Podcast
Questions and Answers
What characteristic distinguishes prokaryotic cells from eukaryotic cells?
What characteristic distinguishes prokaryotic cells from eukaryotic cells?
- Ability to undergo photosynthesis
- Larger size
- Complex organelles
- Presence of a defined nucleus (correct)
Which organelle is known as the 'powerhouse of the cell'?
Which organelle is known as the 'powerhouse of the cell'?
- Lysosome
- Ribosome
- Mitochondria (correct)
- Nucleus
What is the primary function of the Golgi apparatus?
What is the primary function of the Golgi apparatus?
- Synthesize proteins
- Facilitate cellular respiration
- Modify and package proteins and lipids (correct)
- Store nutrients and waste
Which structure is not found in animal cells but is present in plant cells?
Which structure is not found in animal cells but is present in plant cells?
What is the role of ribosomes in a cell?
What is the role of ribosomes in a cell?
Which of the following describes the structure of the cytoskeleton?
Which of the following describes the structure of the cytoskeleton?
What function does the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER) perform?
What function does the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER) perform?
Which component of a plant cell is responsible for photosynthesis?
Which component of a plant cell is responsible for photosynthesis?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
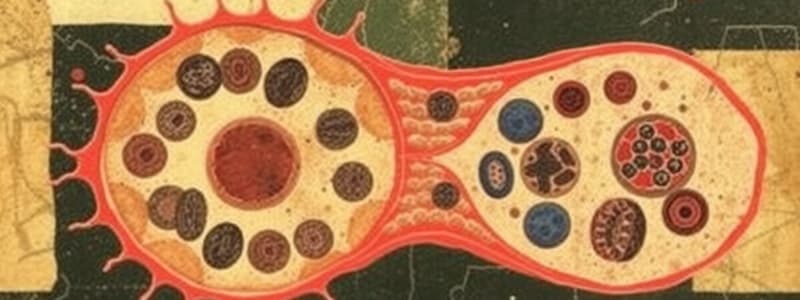
Overview of Cell Structure
- Basic Unit of Life: Cells are the fundamental building blocks of all living organisms.
Types of Cells
-
Prokaryotic Cells
- Lack a defined nucleus.
- Smaller and simpler than eukaryotic cells.
- Examples: Bacteria and Archaea.
-
Eukaryotic Cells
- Have a defined nucleus containing DNA.
- Larger and more complex.
- Examples: Animal cells, plant cells, fungi, and protists.
Common Cell Structures
-
Plasma Membrane
- Semi-permeable barrier that controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
- Composed of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins.
-
Cytoplasm
- Jelly-like substance where cellular processes occur.
- Contains organelles, cytosol, and various molecules.
-
Nucleus
- Control center of the cell.
- Contains DNA and governs cellular activities.
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells
-
Mitochondria
- Powerhouse of the cell, responsible for energy (ATP) production through cellular respiration.
-
Ribosomes
- Site of protein synthesis.
- Can be free in cytoplasm or bound to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Rough ER: Studded with ribosomes; synthesizes proteins.
- Smooth ER: Lacks ribosomes; involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification.
-
Golgi Apparatus
- Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to organelles.
-
Lysosomes
- Contains digestive enzymes to break down waste materials and cellular debris.
-
Peroxisomes
- Contains enzymes for oxidation and detoxification, such as breaking down fatty acids.
-
Cytoskeleton
- Network of protein filaments providing structure, shape, and the ability for movement.
- Composed of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules.
Additional Structures in Plant Cells
-
Cell Wall
- Rigid outer layer providing structure and protection; made of cellulose.
-
Chloroplasts
- Site of photosynthesis; contain chlorophyll.
-
Vacuoles
- Storage sacs for nutrients, waste products, and maintaining turgor pressure in plant cells.
Key Points
- Cells can be classified as prokaryotic or eukaryotic based on structure.
- Eukaryotic cells contain various organelles, each with specific functions.
- Understanding cell structure is vital for exploring functions and processes within living organisms.
Basic Unit of Life
- Cells are the fundamental building blocks of all living organisms.
Types of Cells
- Prokaryotic Cells
- Lack a defined nucleus
- Smaller and simpler
- Examples: Bacteria and Archaea.
- Eukaryotic Cells
- Have a defined nucleus containing DNA
- Larger and more complex
- Examples: Animal cells, plant cells, fungi, and protists
Common Cell Structures
- Plasma Membrane
- Controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell
- Composed of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins
- Cytoplasm
- Jelly-like substance where cellular processes occur
- Contains organelles, cytosol, and various molecules
- Nucleus
- Control center of the cell
- Contains DNA and governs cellular activities
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells
- Mitochondria
- The powerhouse of the cell
- Responsible for energy (ATP) production through cellular respiration
- Ribosomes
- Site of protein synthesis
- Can be free in cytoplasm or bound to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- Rough ER: Studded with ribosomes; synthesizes proteins
- Smooth ER: Lacks ribosomes; involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification
- Golgi Apparatus
- Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to organelles
- Lysosomes
- Contains digestive enzymes to break down waste materials and cellular debris
- Peroxisomes
- Contains enzymes for oxidation and detoxification, such as breaking down fatty acids
- Cytoskeleton
- Network of protein filaments providing structure, shape, and the ability for movement
- Composed of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules
Additional Structures in Plant Cells
- Cell Wall
- Rigid outer layer providing structure and protection; made of cellulose
- Chloroplasts
- Site of photosynthesis; contain chlorophyll
- Vacuoles
- Storage sacs for nutrients, waste products, and maintaining turgor pressure in plant cells
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.