
What does the presence of leukocytes in urine indicate?
What does the presence of leukocytes in urine indicate?
- Ketosis
- Low specific gravity
- High protein content
- Urinary tract infection (correct)
What does the specific gravity of urine measure?
What does the specific gravity of urine measure?
- Leukocyte concentration
- Urine acidity
- Color intensity
- Amount of solutes (correct)
What does the term polyuria refer to?
What does the term polyuria refer to?
What do ketones in urine indicate about the body's metabolism?
What do ketones in urine indicate about the body's metabolism?
In what condition do urethra and urinary sphincters play a regulatory role?
In what condition do urethra and urinary sphincters play a regulatory role?
What is the active form of vitamin D?
What is the active form of vitamin D?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for increasing erythrocyte production?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for increasing erythrocyte production?
What is the main function of vitamin D receptors found in almost all cells?
What is the main function of vitamin D receptors found in almost all cells?
Which of the following is NOT involved in regulating blood pressure?
Which of the following is NOT involved in regulating blood pressure?
What is the primary function of the kidneys in terms of osmolarity regulation?
What is the primary function of the kidneys in terms of osmolarity regulation?
What is the medical term for urination?
What is the medical term for urination?
At what fluid volume in the bladder is the urge to urinate first felt?
At what fluid volume in the bladder is the urge to urinate first felt?
Which structure regulates renin release to influence blood volume?
Which structure regulates renin release to influence blood volume?
What happens to smooth muscle if blood pressure increases?
What happens to smooth muscle if blood pressure increases?
What causes aquaporin channel proteins to work on the cell membrane in the collecting ducts?
What causes aquaporin channel proteins to work on the cell membrane in the collecting ducts?
Which component of the nephron has the most abundant mitochondria for ATP production?
Which component of the nephron has the most abundant mitochondria for ATP production?
What is the size difference between the female and male urethras mentioned in the text?
What is the size difference between the female and male urethras mentioned in the text?
What is the function of the Loop of Henle in the nephron?
What is the function of the Loop of Henle in the nephron?
What characteristic describes the ascending Loop of Henle?
What characteristic describes the ascending Loop of Henle?
How does urea help in the kidney's function?
How does urea help in the kidney's function?
What is the role of Aldosterone in the Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)?
What is the role of Aldosterone in the Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)?
Which hormone influences the production of calcium binding proteins?
Which hormone influences the production of calcium binding proteins?
What causes the release of Aldosterone in the renal system?
What causes the release of Aldosterone in the renal system?
Which substance increases vasodilation in the nephron?
Which substance increases vasodilation in the nephron?
What is the impact of Glucose in urine?
What is the impact of Glucose in urine?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
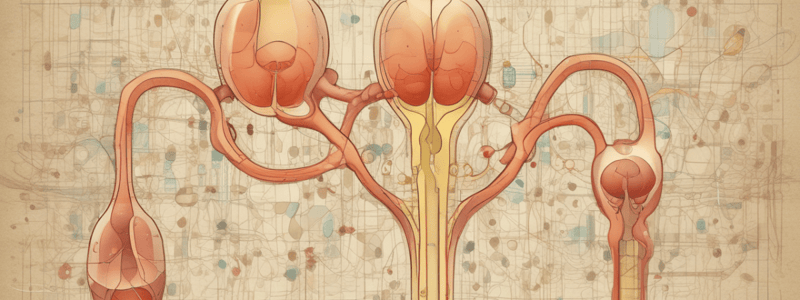
The Urinary System
- The glomerulus is the first part of the nephron, creating about 200 liters of filtrate each day.
- Urine production is affected by water intake, exercise, environmental temperature, nutrient intake, and other factors.
Urine Analysis (Urinalysis)
- Urine analysis is used to determine urine content.
- Normally, there are few proteins in urine.
- Color can be affected by certain foods, bile obstruction, dehydration, or bleeding.
- Specific gravity measures the amount of solutes in the urine, with pure water having a specific gravity of 1.0.
Urine Abnormalities
- Leukocytes in the urine indicate a urinary tract infection.
- Ketones in the urine indicate the body is using fat for energy instead of glucose or that the diet is low in carbs and proteins.
- Nitrates are normally found in the urine.
- Anuria is the absence of urine production, polyuria is the overproduction of urine, and oliguria is the term for renal disease causing little urine production.
Regulation of Urine pH
- Meats lower urine pH, while citrus fruits, vegetables, and dairy raise pH.
- Chronic levels can lead to kidney stones or osteomalacia.
The Urethra and Bladder
- The urethra transports urine from the bladder to outside the body.
- The bladder collects urine from both ureters and can hold about 600 mL of urine.
- Micturition is the medical term for urination.
Vitamin D and Hematopoiesis
- Vitamin D must undergo hydroxylation in the kidney to become active.
- Active vitamin D (calcitriol) regulates calcium in the blood.
- Vitamin D receptors are present in almost all cells, and some scientists consider it a hormone.
- Inadequate vitamin D can lead to osteoporosis.
- Hematopoiesis is the production of red blood cells, and erythropoietin (EPO) is produced primarily in the kidneys.
Kidney Function
- The kidneys regulate blood pressure, osmolarity, and electrolyte balance.
- They help recover electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and calcium.
- The kidneys regulate blood pH levels.
Nephron Structure and Function
- Nephrons in the kidney make urine, which flows through ducts to the ureters.
- The nephron works through filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.
- Filtration occurs in the glomerulus, and most solutes are reabsorbed in the PCT.
- The DCT and collecting ducts also reabsorb solutes and water.
Glomerular Filtration Rate and Urine Production
- Glomerular filtration rate is the amount of filtrate produced per minute.
- The rate is important to know if renal failure is an issue and if toxicity of drug doses may occur.
Blood Pressure Regulation
- Smooth muscle contracts if BP increases and relaxes if BP decreases.
- BP below a mean arterial pressure of 60 mm Hg will impair renal function and can cause shock.
Hormonal Regulation of Kidney Function
- ADH causes aquaporin channel proteins to reabsorb water in the collecting ducts.
- Aldosterone increases the number of sodium pumps in the DCT.
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH) increases calcium channels in the DCT.
- Calcitriol produces calcium-binding proteins to enhance calcium recovery.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.