Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is a cap table, also known as a capitalization table?
What is a cap table, also known as a capitalization table?
- A spreadsheet listing the company's securities, ownership, and prices paid by investors. (correct)
- A report detailing the company's revenue and expenses.
- A document outlining the company's marketing strategy.
- A legal document outlining the company's articles of incorporation.
Which of the following items would you typically find listed on a company's cap table?
Which of the following items would you typically find listed on a company's cap table?
- Outstanding shares held by shareholders (correct)
- Detailed marketing campaign analytics
- Customer acquisition costs
- Employee salaries and benefits
Which term defines the number of shares a company is legally allowed to issue?
Which term defines the number of shares a company is legally allowed to issue?
- Unissued shares
- Outstanding shares
- Authorized shares (correct)
- Treasury shares
What do 'shares reserved for stock option plan' represent on a cap table?
What do 'shares reserved for stock option plan' represent on a cap table?
On a cap table, what does 'fully diluted shares' refer to?
On a cap table, what does 'fully diluted shares' refer to?
In the context of a cap table, what is the primary purpose of tracking 'fully diluted shares'?
In the context of a cap table, what is the primary purpose of tracking 'fully diluted shares'?
What is a 'pro forma' cap table?
What is a 'pro forma' cap table?
Which scenario describes a situation where a pro forma cap table would be MOST useful?
Which scenario describes a situation where a pro forma cap table would be MOST useful?
What is the main purpose of using SAFEs and convertible notes in startup financing?
What is the main purpose of using SAFEs and convertible notes in startup financing?
In what way do SAFEs and convertible notes differ from traditional equity financing?
In what way do SAFEs and convertible notes differ from traditional equity financing?
What does SAFE stand for in the context of startup financing?
What does SAFE stand for in the context of startup financing?
Which organization is credited with introducing the SAFE financing instrument?
Which organization is credited with introducing the SAFE financing instrument?
What is a 'valuation cap' in a SAFE agreement?
What is a 'valuation cap' in a SAFE agreement?
How does a 'discount rate' in a SAFE agreement benefit an investor?
How does a 'discount rate' in a SAFE agreement benefit an investor?
What does a 'Most Favored Nation' (MFN) clause in a SAFE agreement ensure for the investor?
What does a 'Most Favored Nation' (MFN) clause in a SAFE agreement ensure for the investor?
In the event of a company sale before a priced equity round, what are the typical options for SAFE holders?
In the event of a company sale before a priced equity round, what are the typical options for SAFE holders?
What is a 'liquidation preference' in the context of a SAFE agreement or convertible note?
What is a 'liquidation preference' in the context of a SAFE agreement or convertible note?
How do convertible notes function in the absence of a conversion event?
How do convertible notes function in the absence of a conversion event?
What is the typical maturity timeframe for a convertible note?
What is the typical maturity timeframe for a convertible note?
How do SAFEs typically handle interest accrual compared to convertible notes?
How do SAFEs typically handle interest accrual compared to convertible notes?
In the event of a liquidation event, how does the payout priority typically compare between convertible noteholders and SAFE holders?
In the event of a liquidation event, how does the payout priority typically compare between convertible noteholders and SAFE holders?
Which of the following is generally considered a benefit of SAFEs over convertible notes?
Which of the following is generally considered a benefit of SAFEs over convertible notes?
Which of the following attributes is MOST directly associated with convertible notes?
Which of the following attributes is MOST directly associated with convertible notes?
When two co-founders issue restricted stock at nominal value and file 83(b) elections, what tax benefit are they primarily seeking?
When two co-founders issue restricted stock at nominal value and file 83(b) elections, what tax benefit are they primarily seeking?
A company needs $1,000,000 to develop a beta version of its enterprise software. Considering only the information provided, which funding option presents the LOWEST immediate dilution for the founders?
A company needs $1,000,000 to develop a beta version of its enterprise software. Considering only the information provided, which funding option presents the LOWEST immediate dilution for the founders?
Company A, bootstrapped with $250,000, requires $1,000,000 for its next stage. They're considering a SAFE with no discount and a $5,000,000 cap, or a convertible note at 8% interest with a $3,000,000 cap. What key factor should they prioritize if they anticipate a significantly higher valuation (>$10M) in their Series A round within 12 months?
Company A, bootstrapped with $250,000, requires $1,000,000 for its next stage. They're considering a SAFE with no discount and a $5,000,000 cap, or a convertible note at 8% interest with a $3,000,000 cap. What key factor should they prioritize if they anticipate a significantly higher valuation (>$10M) in their Series A round within 12 months?
A startup is deciding between a SAFE and a convertible note. Which of the following scenarios would MOST strongly favor using a convertible note over a SAFE?
A startup is deciding between a SAFE and a convertible note. Which of the following scenarios would MOST strongly favor using a convertible note over a SAFE?
Consider this simplified scenario: A company has 1,000,000 common shares outstanding. It issues a SAFE with a $5,000,000 valuation cap. Later, the company raises a Series A at a $10,000,000 pre-money valuation. If the SAFE investor invested $500,000, approximately how many shares will the SAFE investor receive upon conversion?
Consider this simplified scenario: A company has 1,000,000 common shares outstanding. It issues a SAFE with a $5,000,000 valuation cap. Later, the company raises a Series A at a $10,000,000 pre-money valuation. If the SAFE investor invested $500,000, approximately how many shares will the SAFE investor receive upon conversion?
A company is considering two financing options. Option 1: a SAFE with a $8 million valuation cap and no discount. Option 2: a Convertible Note with a $6 million valuation cap and a 20% discount. If the company successfully raises a Series A round at a $12 million valuation, which option would result in the SAFE/Note holder receiving more shares upon conversion, assuming an initial investment of $250,000?
A company is considering two financing options. Option 1: a SAFE with a $8 million valuation cap and no discount. Option 2: a Convertible Note with a $6 million valuation cap and a 20% discount. If the company successfully raises a Series A round at a $12 million valuation, which option would result in the SAFE/Note holder receiving more shares upon conversion, assuming an initial investment of $250,000?
A company issues SAFE agreements totaling $1,000,000 with a 'Most Favored Nation' (MFN) clause. Later, to attract a key investor, they offer a SAFE with a lower valuation cap. What is the company's obligation to the previous SAFE investors with the MFN clause?
A company issues SAFE agreements totaling $1,000,000 with a 'Most Favored Nation' (MFN) clause. Later, to attract a key investor, they offer a SAFE with a lower valuation cap. What is the company's obligation to the previous SAFE investors with the MFN clause?
What is the MOST likely reason a startup would choose to use SAFEs instead of convertible notes for early-stage financing?
What is the MOST likely reason a startup would choose to use SAFEs instead of convertible notes for early-stage financing?
Two companies, A and B, are seeking seed funding. Company A chooses SAFEs with a $7 million cap. Company B selects convertible notes at 6% interest with a $5 million cap. If neither company raises a priced equity round and both are acquired for $4 million before the notes' maturity, what is the likely outcome for the SAFE and note holders?
Two companies, A and B, are seeking seed funding. Company A chooses SAFEs with a $7 million cap. Company B selects convertible notes at 6% interest with a $5 million cap. If neither company raises a priced equity round and both are acquired for $4 million before the notes' maturity, what is the likely outcome for the SAFE and note holders?
A founder is bootstrapping but needs $750,000 to reach a milestone. They are considering a SAFE with no discount, or convertible note structure with 12% interest rate. If the founder anticipates a significant chance (50% or higher) of not reaching a subsequent priced round due to market conditions, what factor becomes MOST critical for them?
A founder is bootstrapping but needs $750,000 to reach a milestone. They are considering a SAFE with no discount, or convertible note structure with 12% interest rate. If the founder anticipates a significant chance (50% or higher) of not reaching a subsequent priced round due to market conditions, what factor becomes MOST critical for them?
Which of the following questions would require the MOST sophisticated understanding of cap tables, SAFEs, and convertible notes to answer correctly?
Which of the following questions would require the MOST sophisticated understanding of cap tables, SAFEs, and convertible notes to answer correctly?
You are presented with the following choice of investment agreements: I) SAFE with 10% discount cap; II) Convertible Note with a $30,000,000 valuation; or III) Priced Equity Round with a $35,000,000 valuation. Knowing your investment target could easily achieve a quarter-billion dollar exit within the next 3 months, what item would be MOST beneficial to consider when selecting the appropriate investment structure?
You are presented with the following choice of investment agreements: I) SAFE with 10% discount cap; II) Convertible Note with a $30,000,000 valuation; or III) Priced Equity Round with a $35,000,000 valuation. Knowing your investment target could easily achieve a quarter-billion dollar exit within the next 3 months, what item would be MOST beneficial to consider when selecting the appropriate investment structure?
Flashcards
What is a Cap Table?
What is a Cap Table?
A spreadsheet that lists all the company's securities, who owns them, and the prices paid by the investors.
What are Authorized Shares?
What are Authorized Shares?
The number of shares the company is allowed to issue.
What are Outstanding Shares?
What are Outstanding Shares?
Number of shares held by all shareholders in the company.
What are Unissued Shares?
What are Unissued Shares?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Shares for stock option plan
Shares for stock option plan
Signup and view all the flashcards
Names of shareholders
Names of shareholders
Signup and view all the flashcards
Shares owned by each shareholder
Shares owned by each shareholder
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stock options
Stock options
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fully diluted shares
Fully diluted shares
Signup and view all the flashcards
Options remaining
Options remaining
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a Pro Forma Cap Table?
What is a Pro Forma Cap Table?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Purpose of SAFEs/Convertible Notes
Purpose of SAFEs/Convertible Notes
Signup and view all the flashcards
SAFEs & Convertible Notes
SAFEs & Convertible Notes
Signup and view all the flashcards
SAFE, investor rights
SAFE, investor rights
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does SAFE stand for?
What does SAFE stand for?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are SAFEs?
What are SAFEs?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a Valuation Cap?
What is a Valuation Cap?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Discount Rate?
What is Discount Rate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Most Favored Nation clause
Most Favored Nation clause
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens in a liquidation event?
What happens in a liquidation event?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a Convertible Note?
What is a Convertible Note?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Maturity dates?
What are Maturity dates?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are Interest rates?
What are Interest rates?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Liquidation Preference?
What is Liquidation Preference?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Class 6 discusses the law of technology, zeroing in on cap tables, startup fundraising, SAFEs, and convertible notes.
Cap Tables: A Deeper Dive
- A cap table, or capitalization table, is a spreadsheet detailing a company's securities, including common and preferred shares, warrants, ownership, and prices paid.
- It shows each investor’s ownership percentage, security value, and dilution over time.
Cap Tables: Important Terms
- Authorized shares: The number of shares a company can issue.
- Outstanding shares: Shares held by all company shareholders.
- Unissued shares: Shares not yet issued.
- Shares reserved for stock option plan: Unissued shares for future hires.
- Names of shareholders: Identity of shareholders who own company shares.
- Shares owned by each shareholder: Number of shares per shareholder.
- Stock options: Stock options owned by each shareholder.
- Fully diluted shares: Total outstanding shares, determining share value.
- Options remaining: Number of shares available for optioning.
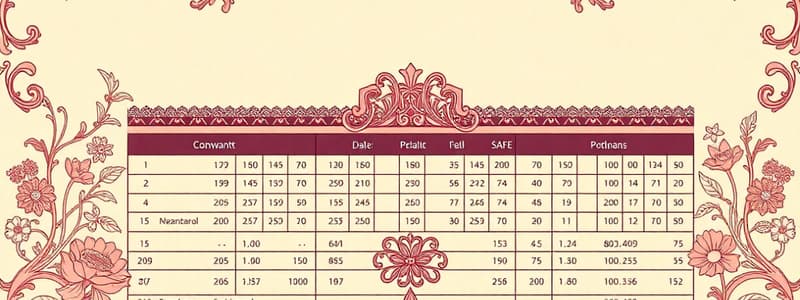
Simple Cap Table Example
- The valuation section includes the current company value and number of shares outstanding.
- The ownership section details the dollar value each investor contributes in the funding round.
Pro Forma Cap Table
- A pro forma cap table shows how the cap table would look after a financing round.
SAFEs and Convertible Notes
- SAFEs and convertible notes delay a "Priced Round."
- These are two types of convertible securities that allow invested money to convert to equity at a later event, like financing.
- Investors do not get equity but equity-linked securities.
SAFEs
- SAFE stands for "Simple Agreement for Future Equity."
- SAFEs, introduced by Y Combinator in 2013, enable investors to convert investments into equity in a future funding or liquidation.
Important SAFE Terms
- Valuation Cap: The maximum SAFE conversion price; lower caps benefit investors with more shares.
- Discount Rate: Discount to the priced round valuation; higher rates benefit investors.
- Some SAFE options include both a valuation cap and discount rate, or a "Most Favored Nation" clause, where SAFE holders get the best terms from the next equity round.
Outcomes of a Company Sale with SAFEs
- If a company sells, an investor receives the original SAFE amount or converts the SAFE into common stock based on the valuation cap.
- The latter option is often preferable if the acquisition surpasses the valuation cap.
Convertible Notes
- Convertible notes are debt financing allowing investors to convert loans into equity upon a financing round, IPO, or liquidation.
- Without conversion, they operate as traditional debt with interest and maturity dates.
Convertible Notes: Important Terms
- Maturity dates: The date when the note and interest must be repaid, typically 12-24 months after investment.
- Interest rates: Indicate interest accrued before repayment or converting to equity. SAFEs do not have this obligation.
- Liquidation Preference: Often 1x-3x the original investment.
Convertible Notes vs. SAFEs
- Both use a valuation cap or discount rate for conversion.
- However, convertible notes and SAFEs are generally faster compared to equity financing, with SAFEs often quicker than convertible notes.
- Convertible notes are more complex than SAFEs
- Convertible notes are classified as debt until conversion to equity.
- SAFEs are neither equity nor debt until conversion to equity.
- Interest rates are associated with convertible notes only.
- Maturity dates are associated with convertible notes only.
- Convertible noteholders are paid before equity holders, and SAFEs are paid also before equity holders, but not before convertible noteholders.
Scenarios for Discussion
-
Company formed 6/1/24.
-
Two co-founders issued restricted stock at nominal value and filed 83(b) elections accordingly.
-
Bootstrapped with $250,000 initial capital.
-
Company needs $1,000,000 to develop beta version of enterprise software and validate product market fit.
-
Group A: (1) Priced Round (Series Seed) at $1,000,000 pre with Tier 1 early-stage VC; (2) Convertible Note with Discount Rate of 10% and Valuation Cap of $3,000,000; or (3) SAFE with no Discount Rate and Valuation Cap of $5,000,000.
-
Group B: (1) Priced Round (Series Seed) at $2,000,000 pre with Tier 1 early-stage VC; (2) Convertible Note with Discount Rate of 20% and no Valuation Cap; or (3) SAFE with no Discount Rate and Valuation Cap of $6,000,000.
-
Group C: (1) Priced Round (Series Seed) at $4,000,000 pre with Tier 2 early-stage VC; (2) Convertible Note with Discount Rate of 20% and no Valuation Cap; or (3) SAFE with and no Discount Rate and Valuation Cap of 10,000,000.
-
Group D: (1) Priced Round (Series Seed) at $9,000,000 pre with Tier 3 early-stage VC; (2) Convertible Note with Discount Rate of 20% and Valuation Cap of $20,000,000 or (3) SAFE with 10% Discount Rate and Valuation Cap of $30,000,000.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.