Podcast
Questions and Answers
What structure connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres?
What structure connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres?
- Thalamus
- Corpus callosum (correct)
- Cerebellum
- Hypothalamus
Which of the following areas forms the central core of the brain?
Which of the following areas forms the central core of the brain?
- Thalamus (correct)
- Hypothalamus
- Cerebellum
- Medulla Oblongata
Where is the arbor vitae located?
Where is the arbor vitae located?
- Cerebrum
- Thalamus
- Brainstem
- Cerebellum (correct)
What part of the corpora quadrigemina is clearly observed in a midsagittal section?
What part of the corpora quadrigemina is clearly observed in a midsagittal section?
Which region of the brain is necessary for consciousness?
Which region of the brain is necessary for consciousness?
Identify cranial nerve I.
Identify cranial nerve I.
Which of the following areas takes visual information from one side of the body and conveys it to the opposite side?
Which of the following areas takes visual information from one side of the body and conveys it to the opposite side?
Which of the following structures is not part of the central nervous system?
Which of the following structures is not part of the central nervous system?
Which of the following glands can be observed on the ventral surface of the sheep brain?
Which of the following glands can be observed on the ventral surface of the sheep brain?
What attaches the pituitary gland to the brain?
What attaches the pituitary gland to the brain?
All three regions of the brain stem can be observed on the ventral surface of the brain.
All three regions of the brain stem can be observed on the ventral surface of the brain.
The cerebellum is present on the ventral surface of the sheep brain.
The cerebellum is present on the ventral surface of the sheep brain.
Which of the following ventricles is found under the corpus callosum?
Which of the following ventricles is found under the corpus callosum?
Which passageway connects the third and fourth ventricles?
Which passageway connects the third and fourth ventricles?
Identify the passageway found in the spinal cord that is continuous with the ventricles.
Identify the passageway found in the spinal cord that is continuous with the ventricles.
Cerebrospinal fluid is produced within the ventricles.
Cerebrospinal fluid is produced within the ventricles.
The ventricles are all interconnected.
The ventricles are all interconnected.
Which ventricles are divided by the septum pellucidum?
Which ventricles are divided by the septum pellucidum?
What type of tissue makes up the cerebral cortex?
What type of tissue makes up the cerebral cortex?
What is the function of white matter?
What is the function of white matter?
The composition of gray matter includes neuron cell bodies.
The composition of gray matter includes neuron cell bodies.
White matter has a fatty consistency.
White matter has a fatty consistency.
The brain is a solid organ that lacks cavities.
The brain is a solid organ that lacks cavities.
How many major regions are contained within the diencephalon?
How many major regions are contained within the diencephalon?
Which part of the diencephalon is connected to the pituitary gland?
Which part of the diencephalon is connected to the pituitary gland?
Which region acts as a relay center for sensory messages ascending to the cerebrum?
Which region acts as a relay center for sensory messages ascending to the cerebrum?
Which region of the diencephalon contains the pineal body?
Which region of the diencephalon contains the pineal body?
The pineal body secretes melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH).
The pineal body secretes melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH).
The diencephalon is found in between the brain stem and the cerebrum.
The diencephalon is found in between the brain stem and the cerebrum.
How many regions make up the brain stem?
How many regions make up the brain stem?
Which area of the brain stem is in contact with the spinal cord?
Which area of the brain stem is in contact with the spinal cord?
Which region contains the corpora quadrigemina?
Which region contains the corpora quadrigemina?
Which ventricle is located within the brain stem?
Which ventricle is located within the brain stem?
The foramen magnum marks the border between the medulla oblongata and spinal cord.
The foramen magnum marks the border between the medulla oblongata and spinal cord.
The inferior colliculi are part of the corpora quadrigemina.
The inferior colliculi are part of the corpora quadrigemina.
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets in the anterior view:
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets in the anterior view:
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets in the lateral view:
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets in the lateral view:
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets in the lateral multi-colored view:
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets in the lateral multi-colored view:
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets in the midsagittal view:
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets in the midsagittal view:
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets:
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets:
Which of the following is the closest layer of the meninges to the brain?
Which of the following is the closest layer of the meninges to the brain?
What characteristic does a spinocerebellar tract neuron share with a sensory neuron originating in the quadriceps femoris?
What characteristic does a spinocerebellar tract neuron share with a sensory neuron originating in the quadriceps femoris?
Which type of glial cells are shown in this figure?
Which type of glial cells are shown in this figure?
What CNS-associated structure is illustrated in this figure?
What CNS-associated structure is illustrated in this figure?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Brain Structures and Functions
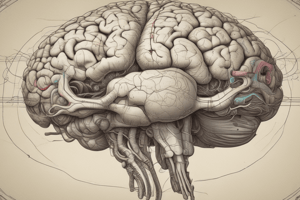
- Corpus Callosum connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres with a large fiber tract of axons.
- Thalamus is the central part of the diencephalon, forming the brain's core region and is enclosed by the cerebrum.
- Arbor Vitae, located in the cerebellum, resembles a tree due to its branching white matter structure, meaning "tree of life."
- Superior Colliculus, part of the corpora quadrigemina visible in a midsagittal section, plays a role in directing eye movements.
- Cerebrum is essential for consciousness, personality, and higher-order functions.
Cranial Nerves and Visual Processing
- Cranial Nerve I is known as the olfactory nerve, responsible for the sense of smell.
- Optic Chiasm is the crossing of optic nerves, enabling visual information from one side of the body to be processed on the opposite brain side.
Central Nervous System Structures
- Nerves belong to the peripheral nervous system and are bundles of axons, distinguishing them from the central nervous system structures.
- Pituitary Gland, located on the ventral surface of the sheep brain, is critical for hormone regulation and is attached to the hypothalamus via the infundibulum.
Brain Stem and Ventricles
- Three regions of the brain stem—midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata—are observable on the brain's ventral surface.
- Lateral Ventricles lie beneath the corpus callosum, separated by the septum pellucidum, with the cerebral aqueduct connecting the third and fourth ventricles.
- The central canal in the spinal cord is continuous with the ventricular system of the brain.
Cerebrospinal Fluid and Matter Composition
- Choroid Plexus produces cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the ventricles, allowing free flow due to interconnections.
- The cerebral cortex is composed of gray matter, primarily neuron cell bodies, whereas white matter consists of myelinated axons for transmitting information.
Diencephalon Structure
- The diencephalon comprises three major regions: hypothalamus, which connects to the pituitary gland; thalamus, relaying sensory messages; and epithalamus, housing the pineal body.
- The diencephalon is positioned between the brain stem and cerebrum.
Brain Stem and Related Structures
- The medulla oblongata is the brain stem area in contact with the spinal cord, while the fourth ventricle is located within the brain stem.
- The corpora quadrigemina, found in the midbrain, includes the inferior and superior colliculi, contributing to visual and auditory processing.
Meninges and Neurons
- The pia mater is the closest meningeal layer to the brain, offering protection and support.
- Both spinocerebellar tract neurons and sensory neurons from the quadriceps femoris carry afferent information.
Glial Cells
- Ependymal cells are a type of glial cell found within the central nervous system, involved in producing and regulating cerebrospinal fluid.
- The choroid plexus is integral for CSF production within the ventricles of the brain.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.