Podcast
Questions and Answers
Match the following cardiovascular terms with their correct definitions:
Match the following cardiovascular terms with their correct definitions:
Aneurysm = Localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel Angina pectoris = Feeling of constriction around the heart due to insufficient blood supply Arrhythmia = Abnormality in the rate or rhythm of the heartbeat Atherosclerosis = Development of fatty patches in the lining of arteries
Match the following vessels with their descriptions:
Match the following vessels with their descriptions:
Arteries = Carry blood away from the heart Veins = Carry blood back to the heart Capillaries = Smallest vessels, exchanges take place Venules = Receive blood from the capillaries
Match the following heart-related terms with their definitions:
Match the following heart-related terms with their definitions:
Sinoatrial (SA) node = Initiates the impulse for each heartbeat Myocardium = Thick middle layer of the heart wall Systole = Contraction phase of the heartbeat cycle Valve = Structure that keeps fluid flowing in one direction
Match the cardiovascular disorders with their characteristics:
Match the cardiovascular disorders with their characteristics:
Match the following terms with their corresponding roots:
Match the following terms with their corresponding roots:
Match the following diagnostic tools with their descriptions:
Match the following diagnostic tools with their descriptions:
Match the following blood-related disorders with their definitions:
Match the following blood-related disorders with their definitions:
Match the following conditions with their descriptions:
Match the following conditions with their descriptions:
Match the following types of veins with their definitions:
Match the following types of veins with their definitions:
Match the following components of the cardiovascular system with their functions:
Match the following components of the cardiovascular system with their functions:
Match the following cardiovascular disorders with their descriptions:
Match the following cardiovascular disorders with their descriptions:
Match the following anatomical terms with their related locations in the heart:
Match the following anatomical terms with their related locations in the heart:
Match the following terms related to blood circulation with their definitions:
Match the following terms related to blood circulation with their definitions:
Match the following types of blood vessels with their characteristics:
Match the following types of blood vessels with their characteristics:
Match the following medical terms with their meanings:
Match the following medical terms with their meanings:
Match the following components of the heart's conduction system to their functions:
Match the following components of the heart's conduction system to their functions:
Match the following terms of cardiac cycle stages with their descriptions:
Match the following terms of cardiac cycle stages with their descriptions:
Match the following medical terms with their definitions:
Match the following medical terms with their definitions:
Match the following types of heart valves with their functions:
Match the following types of heart valves with their functions:
Match the following symptoms with their potential cardiovascular issues:
Match the following symptoms with their potential cardiovascular issues:
Match the following medical terms with their definitions:
Match the following medical terms with their definitions:
Match the following blood vessels with their functions:
Match the following blood vessels with their functions:
Match the following phases of the heartbeat with their definitions:
Match the following phases of the heartbeat with their definitions:
Match the following cardiac conditions with their definitions:
Match the following cardiac conditions with their definitions:
Match the following conditions with their descriptions:
Match the following conditions with their descriptions:
Match the following cardiovascular terms with their actions:
Match the following cardiovascular terms with their actions:
Match the following terms with their characteristics:
Match the following terms with their characteristics:
Match the following vascular emergencies with their explanations:
Match the following vascular emergencies with their explanations:
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Cardiovascular System
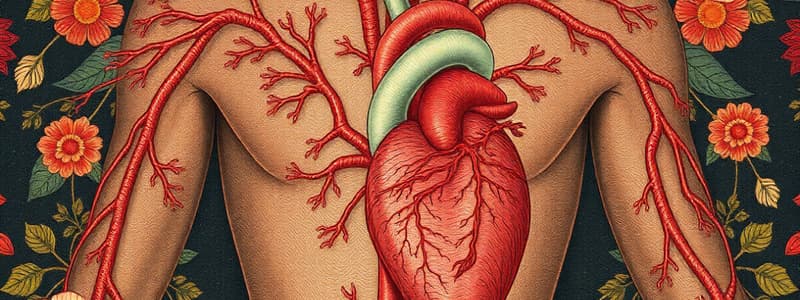
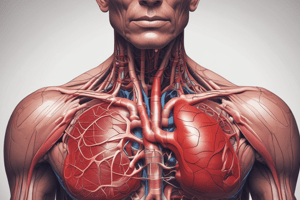
- The cardiovascular system is responsible for transporting blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products.
- It consists of the heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries), and blood.
- The heart's right atrium receives de-oxygenated blood from the body through the superior and inferior vena cava.
- The blood then enters the right ventricle and is pumped to the lungs through the pulmonary artery.
- Oxygenated blood returns from the lungs to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.
- The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta, distributing it to the body.
- Arteries carry blood away from the heart, except for the pulmonary and umbilical arteries, which carry de-oxygenated blood.
- Veins carry blood back to the heart, except for the pulmonary and umbilical veins, which carry oxygenated blood.
- Capillaries are the smallest vessels where exchanges occur between blood and tissues.
Cardiovascular Terminology
- artery: carries blood away from the heart (roots: arter, arteri/o).
- arteriole: small vessel carrying blood from arteries to capillaries (root: arteriol/o).
- vein: carries blood back to the heart (roots: ven/o, phleb/o).
- venule: small vessel carrying blood from capillaries to veins.
- valve: structure preventing backward flow of fluid (roots: valv/o, valvul/o).
- sinoatrial (SA) node: initiates the heartbeat impulse, acts as the pacemaker.
- systole: contraction phase of the heartbeat cycle.
- myocardium: the heart's muscular middle layer.
Cardiovascular Disorders
- Aneurysm: localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel, usually an artery, caused by weakened vessel walls.
- Angina pectoris: chest pain or constriction, may radiate to the left arm or shoulder, caused by insufficient blood supply to the heart.
- Arrhythmia (dysrhythmia): irregular heart rhythm or rate.
- Atherosclerosis: fatty deposits (plaques) in artery linings, causing narrowing and hardening of the vessel wall.
- Dyslipidemia: abnormal serum lipid levels, a factor in atherosclerosis; includes hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertriglyceridemia.
- Bradycardia: slow heart rate (<60 bpm).
- Tachycardia: fast heart rate (>100 bpm at rest).
- Dyspnea: difficult or labored breathing.
- Edema: tissue swelling due to excess fluid caused by various factors, including cardiovascular disturbances.
- Heart failure: inability of the heart to maintain adequate blood circulation.
- Hypertension: high blood pressure, with essential hypertension having no known cause.
- Myocardial infarction (MI): death of heart muscle tissue due to blocked coronary artery supply.
- Embolism: blood vessel obstruction by a clot or other material.
- Ischemia: local blood supply deficiency due to circulatory obstruction.
- Stroke (cerebrovascular accident): sudden brain damage from reduced blood flow, caused by various factors like atherosclerosis.
- Shock: circulatory failure with inadequate tissue blood supply, caused by different conditions like heart failure.
Cardiovascular Diagnostics and Treatment
- Coronary angiography: X-ray study of coronary arteries using an opaque dye introduced through a catheter.
- Echocardiography (ECG): non-invasive imaging of internal heart structures using ultrasound.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.