Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the typical size range of animal cells such as those from the lining of a human cheek?
What is the typical size range of animal cells such as those from the lining of a human cheek?
- 15 - 20 µm
- 20 - 30 µm
- 10 - 50 µm (correct)
- 5 - 10 µm
Which type of cell is primarily involved in photosynthesis?
Which type of cell is primarily involved in photosynthesis?
- Muscle cells
- Cheek cells
- Root cells
- Leaf cells (correct)
Which process enables cells to develop specialized functions from unspecialized cells?
Which process enables cells to develop specialized functions from unspecialized cells?
- Cell fusion
- Cell division
- Cell differentiation (correct)
- Cell replication
What characteristic distinguishes plant cells from animal cells?
What characteristic distinguishes plant cells from animal cells?
What is the primary purpose of cell division in organisms?
What is the primary purpose of cell division in organisms?
What is the role of the cell wall in plant cells?
What is the role of the cell wall in plant cells?
Which of the following statements accurately describes cheek cells?
Which of the following statements accurately describes cheek cells?
What is one of the main differences between unicellular and multicellular organisms regarding cell specialization?
What is one of the main differences between unicellular and multicellular organisms regarding cell specialization?
Which of the following structures is typically absent in red blood cells?
Which of the following structures is typically absent in red blood cells?
What is a common feature of all cells in 'higher' organisms?
What is a common feature of all cells in 'higher' organisms?
Which of the following statements about cell types in humans is correct?
Which of the following statements about cell types in humans is correct?
Which component of the cell is responsible for regulating the entry and exit of substances?
Which component of the cell is responsible for regulating the entry and exit of substances?
What are the basic units of life that allow organisms to grow and reproduce?
What are the basic units of life that allow organisms to grow and reproduce?
What distinguishes plant cells from animal cells?
What distinguishes plant cells from animal cells?
Which of the following is NOT a common feature of all living cells?
Which of the following is NOT a common feature of all living cells?
How do cells contribute to the diversity of living organisms?
How do cells contribute to the diversity of living organisms?
In the context of cell differentiation, what occurs as cells become more specialized?
In the context of cell differentiation, what occurs as cells become more specialized?
Which type of cell typically has a more complex structure due to various specialized functions?
Which type of cell typically has a more complex structure due to various specialized functions?
During which process do cells generate more organisms?
During which process do cells generate more organisms?
What part of the cell is primarily responsible for genetic information storage?
What part of the cell is primarily responsible for genetic information storage?
Which type of cell is primarily responsible for creating multicellular organisms?
Which type of cell is primarily responsible for creating multicellular organisms?
What is the primary function of cell differentiation?
What is the primary function of cell differentiation?
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between cell structure and function?
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between cell structure and function?
What characterizes the process of cell division?
What characterizes the process of cell division?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Cell Structure in Higher Organisms
- Higher organisms, including animals, plants, and fungi, have complex cell structures compared to bacteria.
- Common cell components include the nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane; however, some cells may lack certain structures.
- Red blood cells notably do not contain a nucleus, highlighting the diversity in cell structure among different cell types.
- "Typical" plant and animal cells are often illustrated in textbooks, but no cell is truly typical due to the vast number of specialized cell types.
- Humans possess a variety of cell types, such as nerve cells, blood cells, skin cells, and liver cells, each fulfilling specific functions.
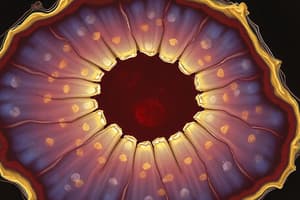
Microscopic Observation of Cells
- Figure 1.4 illustrates animal and plant cells using a light microscope:
- (a) Cells from the lining of a human cheek, measuring approximately 10µm.
- (b) Cells from a leaf's photosynthetic tissue, measuring around 25µm.
Importance of Cells
- All living organisms are composed of cells, which act as the fundamental building blocks of life.
- Cells share common features enabling growth, reproduction, and the generation of new organisms.
- Despite their structural similarities, cells contribute to the existence of millions of diverse species.
- The study of cell structure and function is essential in understanding the life processes occurring within cells.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.