Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the mitochondria in sperm?
What is the primary function of the mitochondria in sperm?
- To provide energy for movement (correct)
- To facilitate fertilization
- To transport nutrients
- To carry genetic information
Oligospermia refers to the presence of a normal number of sperm in semen.
Oligospermia refers to the presence of a normal number of sperm in semen.
False (B)
What is necrospermia?
What is necrospermia?
Presence of dead sperm.
The process of producing a mature ovum is known as __________.
The process of producing a mature ovum is known as __________.
What chromosome number does a primary oocyte have?
What chromosome number does a primary oocyte have?
The second meiotic division of the secondary oocyte results in two polar bodies.
The second meiotic division of the secondary oocyte results in two polar bodies.
What occurs during the stage of proliferation in oogenesis?
What occurs during the stage of proliferation in oogenesis?
Match the terms with their definitions:
Match the terms with their definitions:
The aim of oogenesis is to reduce the number of chromosomes from __________ to __________.
The aim of oogenesis is to reduce the number of chromosomes from __________ to __________.
Which of the following is NOT a type of sperm abnormality?
Which of the following is NOT a type of sperm abnormality?
What is the primary outcome of meiosis in germ cells?
What is the primary outcome of meiosis in germ cells?
Spermatogenesis occurs in the ovaries.
Spermatogenesis occurs in the ovaries.
What are the two major steps involved in spermatogenesis?
What are the two major steps involved in spermatogenesis?
During meiosis, a primary spermatocyte divides into ______ secondary spermatocytes.
During meiosis, a primary spermatocyte divides into ______ secondary spermatocytes.
Which of the following correctly describes mitosis and meiosis?
Which of the following correctly describes mitosis and meiosis?
Match the parts of the sperm with their descriptions:
Match the parts of the sperm with their descriptions:
Gametogenesis occurs only in males.
Gametogenesis occurs only in males.
What type of cell division results in the formation of two identical daughter cells?
What type of cell division results in the formation of two identical daughter cells?
The mature female gametes are formed through a process called ______.
The mature female gametes are formed through a process called ______.
Which process does NOT reduce the chromosome number?
Which process does NOT reduce the chromosome number?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Cell Division
- Cell division is a process of creating two or more daughter cells from a single parent cell.
- There are two types of cell divisions: mitosis and meiosis.
- Mitosis creates two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell.
- Meiosis creates four daughter cells that are genetically different from the parent cell.
- Mitosis is used for growth and repair.
- Meiosis is used for sexual reproduction.
Gametogenesis
- Gametogenesis is the process of formation of mature male gametes (spermatogenesis) and female gametes (oogenesis) from immature germ cells inside the gonads.
Spermatogenesis
- It is the process of formation of sperms (male gametes) in the seminiferous tubules of the testis (male gonads).
- Spermatogenesis has two major stages:
- Spermatocytogenesis: The germ cells divide and mature into spermatids.
- Spermiogenesis: The spermatids transform into mature sperm.
- The goal of spermatogenesis is to:
- Reduce the number of chromosomes from 46 to 23.
- Change the shape of the male germ cell to become ready for fertilization.
Spermatocytogenesis
- Stage of proliferation: The spermatogonia divide by mitosis to form two daughter spermatogonia.
- Stage of growth: The daughter spermatogonia enlarge to form a primary spermatocyte.
- Stage of maturation: The primary spermatocytes go through two divisions:
- Meiosis: The primary spermatocyte divides by meiosis to form two secondary spermatocytes.
- Equational division: Each secondary spermatocyte divides by equational division (similar to mitosis) to form two spermatids.
Spermiogenesis
- In the stage of transformation, the spermatid changes into a motile sperm.
Sperm structure
- Head: Contains the condensed nucleus and the acrosomal cap covering its anterior two-thirds.
- Neck: A constriction behind the head, contains the two centrioles.
- Body: The middle piece contains the plasma membrane, mitochondrial sheath, and nine bundles of microfilaments.
- Tail: Includes the principle piece and the terminal piece.
Abnormal sperm
- In form: The sperm can be abnormally large, small, bicephalic (two heads), or bicaudal (two tails).
- In number:
- Azospermia: Absence of sperms in the semen.
- Oligospermia: The presence of few sperms in the semen.
- Dead: Necrospermia: The presence of dead sperms in the semen.
Oogenesis
- Oogenesis is the process of production of a mature ovum in the cortex of the ovary.
- It starts during fetal life and continues after puberty (during each ovarian cycle) and after fertilization.
- The goal of oogenesis is to:
- Reduce the number of chromosomes from 46 to 23.
- Increase the size of the ovum from 30 µ to 120 µ.
Oogenesis stages
- Prenatal Development:
- Stage of proliferation: The oogonia divide by mitosis to form two daughter oogonia.
- Stage of growth: Most oogonia degenerate, while surviving ones increase in size to form primary oocytes.
- Postnatal (after puberty):
- Stage of maturation:
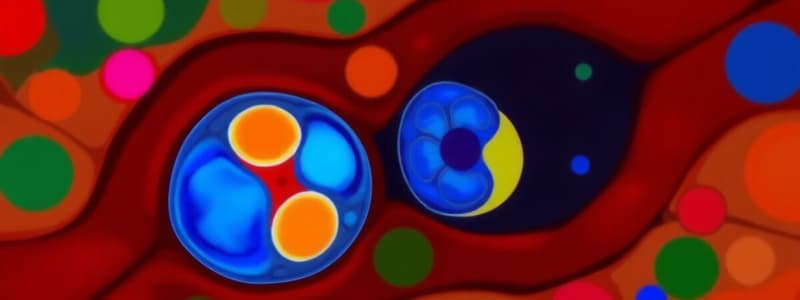
- Meiosis: Each primary oocyte (44 + XX) undergoes the first meiotic division to give rise to:
- 1st polar body: A small cell that receives little cytoplasm.
- 2ry oocyte: A large cell that receives most of the cytoplasm.
- Equational division: The secondary oocyte (22 + X) undergoes a second meiotic division to give rise to:
- 2nd polar body.
- Ovum.
- Growing follicles: The simple flat epithelial cells start to enlarge and become cubical, then simple columnar, then they divide forming many layers around the oocyte.
- Meiosis: Each primary oocyte (44 + XX) undergoes the first meiotic division to give rise to:
- Stage of maturation:
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.