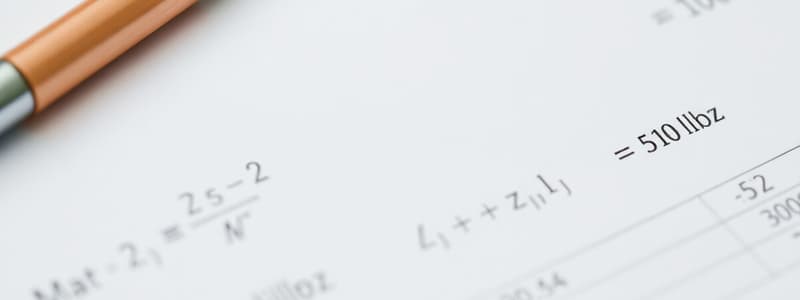Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following formulas is used to calculate the Break-even Point?
Which of the following formulas is used to calculate the Break-even Point?
- Selling Price per Unit - Variable Cost per Unit
- Fixed Costs / (Selling Price per Unit - Variable Cost per Unit) (correct)
- Fixed Costs / (Selling Price per Unit + Variable Cost per Unit)
- (Selling Price per Unit - Variable Cost per Unit) / Fixed Costs
A company has a gross profit of $500,000 and revenue of $1,000,000. What is the Gross Profit Margin?
A company has a gross profit of $500,000 and revenue of $1,000,000. What is the Gross Profit Margin?
- 50% (correct)
- 75%
- 100%
- 25%
What does a high Inventory Turnover Ratio generally indicate?
What does a high Inventory Turnover Ratio generally indicate?
- Inefficient inventory management
- A large amount of obsolete inventory
- Strong sales and efficient inventory management (correct)
- Low demand for products
Company A has total absences of 500 days and a total of 10,000 working days. What is the Absenteeism Rate?
Company A has total absences of 500 days and a total of 10,000 working days. What is the Absenteeism Rate?
Which of the following ratios would be MOST helpful in determining a company's ability to pay off its short-term liabilities?
Which of the following ratios would be MOST helpful in determining a company's ability to pay off its short-term liabilities?
A company issues 1,000,000 shares and has total annual dividends of $500,000. If the market price per share is $10, what is the Dividend Yield?
A company issues 1,000,000 shares and has total annual dividends of $500,000. If the market price per share is $10, what is the Dividend Yield?
A project requires an initial investment of $50,000. The cumulative cash inflow at the end of year 3 is $40,000, and the cash inflow during the last year is $20,000. What is the payback period?
A project requires an initial investment of $50,000. The cumulative cash inflow at the end of year 3 is $40,000, and the cash inflow during the last year is $20,000. What is the payback period?
A company's promotional elasticity of demand is 2.5. If the company increases its promotional spending by 10%, what will be the approximate percentage change in demand?
A company's promotional elasticity of demand is 2.5. If the company increases its promotional spending by 10%, what will be the approximate percentage change in demand?
What is a primary risk associated with external growth strategies, such as mergers and acquisitions?
What is a primary risk associated with external growth strategies, such as mergers and acquisitions?
Which costing and pricing strategy involves setting an initially low price to attract customers and gain market share, particularly suitable for new businesses?
Which costing and pricing strategy involves setting an initially low price to attract customers and gain market share, particularly suitable for new businesses?
A company started as a local bakery and expanded to three more locations within the same city in a span of five years. Which of the following growth strategies did the company implement?
A company started as a local bakery and expanded to three more locations within the same city in a span of five years. Which of the following growth strategies did the company implement?
Which factor is LEAST relevant when determining the most effective pricing strategy for a business?
Which factor is LEAST relevant when determining the most effective pricing strategy for a business?
A tech company initially launches its flagship smartphone at a very high price, targeting tech enthusiasts and early adopters willing to pay a premium. After several months, the company gradually reduces the price to attract a broader customer base. This approach is characteristic of which pricing strategy?
A tech company initially launches its flagship smartphone at a very high price, targeting tech enthusiasts and early adopters willing to pay a premium. After several months, the company gradually reduces the price to attract a broader customer base. This approach is characteristic of which pricing strategy?
Which of the following is a potential advantage of cost-based pricing strategies?
Which of the following is a potential advantage of cost-based pricing strategies?
What is a major drawback of using the payback period method for investment appraisal?
What is a major drawback of using the payback period method for investment appraisal?
Which investment appraisal method calculates the discount rate at which the Net Present Value (NPV) is zero?
Which investment appraisal method calculates the discount rate at which the Net Present Value (NPV) is zero?
How does inflation typically affect businesses?
How does inflation typically affect businesses?
What does break-even analysis primarily help a business determine?
What does break-even analysis primarily help a business determine?
What is a primary disadvantage of rising interest rates for businesses?
What is a primary disadvantage of rising interest rates for businesses?
Which of the following metrics directly assesses how well a business is using its available production resources?
Which of the following metrics directly assesses how well a business is using its available production resources?
Which type of government policy involves taxation and government spending?
Which type of government policy involves taxation and government spending?
What is the purpose of sensitivity analysis in investment appraisal?
What is the purpose of sensitivity analysis in investment appraisal?
Why might frequent price changes be considered a disadvantage of cost-based pricing?
Why might frequent price changes be considered a disadvantage of cost-based pricing?
Which investment appraisal technique uses probability models to predict various investment outcomes?
Which investment appraisal technique uses probability models to predict various investment outcomes?
In what scenario might the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) provide a misleading result?
In what scenario might the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) provide a misleading result?
A company wants to protect itself from potential increases in the price of raw materials. Which financial instrument is most suitable for this purpose?
A company wants to protect itself from potential increases in the price of raw materials. Which financial instrument is most suitable for this purpose?
A company is considering two mutually exclusive projects: Project A has a shorter payback period but lower overall profitability, while Project B has a longer payback period but higher profitability. According to the content, which approach is most suitable for making the final investment decision?
A company is considering two mutually exclusive projects: Project A has a shorter payback period but lower overall profitability, while Project B has a longer payback period but higher profitability. According to the content, which approach is most suitable for making the final investment decision?
A business has a low capacity utilization rate. What strategic action should they take to improve business efficiency?
A business has a low capacity utilization rate. What strategic action should they take to improve business efficiency?
What is the key benefit of using advanced investment appraisal techniques compared to traditional methods?
What is the key benefit of using advanced investment appraisal techniques compared to traditional methods?
A company uses only Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) to evaluate projects. What critical aspects of investment appraisal are they most likely overlooking, potentially leading to suboptimal investment decisions?
A company uses only Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) to evaluate projects. What critical aspects of investment appraisal are they most likely overlooking, potentially leading to suboptimal investment decisions?
How can government subsidies during economic downturns benefit businesses?
How can government subsidies during economic downturns benefit businesses?
A business anticipates interest rates will rise. To mitigate risk, they agree to exchange variable interest rate payments for fixed payments with another party. What financial instrument are they using?
A business anticipates interest rates will rise. To mitigate risk, they agree to exchange variable interest rate payments for fixed payments with another party. What financial instrument are they using?
A company uses Monte Carlo simulation to evaluate a potential investment. The simulation reveals a wide range of possible NPV outcomes, some positive and some negative, clustering around a slightly positive mean. Which of the following actions would indicate the MOST sophisticated understanding of the simulation's implications?
A company uses Monte Carlo simulation to evaluate a potential investment. The simulation reveals a wide range of possible NPV outcomes, some positive and some negative, clustering around a slightly positive mean. Which of the following actions would indicate the MOST sophisticated understanding of the simulation's implications?
Which of the following is NOT a component analyzed in a PEST analysis?
Which of the following is NOT a component analyzed in a PEST analysis?
What is the primary purpose of the cash flow statement?
What is the primary purpose of the cash flow statement?
Which financial statement would a lender most likely review to determine a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations?
Which financial statement would a lender most likely review to determine a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations?
A company's strategic planning is most likely to fail due to:
A company's strategic planning is most likely to fail due to:
Which strategic analysis tool helps businesses anticipate market trends and changes by evaluating external influences?
Which strategic analysis tool helps businesses anticipate market trends and changes by evaluating external influences?
Which financial statement provides insights into a company's solvency?
Which financial statement provides insights into a company's solvency?
What is a significant disadvantage of relying solely on financial statements for decision-making?
What is a significant disadvantage of relying solely on financial statements for decision-making?
Senior management is considering a strategic shift that involves a significant capital investment in new technology. Which of the following factors would NOT be a typical disadvantage associated with this type of strategic decision?
Senior management is considering a strategic shift that involves a significant capital investment in new technology. Which of the following factors would NOT be a typical disadvantage associated with this type of strategic decision?
A company's creative accounting practices have artificially inflated its reported profits, which statement is most likely to reveal this manipulation to a skeptical analyst?
A company's creative accounting practices have artificially inflated its reported profits, which statement is most likely to reveal this manipulation to a skeptical analyst?
A multinational corporation is contemplating entering a new foreign market. Their strategic planning team has conducted a thorough SWOT and PEST analysis. However, recent geopolitical events have introduced a level of uncertainty that wasn't accounted for in their initial risk assessment.
Which of the following adjustments would provide the most robust enhancement to their strategic decision-making process under these circumstances?
A multinational corporation is contemplating entering a new foreign market. Their strategic planning team has conducted a thorough SWOT and PEST analysis. However, recent geopolitical events have introduced a level of uncertainty that wasn't accounted for in their initial risk assessment.
Which of the following adjustments would provide the most robust enhancement to their strategic decision-making process under these circumstances?
Flashcards
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
Percentage change in demand divided by percentage change in price.
Income Elasticity of Demand (YED)
Income Elasticity of Demand (YED)
Percentage change in demand divided by percentage change in consumers' income.
Promotional Elasticity of Demand
Promotional Elasticity of Demand
Percentage change in demand divided by percentage change in promotional spending.
Labour Productivity
Labour Productivity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Capacity Utilization
Capacity Utilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Break-even Point
Break-even Point
Signup and view all the flashcards
Contribution per Unit
Contribution per Unit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Return on Capital Employed (ROCE)
Return on Capital Employed (ROCE)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Business Growth Strategies
Business Growth Strategies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal (Organic) Growth
Internal (Organic) Growth
Signup and view all the flashcards
External Growth (M&A)
External Growth (M&A)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Full Cost Pricing
Full Cost Pricing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Penetration Pricing
Penetration Pricing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inflation
Inflation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interest Rates
Interest Rates
Signup and view all the flashcards
Government Policies
Government Policies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Government Support in Downturns
Government Support in Downturns
Signup and view all the flashcards
Investment Appraisal
Investment Appraisal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Analysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Monte Carlo Simulation
Monte Carlo Simulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Futures Contracts
Futures Contracts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Options
Options
Signup and view all the flashcards
Competitive Pricing
Competitive Pricing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Payback Period
Payback Period
Signup and view all the flashcards
Accounting Rate of Return (ARR)
Accounting Rate of Return (ARR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Net Present Value (NPV)
Net Present Value (NPV)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Break-even Analysis
Break-even Analysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Productivity Ratios
Productivity Ratios
Signup and view all the flashcards
Payback Period (details)
Payback Period (details)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pricing Strategy Balance
Pricing Strategy Balance
Signup and view all the flashcards
SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
PEST Analysis
PEST Analysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Income Statement
Income Statement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Balance Sheet
Balance Sheet
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cash Flow Statement
Cash Flow Statement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Assessing Financial Health
Assessing Financial Health
Signup and view all the flashcards
Informed Investment Decisions
Informed Investment Decisions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Track Profitability
Track Profitability
Signup and view all the flashcards
Financial Planning and Forecasting
Financial Planning and Forecasting
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Economic factors like inflation, interest rates, and government policies critically shape business growth by affecting demand, production costs, and investment decisions.
External Economic Influences:
- Inflation reduces purchasing power and increases production costs.
- High interest rates increase borrowing costs, making expansion more expensive.
- Government policies (fiscal and monetary) affect business growth.
- Government support in downturns (stimulus, subsidies) advantages businesses.
- Lower interest rates encourage borrowing and investment.
- Stable inflation leads to predictable pricing and wages.
- High inflation increases costs and reduces demand creating a disadvantages.
- Rising interest rates discourage business expansion.
- Government policy changes creates uncertainty for businesses.
Investment Appraisal Techniques:
- Investment appraisal assesses whether business investments are worthwhile focusing on risk assessment.
- Sensitivity Analysis examines how changes in variables impact outcomes.
- Risk Assessment identifies potential risks and their impact on profitability.
- Monte Carlo Simulation uses probability models to predict investment outcomes.
- Advanced methods allow preparation for worst-case scenarios.
- Risk evaluation is more accurate than traditional methods.
- These techniques aid in decision-making under uncertainty.
Disadvantages of Advanced Investment Appraisal Techniques:
- Complex calculations reliance on assumptions.
- These techniques are time-consuming, and require expertise.
- Results depend on data accuracy, making them potentially unreliable thus have disadvantages
Financial Instruments for Risk Management:
- Financial instruments hedge against currency fluctuations, interest rate changes, and commodity price swings.
- Futures Contracts are agreements to buy/sell assets at a fixed price in the future, commonly for commodities.
- Options provide the right (not obligation) to buy/sell assets at a predetermined price.
- Swaps exchange cash flows to manage interest rate or currency risks.
Advantages of Financial Instruments
- These instruments protect against market volatility, such as currency depreciation.
- They provide businesses with financial stability.
- These instruments can be customized to fit specific business needs.
Disadvantages of Financial Instruments for Risk Management:
- These instruments can be complex to understand and implement.
- There are high costs associated with some hedging strategies.
- Incorrect hedging can lead to losses rather than protection.
Corporate Governance and Ethical Dilemmas:
- Corporate governance encompasses the systems and processes by which businesses are directed and controlled. Ethical dilemmas arise when businesses must balance profit-making with social responsibility.
- Board of Directors ensures transparency and accountability in decision-making.
- Shareholder vs. Stakeholder Interests creates conflict between maximizing shareholder wealth and considering social/environmental impact.
- Whistleblowing & Ethical Leadership encourages ethical behavior and accountability.
- These factors enhance company reputation and investor confidence.
- They prevent fraud and financial scandals.
- They ensure fair treatment of employees and customers.
Disadvantages of Financial Instruments for Risk Management:
- Compliance with governance rules can be costly.
- Decision-making may slow down due to regulatory requirements.
- Conflicts arise between profit goals and ethical responsibilities.
Technology and Automation in Business Efficiency:
- Technological advancements, including automation and AI, improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive tasks.
- AI & Machine Learning improves decision-making with predictive analytics.
- Internet of Things (IoT) enhances supply chain management and production tracking.
- These advancements reduce labor costs and increase efficiency.
- They improve accuracy and reduce human errors.
- They allow businesses to scale operations more easily.
Disadvantages of Technology and Automation:
- High initial investment in technology and training
- Potential job losses due to automation
- Cybersecurity risks from reliance on digital systems
Cultural Impact in Mergers and Acquisitions:
- Differences in organizational culture can lead to integration challenges.
- Communication Barriers: different workplace cultures lead to misunderstandings.
- Employee Resistance: Workers may resist changes in policies or leadership.
- Operational Differences: different corporate structures create inefficiencies leads to disadvantages
- They create new opportunities for growth and market expansion advantage
- They allow access to new skills, resources, and technologies which is an advantage
- Potential for cost savings through economies of scale is an advantage
Disadvantages of Cultural Impact in Mergers and Acquisitions:
- Cultural clashes can lead to poor employee morale and productivity
- There is difficulty integrating different management styles and systems
- High costs can occur when restructuring and ensuring legal compliance
Scenario Analysis & Stress Testing in Budgeting:
- Scenario analysis helps plan for future uncertainties by evaluating different financial scenarios.
- Best-Case Scenario assumes favorable market conditions.
- Worst-Case Scenario assumes economic downturns and high costs.
- Most Likely Scenario: A balanced projection based on market trends.
- Prepares businesses for financial risks and unexpected challenges.
Advantages/Disadvantages of Scenario Analysis
- Improves strategic decision-making and enhances investor confidence in financial planning.
- It is difficult to predict all possible future events so is a disadvantage
- Assumptions in models may not always be accurate which is a disadvantage
- It can be time-consuming and require significant resources which is a disadvantage
Advanced Strategic Decision-Making Tools:
- Businesses use tools to improve decision-making in uncertain environments.
- Game Theory helps anticipate competitors' moves and responses.
- Decision Trees maps out different choices and their potential outcomes.
- Real Options Analysis evaluates flexibility in investment decisions (e.g., delaying, expanding, or abandoning projects).
- These tools improve accuracy in complex decision-making.
- They help businesses navigate competitive markets.
- Provides a structured way to analyze risks and rewards.
Disadvantages of Advanced Strategic Decision-Making Tools:
- Tool use is complex and requires expertise to implement effectively
- These tools can be costly and time-consuming
- There is a reliance on assumptions that may not always hold true
Strategic Decision-Making in Business:
- Strategic decision-making involves long-term planning to achieve business objectives while considering internal and external factors.
- Decisions affect the overall direction of the company, requiring analysis of market conditions, competition, and financial resources.
- Businesses use SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) and PEST (Political, Economic, Social, Technological) analyses.
- SWOT is used to assess their position and PEST to evaluate external influences.
- Effective strategic planning leads to sustainable competitive advantages and helps companies adapt to market trends.
Internal Factors that Influence Strategic Decision-Making in Business:
- Specialist marketing expertise
- Innovative products or services
- Business location
- Quality products and processes.
- Lack of marketing expertise
- Undifferentiated products or services
- Poor-quality goods or services
- Damaged reputation and weak brand image
External Factors that Influence Strategic Decision-Making in Business:
- Developing market, like the internet
- Mergers, joint ventures, or strategic alliances
- Moving into new market segments offering improved profits
- New international markets
- Markets vacated by ineffective competitors
- New competitor in the home market and Price wars
- Competitor with a new, innovative product or service
- Competitors with superior access to channels of distribution
- Taxation of the product or service
PEST Analysis: Political & Legal
- Stability of the government
- Likely legal changes impacting the industry
- Environmental regulations
- Employment law & competition regulations
- Consumer protection laws
- Government attitude to free market and legal controls over business
PEST Analysis: Economical
- Rate of economic growth
- Exchange rate stability
- Country's membership of free-trade areas & Common currency
PEST Analysis: Social & Technological
- Demographic changes (ageing or youthful population)
- Dominant religion and its impact on marketing strategies
- Education standards and their impact on labor skills
- Roles of men and women in society
- Government support for research spending
- Impact of internet access and speed on marketing and other strategies
SWOT & PEST Analysis Advantages:
- Provides a long-term vision for the company.
- Helps businesses anticipate market trends and changes.
- Encourages informed decision-making through SWOT & PEST analysis.
- Increases competitiveness and long-term sustainability.
- Aligns business operations with strategic goals.
SWOT & PEST Analysis Disadvantages:
- Requires significant time and effort from senior management.
- Involves high risk due to long-term commitments.
- May fail due to poor market predictions.
- Resistance from employees can slow down implementation.
- Expensive to conduct thorough market research.
Financial Statements and Their Use:
- Financial statements offer crucial data about a company's financial health, performance, and liquidity.
- Income Statement (Profit & Loss Statement) shares a company's revenues, expenses, and profit/loss over a period.
- Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position) reveals a company's assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity at a specific time.
- Cash Flow Statement records cash inflows and outflows.
Advantages/Disadvantages of Financial Statements and Their Use
- Helps to assess and manage cash flow, secure investments and loans, and ensure transparency in financial planning
- Requires accounting expertise, may not be real-time, can be manipulated
Business Growth Strategies: Types
- Internal Growth (Organic Growth): Expanding production, opening new locations, or launching new products.
- External Growth (Mergers & Acquisitions): Companies join forces or acquire competitors to increase market share and resources.
- Diversification: Expanding into new industries to spread risk. An example of this is, Amazon started as an online bookstore but later diversified into e-commerce, cloud computing, and AI.
Business Growth Strategies: Pros
- Can lead to increased market share and revenue potential.
- Diversification reduces dependence on a single product/market.
- Economies of scale lower production costs.
- Improves brand recognition and customer base.
- Increases access to new customer segments and geographies.
Business Growth Strategies: Cons
- Requires significant investment and funding.
- Can lead to operational inefficiencies if not managed well.
- High risk of market saturation and overexpansion.
- Mergers & acquisitions create cultural conflicts.
- New market entry faces regulatory and legal barriers.
Costing and Pricing Strategies:
- Setting price impacts profitability and competitive positioning.
- Full Cost Pricing adds a markup to total production costs.
- Contribution Pricing covers variable costs first, contributing to fixed costs.
- Penetration Pricing sets a low price to attract customers and gain market share.
- Skimming Pricing maximizes revenue from early adopters by using a high initial pricing before lowering the price. Common in technology industries
- Businesses should consider consumer demand, competitor pricing, and production costs.
- It's important to set prices while ensuring profitability, respond to market changes, and maintain competitiveness
Investment Appraisal Methods:
- Investment appraisal techniques assess the viability of projects before committing capital.
- Payback Period measures how long it takes for an investment to recover its initial cost.
- Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) calculates return as a percentage of investment, considering accounting profits.
- Net Present Value (NPV) discounts future cash flows to present value.
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR) determines the discount rate at which NPV is zero.
- Can have the advantage to make informed investment decision
- Can have the disadvantage of the Payback period ignoring long term profitability
Business Efficiency Metrics:
- Measuring efficiency ensures optimal use of resources and cost control.
- Break-even Analysis identifies the sales volume at which revenue equals costs.
- Capacity Utilization measures how effectively a business uses its production capacity.
- Productivity Ratios evaluate efficiency in using labor and capital.
- Lead Time Reduction reduces the time taken to produce and deliver goods.
- Waste Minimization cuts waste in raw materials and energy consumption.
- Has the advantage to allocate resources, set business targets and improve productivity
- Can be hard to measure due to the qualitative aspects of business which is a disadvantage
Risk Management:
- Risk management identifies, assesses, and mitigates potential business threats.
- Financial Risks: exchange rate fluctuations, interest rate changes, and credit defaults.
- Operational Risks: supply chain disruptions, equipment failures, and compliance violations.
- Strategic Risks: poor business decisions, technological changes, and shifting consumer preferences.
- Reputation Risks: negative publicity, legal disputes, and unethical practices.
- Cybersecurity Risks: data breaches and hacking.
- This helps prevent financial and operational losses
- Enhances regulators compliance and reduces legal risks
Ethical and Social Responsibility in Business:
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) ensures ethical and sustainable business operations.
- Ethical Sourcing utilizes fair labor practices and environmentally friendly materials enhancing brand reputation.
- Employee Welfare: providing fair wages and safe working conditions boosts motivation and productivity.
- Environmental Responsibility: Reducing carbon footprint and waste disposal helps businesses comply with the regulations.
- Engagement with local customers and charities fosters public trust boosts customer approval
Ethical and Social Responsibility in Business:
- Strong leadership and culture shape business success.
- Autocratic: Centralized decision-making with strict control.
- Democratic Leadership encourages employee participation.
- Laissez-faire Leadership grants employee autonomy and minimal supervision.
- Organizational Culture: the shared values, behaviors, and attitudes that define a company's environment.
- Transformational Leadership: Inspires with a clear vision and motivates them.
- These leaders can drive employee motivation and enhance team work
Budgeting and Financial Planning:
- Zero-Based Budgeting:Requires every expense to be justified from scratch, promoting cost control and efficiency.
- Incremental Budgeting slightly adjusts which may not address inefficiencies.
- Flexible Budgeting adjusts expenditures based on performance and conditions.
- Rolling Budgets are continuously updated to adapt to market change.
- Cash Flow Forecasting predicts cash inflows and outflows, helping avoid liquidity issues.
- These tools help manage cash flow and ensure the business has a long term vision
- This can be time consuming, difficult to forcast accurately and may miss out important market changes
Porter's 5 Forces Analysis:
a. Barriers to Entry
- Greatest when economies of scale are low, technology is cheap, distribution channels are easily accessible, there are no legal or patent restrictions, and product differentiation is low. b. Power of Buyers
- If there are few buyers with a large market share, with other undifferentiated companies, buyer power will be higher c. Power of Suppliers
- Suppliers will have more power when the cost of switching is high, the brand is popular and well known and products cannot be forward integrated d. Threat of Substitutes
- Aluminium products can be affecte by the price of glass and plastic for containers e. Competitive Rivalry
- Is likely to be higher if it is cheap and easy for new firms to enter and buyer/supplier power
- High fixed costs try to use economies of scale
Ansoff Matrix:
- Market penetration (least risky), product development, market development, diversification (most risky).
- Advantage is that clear strategic options for business growth.
- Disadvantage is that there is risk of price wars and growth strategies may not be guaranteed
FORMULAS
- Price Elasticity of Demand (PED) = % Change in Demand / % Change in price
- Income Elasticity of Demand (YED) = % Change in Demand / % Change in Consumers' Income
- Promotional Elasticity of Demand = % Change in Demand / % Change in Promotional Spending
- Absenteeism Rate = (Total Absences×100) / Total Working Days
- Labour Productivity = Total Output / Number of employees
- Capacity Utilization = (Actual Output / Maximum Possible Output)×100
- Break-even Point = Fixed Costs / (Selling Price per Unit-Variable Cost per Unit)
- Contribution per Unit = Selling Price per Unit-Variable Cost per Unit
- Total Contribution = Contribution per Unit * Quantity
- Gross Profit Margin = (Gross Profit / Revenue) * 100
- Operating Profit Margin = (Operating Profit / Revenue) * 100
- Net Profit Margin = (Net Profit / Revenue) * 100
- Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) = (Operating Profit / Capital Employed) * 100
- Capital Employed = Non-Current Liabilities + Shareholders' Equity
- Shareholder's Equity = Issued Shares + Reserves
- Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
- Acid Test Ratio = (Current Assets-Inventory) / Current Liabilities
- Gearing Ratio = (Long-term Liabilities / Capital Employed) * 100
- Inventory Turnover Ratio = (Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory)
- Dividend Yield = (Dividend per Share / Market Price per Share) * 100
- Dividend per share = Total Annual Dividends / Total Number of Shares Issued
- Price/earning ratio = Market share price / EPS
- EPS= Net Profit / Number of Shares Outstanding
- Critical Path Analysis (CPA)
- Earliest Start Time (EST) - EST= Earliest time the previous activity finishes
- Latest Finish Time (LFT) - LFT= Latest time an activity can finish without delaying the project
- Payback period = (12 * additional cashflow) / inflow of last year
- Additional Cashflow = Total of Cumulative Inflow (or Discounted Cashflows) – investment
- ARR = (avg profit / avg investment) * 100
- avg profit = total profit / years
- avg investment = investment / 2
- NPV = Total amount for all years
Answer Structures:
- Answer Structure (8 Marks)
- Definition/Context (1-2 sentences)
- Two clear impacts (each impact = explanation + analysis)
- Use business concepts
- Link back to the business scenario
- Answer Structure (12 Marks)
- Introduction (1-2 sentences) - Define the topic stated in the question and set the context based on the insert.
- Three methods (Explain + Pros + Cons of each)
- Evaluation (Which is most effective & Why?)
- Conclusion (2 sentences summarizing your evaluation)
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.