Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following best describes the primary function of the plasma membrane?
Which of the following best describes the primary function of the plasma membrane?
- Generating energy for the cell
- Directing protein synthesis within the cell
- Manufacturing cellular materials
- Separating the cell's internal environment from the outside world (correct)
What characteristic of phospholipids allows for the spontaneous formation of a bilayer in an aqueous environment?
What characteristic of phospholipids allows for the spontaneous formation of a bilayer in an aqueous environment?
- Having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions (correct)
- The ability to form covalent bonds with water molecules
- Their rigid, inflexible structure
- Their uniform distribution of charge across the molecule
How does cholesterol contribute to the structure and function of the plasma membrane?
How does cholesterol contribute to the structure and function of the plasma membrane?
- By preventing membrane protein movement within the lipid bilayer
- By increasing membrane rigidity at all temperatures
- By facilitating the transport of water-soluble molecules
- By maintaining membrane fluidity over a range of temperatures (correct)
What is the primary role of membrane proteins?
What is the primary role of membrane proteins?
A cell needs to import glucose rapidly. Which type of membrane protein would be MOST effective for this task?
A cell needs to import glucose rapidly. Which type of membrane protein would be MOST effective for this task?
What cellular process involves membrane proteins relaying messages from the body or environment into the cell, influencing cellular behavior such as growth and division?
What cellular process involves membrane proteins relaying messages from the body or environment into the cell, influencing cellular behavior such as growth and division?
Which function of membrane proteins is crucial for tissue formation during embryonic development?
Which function of membrane proteins is crucial for tissue formation during embryonic development?
A researcher is studying a protein that anchors the cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix. What type of membrane protein is MOST LIKELY being investigated?
A researcher is studying a protein that anchors the cytoskeleton to the extracellular matrix. What type of membrane protein is MOST LIKELY being investigated?
What mechanism describes the movement of oxygen across the plasma membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration without the assistance of membrane proteins?
What mechanism describes the movement of oxygen across the plasma membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration without the assistance of membrane proteins?
In facilitated diffusion, what role do transport proteins play?
In facilitated diffusion, what role do transport proteins play?
Aquaporins are primarily involved in:
Aquaporins are primarily involved in:
What process allows cells to maintain different internal concentrations of specific substances compared to their surroundings?
What process allows cells to maintain different internal concentrations of specific substances compared to their surroundings?
Which of the following is a key characteristic of co-transport?
Which of the following is a key characteristic of co-transport?
Which of the events is LEAST likely to occur due to the selective permeability of the plasma membrane?
Which of the events is LEAST likely to occur due to the selective permeability of the plasma membrane?
What is a primary benefit of having organelles within eukaryotic cells?
What is a primary benefit of having organelles within eukaryotic cells?
What is a common structural feature shared by all cellular organelles in eukaryotic cells?
What is a common structural feature shared by all cellular organelles in eukaryotic cells?
What statement accurately describes the composition of all cellular membranes, including the plasma membrane and organelle membranes?
What statement accurately describes the composition of all cellular membranes, including the plasma membrane and organelle membranes?
Which of the following statements BEST explains why cells require both a plasma membrane and internal organelles?
Which of the following statements BEST explains why cells require both a plasma membrane and internal organelles?
A cell is exposed to a toxin that disrupts the function of its organelles. Which of the following outcomes would be LEAST likely, assuming that it does not lead to cell death?
A cell is exposed to a toxin that disrupts the function of its organelles. Which of the following outcomes would be LEAST likely, assuming that it does not lead to cell death?
Which of the following properties affects how 'fluid' the plasma membrane is?
Which of the following properties affects how 'fluid' the plasma membrane is?
How does a greater surface area to volume ratio relate to smaller cells?
How does a greater surface area to volume ratio relate to smaller cells?
Which of these numbers is closest to the number of human cells in your body?
Which of these numbers is closest to the number of human cells in your body?
Which of the these MUST a cell be able to do in order to maintain its function?
Which of the these MUST a cell be able to do in order to maintain its function?
Which of the following processes is NOT a function of membrane proteins?
Which of the following processes is NOT a function of membrane proteins?
Which of the following processes requires energy?
Which of the following processes requires energy?
Which of the following statements is false about the plasma membrane?
Which of the following statements is false about the plasma membrane?
Why are organelles membrane-bound?
Why are organelles membrane-bound?
How does the plasma membrane help a cell?
How does the plasma membrane help a cell?
What sort of molecules can passively diffuse across the plasma membrane?
What sort of molecules can passively diffuse across the plasma membrane?
What happens during co-transport of molecules?
What happens during co-transport of molecules?
Which structures can be described as common to both animal and plant cells?
Which structures can be described as common to both animal and plant cells?
Which are the key functions of membrane proteins?
Which are the key functions of membrane proteins?
Why is the plasma membrane described as semi-permeable?
Why is the plasma membrane described as semi-permeable?
To what does the term 'signal transduction' refer?
To what does the term 'signal transduction' refer?
Which transport mechanism is responsible for moving water molecules across a cell membrane?
Which transport mechanism is responsible for moving water molecules across a cell membrane?
What is one substance that can cross via simple diffusion?
What is one substance that can cross via simple diffusion?
How would you compare active and passive diffusion?
How would you compare active and passive diffusion?
How is facilitated diffusion similar to active transport?
How is facilitated diffusion similar to active transport?
Which of the following statements would someone use to compare a plant cell with an animal cell?
Which of the following statements would someone use to compare a plant cell with an animal cell?
What is the approximate size of most plant and animal cells?
What is the approximate size of most plant and animal cells?
What are the main kinds of lipids?
What are the main kinds of lipids?
What would occur if there was no cholesterol within the animal cell membrane?
What would occur if there was no cholesterol within the animal cell membrane?
Flashcards
Plasma Membrane
Plasma Membrane
A double layer of phospholipids with various embedded or attached proteins, forming the boundary of a cell.
Signal Transduction
Signal Transduction
Membrane proteins responsible for transmitting signals from outside the cell to inside, influencing cellular activities.
Semi-permeable Barrier
Semi-permeable Barrier
The ability of a cell membrane to selectively allow certain molecules to pass through while restricting others.
Cell Recognition
Cell Recognition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intercellular Joining
Intercellular Joining
Signup and view all the flashcards
Linking Cytoskeleton & Extracellular Matrix
Linking Cytoskeleton & Extracellular Matrix
Signup and view all the flashcards
Membrane Transport
Membrane Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Passive Transport
Passive Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Facilitated Diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osmosis
Osmosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aquaporins
Aquaporins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Active Transport
Active Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Co-transport
Co-transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organelle
Organelle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phospholipid Bilayer
Phospholipid Bilayer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Membrane-bound Organelles
Membrane-bound Organelles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Active and passive transport
Active and passive transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- This lecture focuses on cell structure and diversity, specifically the plasma membrane and organelles
- Dr. Rebecca Bird from the Department of Anatomy presents this lecture
Lecture 3 Objectives
- Describe the structure of the plasma membrane and its importance to cell function
- Outline the role of membrane proteins
- Explain the mechanisms by which substances cross the plasma membrane, including passive transport, active transport, and co-transport
- Outline the importance of organelles and subcellular compartments
- Identify the key organelles in eukaryotic cells
Cell Pop Quiz
- Consider how many cells you think are in the human body
- Consider how long you spent as one cell
- What are the largest human cells in terms of diameter and length?
Cell Function
- Cells must manufacture cellular materials
- Cells need to obtain raw building block materials from either inside or outside the cell
- Waste materials must be removed from the cell
- Cells must generate the required energy to function
- Cells control all of the above functions
Plasma Membrane
- Cells need to be separated from the outside world
- The inside of cells are alive, while the outside is not
- The plasma membrane is at the boundary of each cell
- The membrane provides special conditions within the cell
- The membrane acts as a semi-permeable barrier
- The plasma membrane is a semi-permeable barrier that bounds cells
- It allows the passage of oxygen, nutrients, and waste
- It controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell
- Interaction with the environment limits the maximum size of a cell
- Smaller cells have a greater surface area to volume ratio than larger cells
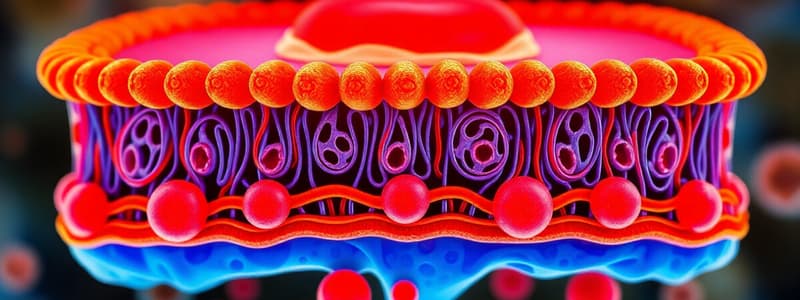
Phospholipid Bilayer
- The plasma membrane is a double layer of phospholipids
- It has various embedded or attached proteins
- The outside of the cell has hydrophilic phosphate groups, and so does the inside of the cell
- The inside of the membrane is composed of fatty acids, whose composition affects membrane fluidity
Membrane Dynamics
- The plasma membrane isn't static, its structure is dependent on saturation, temperature, and cholesterol
- Saturated lipids pack tightly together, reducing fluidity, whereas unsaturated lipids tails prevent tight packing, which increases fluidity
- High temperatures increase fluidity, while low temperatures decrease it
- Cholesterol stabilizes membrane fluidity, preventing it from responding too much to extremes
Membrane Proteins
- They are essential for cells to function
- Proteins determine the function of the membrane
- Thousands of membrane proteins have been identified and classified
- Proteins are often specific to a given cell type
- Each cell can have many different proteins
- Proteins can have multiple functions
Signal Transduction
- Membrane proteins are involved in this process
- Signal transduction relays messages from the body or environment into the cell for processes like cell growth, division, movement, etc.
Cell Recognition
- Membrane proteins are involved in this process
- This often involves glycoproteins
Intercellular Joining
- Membrane proteins are involved in this process
- Some proteins form long-lasting connections between cells
Linking Cytoskeleton and Extracellular Matrix
- Membrane proteins are involved in this process
- Membrane proteins allow a cell to physically connect with protein structures outside the cell via the extracellular matrix
Membrane Transport
- Membrane proteins are involved in this process
- Allows small amounts of molecules to move across the membrane
- Transport can be either passive or active
Movement Across Membranes
- How substances move across membranes depends on what the molecules are, how big they are, and how much is moving at once
- Bulk transport is for large substances or large volumes
- Small molecules in small volumes use membrane transport
Transport Types
- Different molecules require different mechanisms
- No energy needed in passive transport, energy is needed for active transport
- Molecules move down the concentration gradient with passive transport
- Molecules move against the concentration gradient with active transport
- There is diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport and co-transport
Passive Transport
- In passive transport, no energy is required
- Membranes are permeable to lipid-soluble and hydrophobic molecules like steroid hormones and gasses
- The molecules move down the concentration gradient and do not require energy
- The membrane restricts movement of water-soluble and charged molecules, like glucose, ions and water
Facilitated Diffusion
- This requires membrane proteins known as channels and carriers
- Channels and carriers aid the movement of specific substances down their concentration gradient
- No energy is required, but some channels open or close in response to signals
- Carriers undergo a shape change to help guide the molecule
Osmosis
- Osmosis is the movement of water across a cell membrane
- The process requires channels called aquaporins
- Water moves from a high-water (low-solute) concentration to a low-water (high-solute) concentration
- Cells osmoregulate to prevent swelling or shrinking under varying conditions
Active Transport
- It requires transport proteins which are carriers that use ATP energy
- Moves specific substances against their concentration gradient
- Allows a cell to have an internal concentration of a substance that is different from its surroundings, even if higher inside than outside
- An example of Active Transport is the sodium-potassium pump
Co-Transport
- It is a type of indirect active transport
- One substance is pumped across the membrane
- The concentration gradient is used to power the movement of a second substance against its concentration gradient
Organelles
- Different processes occur in different conditions, so there are separate compartments
- The existence of organelles allows for creation of different compartments
- These compartments can be used to provide special conditions for processes, keep incompatible processes apart, allow concentration, form concentration gradients, and package substances for transport
Organelle Features
- Cellular organelles are bounded by membranes
- Each organelle provides its own special conditions
- The endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for making and packing proteins, and releasing vesicles that carry the proteins elsewhere
- Lysosomes are organelles
- Mitochondria have two membranes
- The nucleus, bound by the nuclear envelope, has two membranes
- All cellular membranes are composed of a phospholipid bilayer
Eukaryotic Cells
- Organelles can be either unique depending on the cell type, or common to all cell types
- Animal and plant cells share some common organelles, these include the nucleus, the golgi apparatus, cell membranes, and endoplasmic reticulum.
Lecture 3 Summary
- Cells are bounded by a dynamic and semi-permeable membrane
- Membranes contain many proteins that have key functions.
- Membrane transport is necessary to move substances across the plasma membrane
- Different molecules require different mechanisms.
- Organelles are separate, specialized compartments within the cell
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.