Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the cytoskeleton in a cell?
What is the primary function of the cytoskeleton in a cell?
- To provide support and a framework for the cell to move things around in the cytoplasm (correct)
- To regulate the flow of substances in and out of the cell
- To contain DNA
- To synthesize proteins
Which type of cell is characterized by the presence of a nucleus?
Which type of cell is characterized by the presence of a nucleus?
- Prokaryote
- Eukaryote (correct)
- Multicellular organism
- Single-celled organism
What is the function of the cell membrane?
What is the function of the cell membrane?
- To contain DNA
- To synthesize proteins
- To regulate the flow of substances in and out of the cell (correct)
- To provide a framework for the cell to move things around in the cytoplasm
What is the fluid that occupies the space inside the cell?
What is the fluid that occupies the space inside the cell?
What is the role of ribosomes in a cell?
What is the role of ribosomes in a cell?
Which type of cell is characterized by the presence of DNA in a nucleoid region?
Which type of cell is characterized by the presence of DNA in a nucleoid region?
What is the term for the specialized structures found in eukaryotic cells that carry out specific functions?
What is the term for the specialized structures found in eukaryotic cells that carry out specific functions?
What is the primary function of the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell?
What is the primary function of the nucleus in a eukaryotic cell?
What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes prokaryotic cells from eukaryotic cells?
What is the primary characteristic that distinguishes prokaryotic cells from eukaryotic cells?
What is the shape of the DNA molecule in prokaryotic cells?
What is the shape of the DNA molecule in prokaryotic cells?
What is the function of the nucleoid region in prokaryotic cells?
What is the function of the nucleoid region in prokaryotic cells?
What is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in terms of their size?
What is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in terms of their size?
What is the term for the layer outside the cell membrane that provides rigid structural support?
What is the term for the layer outside the cell membrane that provides rigid structural support?
What is the function of flagella in prokaryotic and some eukaryotic cells?
What is the function of flagella in prokaryotic and some eukaryotic cells?
Which of the following is an example of a single-celled eukaryotic organism?
Which of the following is an example of a single-celled eukaryotic organism?
What is the term for the component of the cell membrane that is made up of a phospholipid bilayer?
What is the term for the component of the cell membrane that is made up of a phospholipid bilayer?
What is the primary reason why prokaryotes were the first cells to appear on Earth?
What is the primary reason why prokaryotes were the first cells to appear on Earth?
What is the main difference between the nucleoid region and the nucleus?
What is the main difference between the nucleoid region and the nucleus?
Which of the following is a characteristic shared by all eukaryotic cells?
Which of the following is a characteristic shared by all eukaryotic cells?
What is the main function of the phospholipid bilayer in the cell membrane?
What is the main function of the phospholipid bilayer in the cell membrane?
Which of the following cells would most likely have a flagellum?
Which of the following cells would most likely have a flagellum?
What is the primary reason why eukaryotic cells are generally larger than prokaryotic cells?
What is the primary reason why eukaryotic cells are generally larger than prokaryotic cells?
Which of the following is a characteristic unique to prokaryotic cells?
Which of the following is a characteristic unique to prokaryotic cells?
What is the primary difference between archaea and bacteria?
What is the primary difference between archaea and bacteria?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Cell Characteristics
- Despite diversity in structure and function, all cells share certain characteristics.
Cell Types
- There are two main types of cells: prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
- Prokaryotes are small, simple cells that make up single-celled organisms, with bacteria being the most prevalent type.
- Eukaryotes are larger, more complex cells that are often multicellular organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi.
Common Cell Features
- All cells have a cell membrane that provides a barrier between the interior and exterior of the cell and regulates the flow of substances in and out of the cell.
- All cells have cytoplasm, the fluid that occupies the space inside the cell, where chemical reactions that enable life take place.
- All cells have a cytoskeleton, a network of filaments that provide support and a framework for the cell to move things around in the cytoplasm.
- All cells contain DNA, which contains the instructions for synthesizing all the cell's proteins, at some point in their life cycle.
- All cells contain ribosomes, the molecular machines that use the instructions contained in the DNA to build all the proteins needed by the cell.
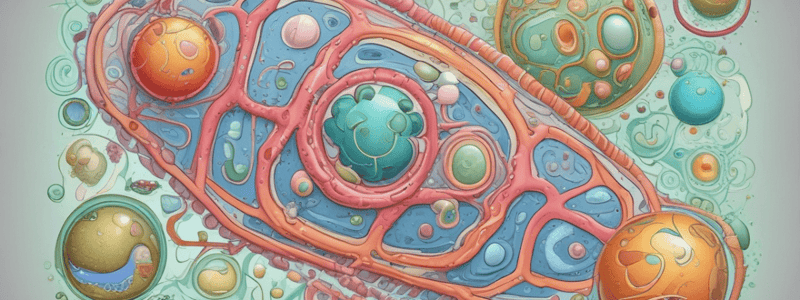
Eukaryotic Cell Features
- Eukaryotic cells are more complex and have specialized structures called organelles.
- Organelles have their own membrane to partition them off from the rest of the cell and to allow them to specialize in a certain function.
- An important example of an organelle is a nucleus, a specialized compartment found in eukaryotic cells for holding DNA.
Prokaryotic Cell Features
- Prokaryotic cells have DNA, but it is localized to one area of the cell, the nucleoid region.
- The nucleoid region is not surrounded by a membrane and is therefore not a nucleus.
- Only eukaryotic cells have a nucleus.
Cell Classification
- Cells on Earth are categorized into two groups: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic Cells
- Prokaryotes were the first cells to appear on the planet.
- All prokaryotes are single-celled.
- Examples of prokaryotes include bacteria and archaea.
- Prokaryotes are smaller cells that lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
- DNA in prokaryote cells is circular, looping around itself like a rubber band, and found in the nucleoid region.
Eukaryotic Cells
- Eukaryotic cells emerged 1.5 billion years after prokaryotes.
- The main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is the presence of a central control structure, the nucleus, where DNA is housed.
- Examples of eukaryotes include plants, animals, and fungi.
- Eukaryotic cells can be part of multicellular organisms or single-celled organisms.
- DNA in eukaryotic cells is linear, with ends, like a piece of spaghetti.
Common Cell Structures
- All cells have a cell membrane, which surrounds and defines the inner environment of the cell.
- The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and additional components.
- All cells also have ribosomes and cytoplasm.
Additional Cell Structures
- Some prokaryotes and eukaryotes have a protective cell wall, a rigid structural support outside the cell membrane.
- Some cells have external appendages, such as cilia and flagella, which help with movement.
- Flagella are long extensions that move back and forth to facilitate cell movement, as seen in sperm cells.
Cell Classification
- Cells on Earth are categorized into two groups: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic Cells
- Prokaryotes were the first cells to appear on the planet.
- All prokaryotes are single-celled.
- Examples of prokaryotes include bacteria and archaea.
- Prokaryotes are smaller cells that lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
- DNA in prokaryote cells is circular, looping around itself like a rubber band, and found in the nucleoid region.
Eukaryotic Cells
- Eukaryotic cells emerged 1.5 billion years after prokaryotes.
- The main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is the presence of a central control structure, the nucleus, where DNA is housed.
- Examples of eukaryotes include plants, animals, and fungi.
- Eukaryotic cells can be part of multicellular organisms or single-celled organisms.
- DNA in eukaryotic cells is linear, with ends, like a piece of spaghetti.
Common Cell Structures
- All cells have a cell membrane, which surrounds and defines the inner environment of the cell.
- The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with proteins and additional components.
- All cells also have ribosomes and cytoplasm.
Additional Cell Structures
- Some prokaryotes and eukaryotes have a protective cell wall, a rigid structural support outside the cell membrane.
- Some cells have external appendages, such as cilia and flagella, which help with movement.
- Flagella are long extensions that move back and forth to facilitate cell movement, as seen in sperm cells.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.