Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary role of the plasma membrane in a cell?
What is the primary role of the plasma membrane in a cell?
- Facilitates communication between cells
- Stores energy in the form of ATP
- Regulates the entry and exit of substances (correct)
- Contains the genetic material of the cell
Which statement best describes the relationship between the extracellular fluid (ECF) and intracellular fluid (ICF) in cells?
Which statement best describes the relationship between the extracellular fluid (ECF) and intracellular fluid (ICF) in cells?
- The ECF and ICF are always in equilibrium.
- They have identical compositions.
- Their constituents and states are different. (correct)
- The ICF acts as a waste disposal system for the ECF.
What does it mean for cells to have specialized functions in a multicellular organism?
What does it mean for cells to have specialized functions in a multicellular organism?
- Every cell can perform every task necessary for organism survival.
- Some cells can replicate indefinitely while others cannot.
- Specialized cells do not share any common functions.
- Cellular functions are integrated through interactions among specialized cells. (correct)
Why might all cells have the same DNA, but not express all genes?
Why might all cells have the same DNA, but not express all genes?
Which mechanism is NOT involved in transport across the cell membrane?
Which mechanism is NOT involved in transport across the cell membrane?
What percentage of body weight is constituted by Extra-cellular Fluid (ECF)?
What percentage of body weight is constituted by Extra-cellular Fluid (ECF)?
Which compartment of ECF contains the largest volume of fluid?
Which compartment of ECF contains the largest volume of fluid?
What is the main cation found in the Extra-cellular Fluid (ECF)?
What is the main cation found in the Extra-cellular Fluid (ECF)?
Which of the following best describes the role of the Na+-K+ pump?
Which of the following best describes the role of the Na+-K+ pump?
Which anion primarily remains outside the cells due to the Donnan effect?
Which anion primarily remains outside the cells due to the Donnan effect?
What percentage of body weight does Intra-cellular Fluid (ICF) represent?
What percentage of body weight does Intra-cellular Fluid (ICF) represent?
What key factor leads to the distribution of solutes in body fluid compartments?
What key factor leads to the distribution of solutes in body fluid compartments?
Which transport mechanism requires energy to move substances across the cell membrane?
Which transport mechanism requires energy to move substances across the cell membrane?
What is the main function of microtubules in a cell?
What is the main function of microtubules in a cell?
What is the structure of centrioles?
What is the structure of centrioles?
Which type of granules is most common in cells?
Which type of granules is most common in cells?
What is the primary role of the nuclear envelope?
What is the primary role of the nuclear envelope?
What is chromatin composed of?
What is chromatin composed of?
What is a characteristic of the nucleolus?
What is a characteristic of the nucleolus?
Which components make up the cell membrane?
Which components make up the cell membrane?
What function do messenger RNA molecules serve in relation to the nuclear pores?
What function do messenger RNA molecules serve in relation to the nuclear pores?
What is a characteristic of positive feedback mechanisms?
What is a characteristic of positive feedback mechanisms?
How does a feed forward mechanism function in the body?
How does a feed forward mechanism function in the body?
What does allostasis emphasize in physiological responses?
What does allostasis emphasize in physiological responses?
Which of the following is NOT an example of positive feedback?
Which of the following is NOT an example of positive feedback?
What might be a consequence of an excessive positive feedback loop in biological systems?
What might be a consequence of an excessive positive feedback loop in biological systems?
What is the main role of allostasis in the body?
What is the main role of allostasis in the body?
What does allostatic load primarily refer to?
What does allostatic load primarily refer to?
Which of the following is a manifestation of allostatic load?
Which of the following is a manifestation of allostatic load?
How does overstimulation by frequent stress affect the body?
How does overstimulation by frequent stress affect the body?
What could be a consequence of failing to inhibit allostatic responses when not needed?
What could be a consequence of failing to inhibit allostatic responses when not needed?
Which type of stress mediators is associated with allostatic regulation?
Which type of stress mediators is associated with allostatic regulation?
What may result from inefficient management of allostatic responses?
What may result from inefficient management of allostatic responses?
Which hormone is primarily involved in the body's stress response through allostasis?
Which hormone is primarily involved in the body's stress response through allostasis?
What characterizes pinocytosis in cellular transport mechanisms?
What characterizes pinocytosis in cellular transport mechanisms?
Which statement correctly describes exocytosis?
Which statement correctly describes exocytosis?
What is the primary purpose of homeostasis within an organism?
What is the primary purpose of homeostasis within an organism?
Which component is NOT part of the homeostatic regulation process?
Which component is NOT part of the homeostatic regulation process?
In negative feedback mechanisms, what occurs in response to a discrepancy from the set point?
In negative feedback mechanisms, what occurs in response to a discrepancy from the set point?
Which of the following is a form of intrinsic regulation in the body?
Which of the following is a form of intrinsic regulation in the body?
What is the main role of receptors in homeostasis?
What is the main role of receptors in homeostasis?
Which feedback mechanism amplifies responses rather than opposing them?
Which feedback mechanism amplifies responses rather than opposing them?
What mechanism is involved in the regulation of temperature as part of homeostasis?
What mechanism is involved in the regulation of temperature as part of homeostasis?
Which system is primarily responsible for rapid adjustments to changes in the body?
Which system is primarily responsible for rapid adjustments to changes in the body?
In the context of physiological adjustments, allostasis refers to:
In the context of physiological adjustments, allostasis refers to:
Which structure assesses and discriminates transmitted signals in a homeostatic loop?
Which structure assesses and discriminates transmitted signals in a homeostatic loop?
What does the error signal represent in homeostatic regulation?
What does the error signal represent in homeostatic regulation?
Which system is involved in long-lasting metabolic adjustments?
Which system is involved in long-lasting metabolic adjustments?
Flashcards
Cell Structure
Cell Structure
Cells are the basic units of life in an organism. Their specialized functions are essential for maintaining the organism's overall well-being.
Plasma membrane
Plasma membrane
The plasma membrane controls what enters and leaves a cell.
Intracellular/Extracellular Fluid
Intracellular/Extracellular Fluid
The internal environment of the cell (intracellular fluid) and the external environment surrounding the cell (extracellular fluid) have different compositions.
Cell Function Complexity
Cell Function Complexity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cellular specialization
Cellular specialization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microtubules
Microtubules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Centrioles
Centrioles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Granules
Granules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fat droplets
Fat droplets
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nuclear envelope
Nuclear envelope
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chromatin
Chromatin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nucleolus
Nucleolus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nuclear Pores
Nuclear Pores
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Major ECF cation
Major ECF cation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Major ICF cation
Major ICF cation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Na+-K+ pump
Na+-K+ pump
Signup and view all the flashcards
Main ICF anion
Main ICF anion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Main ECF anions
Main ECF anions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Body Fluid Compartments
Body Fluid Compartments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Positive Feedback
Positive Feedback
Signup and view all the flashcards
Positive Feedback Example
Positive Feedback Example
Signup and view all the flashcards
Negative Feedback
Negative Feedback
Signup and view all the flashcards
Feed Forward Mechanism
Feed Forward Mechanism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Allostasis
Allostasis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stress Mediators
Stress Mediators
Signup and view all the flashcards
Allostatic Load
Allostatic Load
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some manifestations of allostatic load?
What are some manifestations of allostatic load?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Overstimulation by Frequent Stress
Overstimulation by Frequent Stress
Signup and view all the flashcards
Failure to Inhibit Allostatic Responses
Failure to Inhibit Allostatic Responses
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inability to Habituate to Stressors
Inability to Habituate to Stressors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Allostasis Load Cascade
Allostasis Load Cascade
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endocytosis
Endocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pinocytosis
Pinocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fluid Endocytosis
Fluid Endocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adsorptive Endocytosis
Adsorptive Endocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exocytosis
Exocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Emeiocytosis
Emeiocytosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Homeostasis
Homeostasis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heterostasis
Heterostasis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Physiological Adjustment
Physiological Adjustment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Set Point
Set Point
Signup and view all the flashcards
Receptor
Receptor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Afferent Path
Afferent Path
Signup and view all the flashcards
Integrating Center
Integrating Center
Signup and view all the flashcards
Efferent Path
Efferent Path
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Introduction to Human Physiology
- Human physiology integrates the functions of all the body's cells, tissues, and organs into a whole.
- Separate organs and systems work together to maintain the body's proper function.
- Feedback controls are crucial for maintaining necessary balances.
Cell Physiology
-
The Cell: The smallest, self-replicating unit of integrated physiological function.
- Specialized cells work together in a complex organism.
- Functional integration results from interactions between specialized cells.
-
Cell Components:
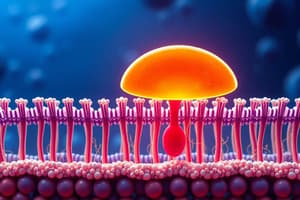
- Plasma membrane: Serves as a permeability barrier, determining what enters and leaves the cell.
- Extracellular fluid (ECF) and intracellular fluid (ICF) have different compositions.
- All cells have the same DNA, but not all genes are expressed equally.
- The organism is composed of cooperating cell types, each contributing unique functions to the whole.
-
Cell Composition:
- CHOS: ~3% of dry mass
- Lipids: ~40% of dry mass
- Proteins: ~50-60% of dry mass
- Nucleic acids: DNA + RNA
-
Cell Functions:
- Obtain food and oxygen from surroundings
- Eliminate waste products
- Perform various chemical reactions
- Synthesize materials for cellular structure, growth, and function
- Respond to changes in surroundings
- Reproduce (most cells, excluding nerve and muscle cells)
- Move materials in and out of the cell and within the cell to carry out cellular activities.
-
Cell Organelles:
- Non-membrane limited: Chromosomes, Nucleoli, Ribosomes, Microtubules, Microfilaments, Centrioles
- Membrane limited: Nucleus, Endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi apparatus (GA), Lysosomes, Mitochondria, Peroxisomes
-
Plasma Membrane Details:
- 7.5nm thick
- Composed of a phospholipid bilayer and protein
- Selective barrier to ion/molecule movement
-
Mitochondria:
- Rod- or oval-shaped, double-membraned organelles
- Major site of ATP production, oxygen utilization, and CO2 formation
- Contain enzymes of the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum:
- Interconnected cell organelle with two opposing membranes
- Granular ER: Ribosomal particles bound to ER membrane, synthesizes proteins meant for secretion.
- Agranular ER: No ribosomes, synthesizes fatty acids and steroid hormones, stores calcium in muscle cells
-
Golgi Apparatus:
- Cup-shaped membranous sacs and vesicles
- Modifies and concentrates proteins prior to secretion
-
Secretory Vesicles:
- Membrane-bound sacs with concentrated protein solutions
- Release proteins into the environment
-
Lysosomes:
- Density-staining oval bodies with hydrolytic enzymes
- Digest engulfed bacteria and damaged cell organelles
-
Peroxisomes:
- Play essential roles in metabolism and ROS (reactive oxygen species) detoxification
-
Free Ribosomes:
- 20nm particles of RNA and protein
- Assemble amino acids into proteins for intracellular use
-
Bound Ribosomes/Filaments:
- Attached to the granular endoplasmic reticulum
- Composed of protein threads, involved in protein synthesis for secretion and cell movements
- Support at cell junctions
-
Microtubules:
- Protein tubules with a hollow core (25nm diameter)
- Maintain cell shape (cytoskeleton)
- Associated with cilia, flagella, and the mitotic spindle
-
Centrioles:
- Two small cylindrical bodies with fused microtubules
- Form the spindle apparatus during cell division
- Involved in cilia formation and movement
-
Granules:
- Aggregates of chemical substance crystals
- Store specialized end products of metabolism, glycogen granules most common.
-
Fat droplets:
- Spherical globules of triacylglycerol
- Store fat
-
Nuclear Envelope:
- Surrounds the nucleus with two membranes
- Nuclear pores (50-70 nm) control molecule movement.
- Messenger RNA exits through pores.
-
Chromatin:
- Coiled DNA and protein threads
- 46 strands per human cell nucleus
- Stores genetic information
- Condenses into chromosomes during cell division
-
Nucleolus:
- Coiled filamentous structure containing granules
- Not membrane bound
- Site of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis
Cell Membrane
-
Composition:
- Lipids: Phospholipids and cholesterol
- Proteins: Peripheral and integral
- Carbohydrates: Polysaccharides
-
Lipids:
- Phospholipids: Amphipathic molecules, glycerol backbone, hydrophobic tails, hydrophilic head; form a bilayer.
-
Proteins:
- Peripheral: hydrophilic, loosely attached, regulate cell function
- Integral: partly hydrophillic and hydrophobic, embedded, transport molecules, receptors.
-
Carbohydrates:
- Hydrophilic polysaccharides bound to proteins or lipids ( glycoproteins and glycolipids)
-
Ion Channels:
- Leak: continuously open
- Voltage-gated: regulated by membrane potential changes
- Ligand-gated: regulated by chemical signals
Cellular Connections
- Tight junctions (zonula occludens): Intercellular complexes controlling paracellular permeability, forming borders between apical and basolateral domains in polarized epithelia.
- Gap junctions: Clusters of intercellular channels facilitating direct ion and small molecule diffusion between adjacent cells, formed by connections (connexons) of trans-membrane proteins (connexins).
- Desmosomes: Intercellular junctions anchoring intermediate filaments to the plasma membrane, critical for stable cell-cell adhesion in tissues experiencing structural stress.
- Adherence junctions (zonula adherens): Cell-cell adhesion complexes allowing for responses to forces and changes in the microenvironment and providing strong mechanical attachments
Cellular Communication
- Cells detect environmental changes by using membrane-embedded receptors.
- Mechanisms of chemical signaling include autocrine, paracrine, synaptic, endocrine, and neuroendocrine mechanisms
Body Fluid Composition and Electrolyte Balance
- **Body Fluid Compartments:**Plasma membrane separates ICF and ECF
- ECF (extracellular fluid): fluids in blood vessels, interstitial fluid, and transcellular fluid.
- ICF (intracellular fluid): fluid inside cells
- Fluid composition: Main cations in ECF = Na+; ICF = K+
- Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase is crucial in maintaining these different concentrations.
- Main anions in ECF = Cl-, HCO3-; Anions in ICF = proteins and phosphates.
- Distribution of solutes: based on electrochemical activity and osmotic activity.
Transport Across the Cell Membrane
- Passive transport: Does not require metabolic energy.
- Simple diffusion: Movement of a substance from higher concentration to lower.
- Facilitated diffusion: Movements of molecules with assistance from membrane proteins.
- Osmosis: Passive movement of water across a membrane from high to low concentrations.
- Filtration: Fluid forced across a membrane due to pressure differences.
- Active transport: Needs metabolic energy.
- Primary active transport: moving substances against concentration gradients using ATP directly.
- Examples: Na(+)-K(+)ATPase, Ca(2+)ATPase, H(+)-K(+)ATPase.
- Secondary active transport: Couples downhill movement of one substance to uphill movement of another.
- Examples: Na(+)-glucose cotransporter, Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger, Na(+)-K(+)-2Cl- cotransporter
- Primary active transport: moving substances against concentration gradients using ATP directly.
- Bulk transport: Transporting large molecules.
- Endocytosis: engulfing material into the cell through invagination of the membrane.
- Phagocytosis: Large molecules, such as bacteria, are engulfed
- Pinocytosis: Liquid is engulfed
- Exocytosis: releasing material from the cell through fusion of secretory vesicles.
- Endocytosis: engulfing material into the cell through invagination of the membrane.
Physiological Adjustment
- Homeostasis: Maintaining a more or less constant internal environment.
- Intrinsic regulation: cells, tissues, and organs self-regulate based on their local conditions.
- Extrinsic regulation: nervous and endocrine systems coordinate long-distance adjustments.
- Allostasis: Maintaining stability via acute changes. Adapting to and coping with stress.
- Allostatic load: The cost of prolonged adaptation to stress.
- Heterostasis (Adaptation): Long-term changes to adapt or cope with the environment (e.g., adjusting to high altitude, cold, or heat).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.