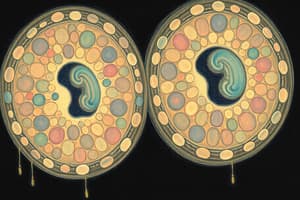
Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main difference between mitosis in plants and animals?
What is the main difference between mitosis in plants and animals?
- Spindle fibers are absent in plant cells.
- Plant cells do not pinch during division. (correct)
- Asters form in plant cells.
- Plants have centrioles for spindle formation.
Which type of asexual reproduction is characterized by the parent dividing equally?
Which type of asexual reproduction is characterized by the parent dividing equally?
- Vegetative Reproduction
- Budding
- Regeneration
- Binary Fission (correct)
What is the role of cyclin in cell cycle regulation?
What is the role of cyclin in cell cycle regulation?
- It facilitates cell division. (correct)
- It prevents cells from entering mitosis.
- It promotes the process of asexual reproduction.
- It maintains cell rigidity.
In which of the following organisms would you typically find spore formation as a method of asexual reproduction?
In which of the following organisms would you typically find spore formation as a method of asexual reproduction?
Which of the following accurately describes vegetative reproduction?
Which of the following accurately describes vegetative reproduction?
What happens during the process of regeneration in asexual reproduction?
What happens during the process of regeneration in asexual reproduction?
Which of the following is NOT a type of asexual reproduction?
Which of the following is NOT a type of asexual reproduction?
What is the primary function of mitosis in multicellular organisms?
What is the primary function of mitosis in multicellular organisms?
During which phase of mitosis do chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate?
During which phase of mitosis do chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate?
Which process occurs during telophase in mitosis?
Which process occurs during telophase in mitosis?
What is chromatin before it condenses into chromosomes during mitosis?
What is chromatin before it condenses into chromosomes during mitosis?
What role do the spindle fibers play during mitosis?
What role do the spindle fibers play during mitosis?
Cytokinesis occurs at which point in relation to telophase?
Cytokinesis occurs at which point in relation to telophase?
Which of the following statements about sister chromatids is true?
Which of the following statements about sister chromatids is true?
Which phase of the cell cycle is characterized as the resting phase?
Which phase of the cell cycle is characterized as the resting phase?
Flashcards
Cell Cycle
Cell Cycle
The period of time between two cell divisions.
Mitosis
Mitosis
The division of the nucleus, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.
Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis
The division of the cytoplasm. It follows mitosis and divides the cell into two daughter cells.
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chromatin
Chromatin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chromosomes
Chromosomes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interphase
Interphase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prophase
Prophase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mitosis Phases Order
Mitosis Phases Order
Signup and view all the flashcards
Budding
Budding
Signup and view all the flashcards
Binary Fission
Binary Fission
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spore Formation
Spore Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Regeneration/Fragmentation
Regeneration/Fragmentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Cell Cycle
- The cell cycle is the period of time between one cell division and the next
- In unicellular organisms, division results in new individuals
- In multicellular organisms, division replaces old or damaged cells
Mitosis
- The process of nuclear division where the number of chromosomes remains the same
- Part of the cell cycle
Cytokinesis
- The division of the cytoplasm occurs after mitosis
Asexual Reproduction
- Reproduction requiring only one parent
- No special reproductive organs are needed
- Offspring have the same genetic information as the parent
Chromatin
- DNA wound around proteins called histones
Chromosomes
- Condensed chromatin, visible during mitosis
- Rod-like structures
Phases of Mitosis
- There are 5 phases of mitosis:
- Interphase
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
Interphase
- Known as the "resting phase"
- Cells grow in size, producing more nucleic acids and proteins
- Cells produce copies of cellular organelles
- Chromosomes replicate but cannot be seen
Prophase
- Double chromosomes become visible
- Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids connected by a centromere
Metaphase
- Centromeres line up on the equator (metaphase plate) of the cell
- By the end, centromeres divide and separate the daughter chromosomes to opposite sides of the cell
Anaphase
- Daughter chromosomes move to opposite sides of the cell (poles)
- Movement is due to shortening of microtubules
Telophase
- Chromosomes uncoil and return to their thread-like appearance
- Nuclear membranes and nuclei reform
- Cytokinesis begins during late anaphase and finishes during Telophase
Mnemonic Device
- A way to remember the order of the phases of mitosis – I PUNCHED MY AUNT TILLY!
Mitosis in Plants
- Similar to animal mitosis, but plants lack centrioles and spindle fibers take their place
- The cell wall does not pinch inward. A cell plate divides the cell into two
Asexual Reproduction continued
- Protein that causes cells to go through the cell cycle is called cyclin
- Occurs only through the process of mitosis
- All offspring have the same genetic information
Types of Asexual Reproduction
- Budding: Parent divides unequally, new individuals develop from buds (e.g., yeast, hydra)
- Binary Fission: Parent divides equally, resulting in two separate individuals (e.g., paramecium)
- Spore Formation: Single specialized cells germinate when released from the parent (usually covered by a protective coating)
- Regeneration/Fragmentation: Ability to regrow new body parts to new organisms (e.g., hydra, planaria, starfish)
- Vegetative Reproduction/Propagation: Roots, stems, and leaves divide and differentiate to produce the same organism (e.g., strawberry plants, pick-a-back plants)
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.