Podcast
Questions and Answers
A nurse is delegating the task of capillary blood glucose testing. Which client condition would allow the nurse to delegate this task to a practical nurse(PN)?
A nurse is delegating the task of capillary blood glucose testing. Which client condition would allow the nurse to delegate this task to a practical nurse(PN)?
- A client newly admitted with fluctuating blood glucose levels.
- A client experiencing symptoms of hypoglycemia.
- A client receiving intravenous insulin for hyperglycemia.
- A client with a history of stable diabetes and consistent blood glucose readings. (correct)
Prior to performing a capillary blood glucose test, a nurse reviews the client's medical record. Which information is most important for the nurse to note?
Prior to performing a capillary blood glucose test, a nurse reviews the client's medical record. Which information is most important for the nurse to note?
- The client's preferred meal times.
- The client's allergy status, medical history and pertinent laboratory values. (correct)
- The client's exercise routine.
- The client's family history of diabetes.
A nurse is preparing to perform a capillary blood glucose test. What is the rationale for gathering all necessary supplies before initiating the procedure?
A nurse is preparing to perform a capillary blood glucose test. What is the rationale for gathering all necessary supplies before initiating the procedure?
- To minimize the client's anxiety by appearing organized.
- To allow the client to participate in their care.
- To adhere to facility waste-reduction protocols regarding supply usage.
- To ensure the nurse is prepared to perform the procedure. (correct)
After introducing self, what should the nurse do next when preparing a client for a capillary blood glucose test?
After introducing self, what should the nurse do next when preparing a client for a capillary blood glucose test?
A client reports feeling lightheaded and sweaty. What is the significance of evaluating these symptoms prior to performing a capillary blood glucose test?
A client reports feeling lightheaded and sweaty. What is the significance of evaluating these symptoms prior to performing a capillary blood glucose test?
Before obtaining a capillary blood sample, the nurse raises the bed to a comfortable height. Which of the following describes the primary rationale for this action?
Before obtaining a capillary blood sample, the nurse raises the bed to a comfortable height. Which of the following describes the primary rationale for this action?
A nurse is preparing a glucose monitor before a capillary blood glucose test. What is the appropriate action?
A nurse is preparing a glucose monitor before a capillary blood glucose test. What is the appropriate action?
A nurse is selecting a site for capillary blood glucose testing. Which site should the nurse avoid?
A nurse is selecting a site for capillary blood glucose testing. Which site should the nurse avoid?
A nurse cleanses the client's finger with an antiseptic wipe before capillary puncture. Why is it important to allow the antiseptic to dry completely?
A nurse cleanses the client's finger with an antiseptic wipe before capillary puncture. Why is it important to allow the antiseptic to dry completely?
What is the rationale for placing the lancet firmly against the outer edge of the selected testing site during capillary blood glucose testing?
What is the rationale for placing the lancet firmly against the outer edge of the selected testing site during capillary blood glucose testing?
A nurse is having difficulty obtaining an adequate drop of blood after puncturing the client's finger. What action should be avoided?
A nurse is having difficulty obtaining an adequate drop of blood after puncturing the client's finger. What action should be avoided?
A nurse is applying a drop of blood to a test strip for glucose monitoring. What is the most important action?
A nurse is applying a drop of blood to a test strip for glucose monitoring. What is the most important action?
Following a capillary blood glucose test, a nurse applies pressure to the puncture site with a cotton ball. What is the primary rationale for this action?
Following a capillary blood glucose test, a nurse applies pressure to the puncture site with a cotton ball. What is the primary rationale for this action?
After obtaining a capillary blood glucose level of 60 mg/dL, what should the nurse consider?
After obtaining a capillary blood glucose level of 60 mg/dL, what should the nurse consider?
A nurse turns off the glucose monitor and disposes of the test strip after use. Why is it important to turn off the glucose monitor?
A nurse turns off the glucose monitor and disposes of the test strip after use. Why is it important to turn off the glucose monitor?
What is the importance of discussing the findings of a capillary blood glucose test with the client?
What is the importance of discussing the findings of a capillary blood glucose test with the client?
Before leaving the room, a nurse ensures the client's safety after a capillary blood glucose test. Which action is most important?
Before leaving the room, a nurse ensures the client's safety after a capillary blood glucose test. Which action is most important?
A client has decreased peripheral perfusion. What alternate site may be considered for capillary blood glucose testing?
A client has decreased peripheral perfusion. What alternate site may be considered for capillary blood glucose testing?
When performing capillary blood glucose testing on an infant, which location is preferred?
When performing capillary blood glucose testing on an infant, which location is preferred?
A capillary glucose result does not match the client’s clinical presentation. What is the most appropriate initial intervention?
A capillary glucose result does not match the client’s clinical presentation. What is the most appropriate initial intervention?
A nurse is unable to obtain an adequate blood sample due to a cool extremity. What intervention should the nurse implement?
A nurse is unable to obtain an adequate blood sample due to a cool extremity. What intervention should the nurse implement?
What information should the nurse accurately document in the client’s medical record after performing capillary blood glucose monitoring?
What information should the nurse accurately document in the client’s medical record after performing capillary blood glucose monitoring?
A nurse is preparing to delegate capillary blood glucose testing to an assistive personnel (AP). Which factor should the nurse consider first?
A nurse is preparing to delegate capillary blood glucose testing to an assistive personnel (AP). Which factor should the nurse consider first?
Why is it important for a nurse to review trends in a client's blood glucose meter results as part of the assessment prior to performing a capillary blood glucose test?
Why is it important for a nurse to review trends in a client's blood glucose meter results as part of the assessment prior to performing a capillary blood glucose test?
A nurse is prioritizing steps in the nursing process when performing a capillary blood glucose test. Which step aligns with the 'planning' phase?
A nurse is prioritizing steps in the nursing process when performing a capillary blood glucose test. Which step aligns with the 'planning' phase?
A nurse is educating a client about capillary blood glucose testing. Which statement best describes the purpose of this procedure?
A nurse is educating a client about capillary blood glucose testing. Which statement best describes the purpose of this procedure?
What is the significance of adhering to standard precautions during capillary blood glucose testing?
What is the significance of adhering to standard precautions during capillary blood glucose testing?
A nurse notes that a client's hands are cold prior to capillary blood glucose testing. How would warming the site improve the accuracy of the test?
A nurse notes that a client's hands are cold prior to capillary blood glucose testing. How would warming the site improve the accuracy of the test?
A nurse is reviewing the manufacturer's directions for a new glucose monitoring system before performing capillary blood glucose testing. Why is this step essential?
A nurse is reviewing the manufacturer's directions for a new glucose monitoring system before performing capillary blood glucose testing. Why is this step essential?
Following a capillary blood glucose test, a nurse observes prolonged bleeding from the puncture site. Which factor from the client's medical record would be most relevant to this finding?
Following a capillary blood glucose test, a nurse observes prolonged bleeding from the puncture site. Which factor from the client's medical record would be most relevant to this finding?
A nurse is preparing to perform a capillary blood glucose test on a client who reports a latex allergy. Which adaptation to the procedure is most appropriate?
A nurse is preparing to perform a capillary blood glucose test on a client who reports a latex allergy. Which adaptation to the procedure is most appropriate?
A nurse is performing capillary blood glucose testing on an older adult client. What age-related change may affect the accuracy of the reading?
A nurse is performing capillary blood glucose testing on an older adult client. What age-related change may affect the accuracy of the reading?
A client newly diagnosed with diabetes is anxious about performing capillary blood glucose testing at home. How can the nurse best promote client adherence and reduce anxiety?
A client newly diagnosed with diabetes is anxious about performing capillary blood glucose testing at home. How can the nurse best promote client adherence and reduce anxiety?
Flashcards
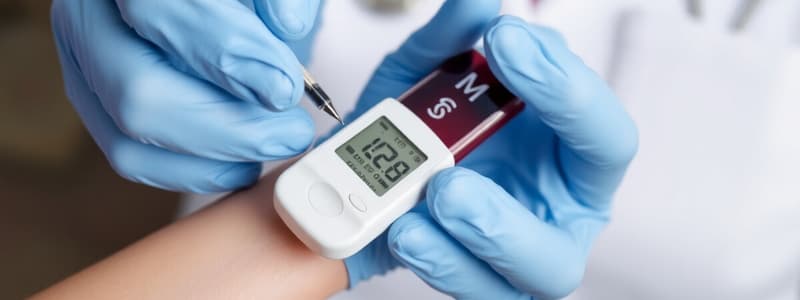
Capillary Blood Glucose Testing
Capillary Blood Glucose Testing
A superficial skin puncture to monitor blood glucose levels using a portable glucose meter.
Delegation of Capillary Blood Glucose Testing
Delegation of Capillary Blood Glucose Testing
Can be delegated to a Practical Nurse (PN) or trained Assistive Personnel (AP) when the client is stable and per facility policy guidelines.
Allergy Assessment
Allergy Assessment
Determining allergies helps prevent allergic reactions.
Client Identification
Client Identification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Standard Precautions
Standard Precautions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Antiseptic Wipes
Antiseptic Wipes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cotton Ball or Gauze Pad
Cotton Ball or Gauze Pad
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucose Meter
Glucose Meter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucose Test Strips
Glucose Test Strips
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medical Record Review
Medical Record Review
Signup and view all the flashcards
Providing Privacy
Providing Privacy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hand Hygiene
Hand Hygiene
Signup and view all the flashcards
Indications of Low Blood Glucose
Indications of Low Blood Glucose
Signup and view all the flashcards
Indications of High Blood Glucose
Indications of High Blood Glucose
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prepare Glucose Monitor
Prepare Glucose Monitor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testing Site Selection
Testing Site Selection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dry Antiseptic
Dry Antiseptic
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lancet Placement
Lancet Placement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Obtain Blood Drop
Obtain Blood Drop
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apply Pressure
Apply Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Expected Glucose Range
Expected Glucose Range
Signup and view all the flashcards
Turn Off and Dispose
Turn Off and Dispose
Signup and view all the flashcards
Discuss Findings
Discuss Findings
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ensure Client Safety
Ensure Client Safety
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infant Testing Site
Infant Testing Site
Signup and view all the flashcards
Repeat Glucose Sample
Repeat Glucose Sample
Signup and view all the flashcards
Warm Cool Site
Warm Cool Site
Signup and view all the flashcards
Documentation
Documentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Poor Perfusion Considerations
Poor Perfusion Considerations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Capillary blood sampling involves a superficial skin puncture to monitor blood glucose levels using a portable glucose meter.
- An RN can delegate capillary blood glucose testing to a PN or trained AP if the patient is in stable condition, as per facility policies.
Safety Considerations
- Check for client allergies to prevent allergic reactions.
- Verify client identity to ensure the correct procedure is performed on the correct client.
- Use standard and infection control precautions to prevent transmission of infectious organisms, with additional measures based on the client’s medical history and protocols.
Required Equipment
- Nonsterile gloves and PPE are needed if contact with blood or bodily fluids is possible.
- Antiseptic wipes are for cleaning the skin before puncture to prevent infection.
- A cotton ball or gauze pad is to apply pressure after puncture to stop bleeding.
- Adhesive bandage is to cover and protect the puncture site after the sample is obtained.
- Skin puncture device/lancet is for obtaining the blood sample.
- Glucose meter is for testing the capillary sample to get glucose results.
- Glucose test strips are for sample collection from the puncture site, for use with the glucose meter.
Step-by-Step Procedure
- Step 1: Review the client’s medical record for:
- Allergies: To determine if alternate equipment is needed (e.g., latex).
- Medical history: To identify conditions affecting the technique or results.
- Medications: To note those affecting blood clotting, which may prolong bleeding.
- Lab results: Such as low platelets.
- Trends: In blood glucose meter results.
- Prescription: To identify the frequency of blood glucose assessment.
- Step 2: Obtain and prepare necessary supplies for the procedure.
- Step 3: Ensure client privacy to maintain confidentiality.
- Step 4: Introduce yourself to the client to promote a therapeutic relationship.
- Step 5: Perform hand hygiene and apply appropriate PPE to prevent infection.
- Step 6: Use two unique identifiers to correctly identify the client.
- Step 7: Confirm the client’s allergy status before beginning.
- Step 8: Educate the client about the procedure to reduce anxiety and ensure understanding.
- Step 9: Evaluate the client for indications of altered blood glucose levels, such as:
- Hypoglycemia: Sweating, shaking, clammy skin, lethargy, confusion, lightheadedness, dizziness, or nausea.
- Hyperglycemia: Increased thirst and urination.
- Step 10: Adjust the bed to a comfortable height and arrange equipment nearby to prevent injury to the nurse.
- Step 11: Prepare the glucose monitor according to the manufacturer's directions.
- Step 12: Put on clean gloves to prevent microorganism transmission.
- Step 13: Assess skin integrity and ask the client their preference for a testing site, ensuring the site is intact and free of bruising.
- Step 14: Cleanse the testing area with an antiseptic and allow it to dry thoroughly.
- Step 15: Remove the protective cap from the lancet tip to maintain sterility.
- Step 16: Place the lancet firmly against the outer edge of the selected testing site.
- Step 17: Activate the lancet following the manufacturer’s directions.
- Step 18: Apply gentle pressure to obtain a large drop of blood.
- Excessive pressure can cause hemolysis and inaccurate readings.
- Step 19: Cover the designated area on the test strip with a drop of blood, then insert the strip into the glucose meter.
- Step 20: Apply pressure to the puncture site with a cotton ball or gauze pad, and apply a bandage if necessary.
- Step 21: Determine if the client’s blood glucose level is within the expected reference range (generally 70-140 mg/dL for adults, but may vary).
- Step 22: Turn the glucose monitor off, and dispose of the test strip to prevent transmission of microorganisms.
- Step 23: Discuss findings with the client to decrease anxiety, promote the nurse-client relationship and encourage client involvement.
- Step 24: Ensure client safety before leaving the room, including:
- Placing the call light within reach.
- Lowering the bed to the lowest position with brakes locked.
- Placing needed items within reach.
Client Considerations
- For clients with impaired peripheral perfusion, use an alternate site like the earlobe.
- In infants, use the outer aspects of the heel to avoid nerve or bone injury.
Interventions for Unexpected Outcomes
- Repeat the capillary glucose sample if results don't match the clinical presentation; a venous sample may be needed for accuracy.
- Warm the site if the extremity is cool to ensure good blood flow and obtain an adequate sample.
Documentation
- Document in the client’s medical record:
- Date, time, and location of glucose monitoring.
- Glucose level obtained and any interventions implemented.
- Accurate documentation allows immediate access to client data by the healthcare team.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.