Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of lipid is primarily found in the central part of the cell membrane?
What type of lipid is primarily found in the central part of the cell membrane?
- Cholesterol
- Phospholipids (correct)
- Triglycerides
- Sphingolipids
Which part of the phospholipid molecule is hydrophilic?
Which part of the phospholipid molecule is hydrophilic?
- Fatty acid tails
- Lipid bilayer
- Nonpolar tails
- Polar hydrophilic head (correct)
In the context of the cell membrane, what does the term 'bimolecular' refer to?
In the context of the cell membrane, what does the term 'bimolecular' refer to?
- Two types of proteins
- The presence of two types of lipids
- Two fatty acid chains
- Two layers of lipid molecules (correct)
The hydrophilic nature of the polar head of phospholipids is important for which of the following functions?
The hydrophilic nature of the polar head of phospholipids is important for which of the following functions?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the composition of the cell membrane?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the composition of the cell membrane?
What is the name of the inner membrane that encloses a large space within an organelle?
What is the name of the inner membrane that encloses a large space within an organelle?
Which characteristic is true about the DNA found within certain organelles?
Which characteristic is true about the DNA found within certain organelles?
What process do self-replicating organelles undergo to increase in number?
What process do self-replicating organelles undergo to increase in number?
Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding self-replicating organelles?
Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding self-replicating organelles?
What is one function of self-replicating organelles?
What is one function of self-replicating organelles?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
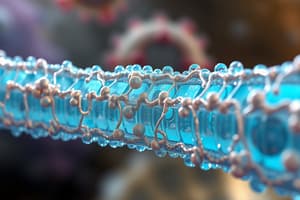
Lipids and Cell Membrane
- Phospholipids are the primary lipids that form the bimolecular layers of the cell membrane.
- Each lipid layer comprises a polar hydrophilic head that has an affinity for water.
- The matrix space is present within the inner membrane, containing its own DNA.
Golgi Apparatus
- Appears as a pale area near the nucleus in cells with basophilic cytoplasm, termed a negative Golgi image.
- Stains brown with silver stain for identification in microscopy.
- Functions include the formation of lysosomes, which involves receiving hydrolytic enzymes from the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
- Hydrolytic enzymes are packaged within vesicles in the Golgi apparatus, processed, and pinched off as lysosomes.
Lysosomes
- Key functions involve digesting macromolecules, microorganisms, cellular debris, and excess organelles.
Ribosomes
- Free ribosomes are responsible for synthesizing proteins directly within the cell cytoplasm.
Cell Inclusions
- Non-living structures within the cell include pigments such as:
- Melanin: a pigment responsible for coloration in various tissues.
- Lipofuscin: a pigment accumulation found in long-lived cells like neurons in the central nervous system (CNS) and cardiac cells.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.