Podcast
Questions and Answers
According to Dale, what is the likely consequence of learning experiences lacking a solid foundation?
According to Dale, what is the likely consequence of learning experiences lacking a solid foundation?
- An increased reliance on rote memorization techniques.
- A diminished capacity to generate new ideas and adapt to unfamiliar situations. (correct)
- Enhanced ability to apply existing knowledge to novel scenarios.
- Greater proficiency in recalling specific details from previous lessons.
How should educators apply the Cone of Experience to foster higher-order thinking skills?
How should educators apply the Cone of Experience to foster higher-order thinking skills?
- Concentrating solely on symbolic or abstract learning to accelerate cognitive growth.
- Avoiding the use of concrete materials to prevent cognitive fixation.
- Balancing concrete experiences with abstract concepts to promote cognitive development. (correct)
- Primarily utilizing concrete experiences to establish a strong foundational understanding.
In Bruner's three-tiered model, at which stage does learning primarily occur through direct physical interaction and manipulation of objects?
In Bruner's three-tiered model, at which stage does learning primarily occur through direct physical interaction and manipulation of objects?
- Abstract stage
- Symbolic stage
- Enactive stage (correct)
- Iconic stage
Which of the following best exemplifies learning within Bruner's enactive stage?
Which of the following best exemplifies learning within Bruner's enactive stage?
Why is the enactive stage considered crucial during early learning?
Why is the enactive stage considered crucial during early learning?
What is the primary mechanism through which understanding is developed during the enactive stage?
What is the primary mechanism through which understanding is developed during the enactive stage?
Which activity aligns with the iconic stage of learning according to Bruner's model?
Which activity aligns with the iconic stage of learning according to Bruner's model?
What distinguishes the symbolic stage from the enactive and iconic stages in Bruner's model?
What distinguishes the symbolic stage from the enactive and iconic stages in Bruner's model?
A student learning to code by physically connecting electronic components before writing the software demonstrates which of Bruner's stages?
A student learning to code by physically connecting electronic components before writing the software demonstrates which of Bruner's stages?
How does engaging in enactive learning potentially influence later stages of cognitive development?
How does engaging in enactive learning potentially influence later stages of cognitive development?
How does mastery in the enactive stage influence cognitive development, according to the provided material?
How does mastery in the enactive stage influence cognitive development, according to the provided material?
In the context of iconic learning, what is the most significant advantage of using visual aids such as charts and graphs?
In the context of iconic learning, what is the most significant advantage of using visual aids such as charts and graphs?
What specific cognitive capability defines the symbolic stage of learning as detailed in the provided material?
What specific cognitive capability defines the symbolic stage of learning as detailed in the provided material?
How does iconic learning specifically benefit the fields of science and mathematics?
How does iconic learning specifically benefit the fields of science and mathematics?
Which of the following best describes the cognitive transition that occurs as learners move from the iconic to the symbolic stage?
Which of the following best describes the cognitive transition that occurs as learners move from the iconic to the symbolic stage?
In what way does the symbolic stage enable individuals to engage with complex subjects such as science and literature?
In what way does the symbolic stage enable individuals to engage with complex subjects such as science and literature?
How does the arrangement of experiences in Dale's Cone relate to the concept of abstraction?
How does the arrangement of experiences in Dale's Cone relate to the concept of abstraction?
Which of the following is a key consideration when integrating experiences from different stages of Dale's Cone?
Which of the following is a key consideration when integrating experiences from different stages of Dale's Cone?
In the context of the Eight M's of Teaching, how does 'Media' primarily function?
In the context of the Eight M's of Teaching, how does 'Media' primarily function?
Considering the Eight M's of Teaching, what is the most accurate way to describe 'Milieu'?
Considering the Eight M's of Teaching, what is the most accurate way to describe 'Milieu'?
How does the 'Mastery' component of the Eight M's of Teaching relate to learning outcomes?
How does the 'Mastery' component of the Eight M's of Teaching relate to learning outcomes?
Considering Dale's Cone of Experience, which activity would typically provide a more concrete learning experience: watching an educational television program or participating in a direct, purposeful experience?
Considering Dale's Cone of Experience, which activity would typically provide a more concrete learning experience: watching an educational television program or participating in a direct, purposeful experience?
How does the 'Motivation' element of the Eight M's of Teaching influence the 'Mastery' element?
How does the 'Motivation' element of the Eight M's of Teaching influence the 'Mastery' element?
In the context of the Eight M's of Teaching, what is the relationship between 'Material' and 'Matter'?
In the context of the Eight M's of Teaching, what is the relationship between 'Material' and 'Matter'?
How does 'Measurement' in the Eight M's of Teaching inform adjustments to other M's such as 'Method' or 'Material' in subsequent lessons?
How does 'Measurement' in the Eight M's of Teaching inform adjustments to other M's such as 'Method' or 'Material' in subsequent lessons?
Considering the Cone of Experience, what is the most significant advantage of providing students with real-world environmental studies over traditional classroom learning?
Considering the Cone of Experience, what is the most significant advantage of providing students with real-world environmental studies over traditional classroom learning?
In the context of the Cone of Experience, what critical element distinguishes 'learning by doing' in exhibitions from passively observing exhibits?
In the context of the Cone of Experience, what critical element distinguishes 'learning by doing' in exhibitions from passively observing exhibits?
How do films and television, as instructional resources, most effectively leverage the principles outlined in the Cone of Experience to impact learners?
How do films and television, as instructional resources, most effectively leverage the principles outlined in the Cone of Experience to impact learners?
According to the Cone of Experience, what potential limitation should educators carefully consider when utilizing visual and auditory devices in instruction?
According to the Cone of Experience, what potential limitation should educators carefully consider when utilizing visual and auditory devices in instruction?
In the context of instructional design, what is the most critical consideration when using symbolic representations such as charts, graphs and diagrams?
In the context of instructional design, what is the most critical consideration when using symbolic representations such as charts, graphs and diagrams?
How does the Cone of Experience inform the strategic selection of instructional materials to optimize student learning outcomes?
How does the Cone of Experience inform the strategic selection of instructional materials to optimize student learning outcomes?
What is the potential consequence of introducing abstract concepts without first establishing a foundation of concrete experiences, according to the Cone of Experience?
What is the potential consequence of introducing abstract concepts without first establishing a foundation of concrete experiences, according to the Cone of Experience?
Within the framework of the Cone of Experience, how might an educator effectively enrich textbook-based instruction to enhance comprehension and retention?
Within the framework of the Cone of Experience, how might an educator effectively enrich textbook-based instruction to enhance comprehension and retention?
In applying the principles of the Cone of Experience, how can educators optimize the use of instructional materials to cater to diverse learning preferences and needs?
In applying the principles of the Cone of Experience, how can educators optimize the use of instructional materials to cater to diverse learning preferences and needs?
Considering the Cone of Experience, how does the strategic integration of multiple instructional media contribute to a more holistic and effective teaching-learning process?
Considering the Cone of Experience, how does the strategic integration of multiple instructional media contribute to a more holistic and effective teaching-learning process?
Which approach most effectively leverages 'contrived experiences' to facilitate learning, particularly when physical space or time constraints pose a challenge?
Which approach most effectively leverages 'contrived experiences' to facilitate learning, particularly when physical space or time constraints pose a challenge?
A history teacher aims to immerse students in the events leading up to a significant historical decision. Which method would best achieve this deep, contextual understanding?
A history teacher aims to immerse students in the events leading up to a significant historical decision. Which method would best achieve this deep, contextual understanding?
A biology teacher wants to demonstrate the process of cellular respiration in a way that is easily understandable. Which method would be the MOST effective?
A biology teacher wants to demonstrate the process of cellular respiration in a way that is easily understandable. Which method would be the MOST effective?
Which of the following scenarios exemplifies the strategic use of 'contrived experiences' in education?
Which of the following scenarios exemplifies the strategic use of 'contrived experiences' in education?
In what way does 'dramatic participation' uniquely enhance the learning experience compared to other instructional methods?
In what way does 'dramatic participation' uniquely enhance the learning experience compared to other instructional methods?
What is the critical advantage of using models and miniatures in education?
What is the critical advantage of using models and miniatures in education?
When is it most appropriate to employ 'virtual experience/simulation' as a teaching method?
When is it most appropriate to employ 'virtual experience/simulation' as a teaching method?
What is the primary goal of educational excursions?
What is the primary goal of educational excursions?
Considering the principles of sensory learning, why would integrating multiple senses typically lead to enhanced and more effective learning outcomes?
Considering the principles of sensory learning, why would integrating multiple senses typically lead to enhanced and more effective learning outcomes?
A teacher wants to expose their students to experiences that heighten their sensitivity to the world, elevate their thinking, and strengthen their foundation of learning. Which type of experiences is best suited for this?
A teacher wants to expose their students to experiences that heighten their sensitivity to the world, elevate their thinking, and strengthen their foundation of learning. Which type of experiences is best suited for this?
Flashcards
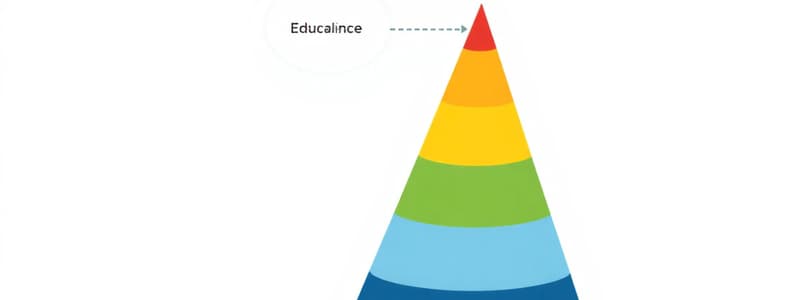
Dale's Cone of Experience
Dale's Cone of Experience
A visual model representing a continuum of learning experiences, ranging from concrete to abstract.
Direct, Purposeful Experiences
Direct, Purposeful Experiences
Learning by direct participation and hands-on activities.
Contrived Experiences
Contrived Experiences
Using models or mock-ups to simulate real situations.
Dramatized Experiences
Dramatized Experiences
Signup and view all the flashcards
Demonstrations
Demonstrations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Trip
Study Trip
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exhibits
Exhibits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Educational Television
Educational Television
Signup and view all the flashcards
Milieu
Milieu
Signup and view all the flashcards
Measurement in Learning
Measurement in Learning
Signup and view all the flashcards
First-Hand Experiences
First-Hand Experiences
Signup and view all the flashcards
Experiential Learning
Experiential Learning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Virtual/Simulated Experience
Virtual/Simulated Experience
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dramatic Participation
Dramatic Participation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Field Trip
Field Trip
Signup and view all the flashcards
Representations
Representations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Effects of Sensory Experiences
Effects of Sensory Experiences
Signup and view all the flashcards
Real Environment Study
Real Environment Study
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exhibitions
Exhibitions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Values via Media
Values via Media
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reality Reconstruction
Reality Reconstruction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Learning Enhancement
Learning Enhancement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abstract Symbols
Abstract Symbols
Signup and view all the flashcards
Visual Aids
Visual Aids
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symbolic Representation
Symbolic Representation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Multi-Material Learning
Multi-Material Learning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Concrete Before Abstract
Concrete Before Abstract
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enactive Stage
Enactive Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Iconic Stage
Iconic Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Examples of Iconic Learning
Examples of Iconic Learning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Benefits of Iconic Learning
Benefits of Iconic Learning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symbolic Thinking
Symbolic Thinking
Signup and view all the flashcards
Symbolic Stage
Symbolic Stage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rootless Experiences
Rootless Experiences
Signup and view all the flashcards
Teaching Beyond Concrete
Teaching Beyond Concrete
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bruner's Learning Model
Bruner's Learning Model
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enactive Stage Importance
Enactive Stage Importance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enactive Characteristics
Enactive Characteristics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enactive Example: Puzzles
Enactive Example: Puzzles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enactive Example: Counting
Enactive Example: Counting
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Ed 4: Technology for Teaching and Learning 1 details the theories and principles for designing technology-driven learning lessons
Learning Outcomes
- Identify learning principles and theories applied in lesson design and development using appropriate media and technologies.
- Compare the SAMR, ASSURE, and TPACK Models of technology integration.
- Familiarize with the ASSURE Model by creating a lesson guide/outline.
Dale's Cone of Experience
- A visual model shows a continuum of learning.
- It is a pictorial device presenting 11 bands of experience, from concrete experiences at the bottom to verbal symbols at the cone's top.
- Arrangement of bands represents degree of abstraction, not difficulty, and the measure of sensory participation.
- Experiences in each stage can be mixed and are interrelated to foster more meaningful learning.
- First-hand experiences form the basis of learning.
- Using senses establishes knowledge.
- More senses involved in learning lead to better learning.
- It is experiential learning focused on learning by doing.
- Providing first-hand sensory experiences may heighten sensitivity, elevate thinking, and strengthen learning foundations.
- Representations like models or miniatures act as close substitutes for reality.
- This level makes learning more accessible.
- Editing reality is called this, and makes it easier to understand.
- Contrived experiences overcome space and time limitations.
- They edit reality to focus on parts or processes, overcome difficulties, and help grasp concepts easily.
- Virtual experience and simulations are considered for near experiences.
- It includes using teaching and learning tools with computers and the Internet to improve students' learning experiences.
- Environment representation ranges from text-based interfaces to 3D graphical output. Dramatic Participation:
- Helps get close to realties that cannot be reached at first hand.
- Learners participate in reconstructed experiences.
- Experiences can improve understanding of the event or concept.
- Provides authentic learning by utilizing most intelligences.
- An example is reliving the Philippine Revolution outbreak by acting out character roles in a drama.
Demonstrations
- Uses photographs, drawings, films, displays, or guided motions
- Provides a visualized explanation of a fact, idea, or process.
- Shows how things are done.
- For example, a P.E. teacher showing basic dance steps.
- Educational excursions and trips are conducted to observe events or locations unavailable in the classroom
- It is a trip by the students to gain firsthand knowledge away from the classroom at museums, factories, geological areas, or in certain environments
- Gives a chance to study something in a real environment vs. the classroom or lab.
- Exhibits consist of working models or photographs with models, charts, and posters.
- May include demonstrating experiments of science devices or a slide projector, motion picture, computer, and television.
- It can enable learners to act as spectators or to handle and manipulate devices.
- Opportunity to handle materials encourages use of sense organs and Learning-by-doing, proving to be meaningful for learning.
- Implies values and relaying values and messages through films and tv
- Can reconstruct the past to effectively bring audiences there.
- Conveys realism with emphasis on personality, presentation, and ability to select, dramatize, highlight, and clarify.
- Visual and auditory devices may be used by individual learners or groups to improve and broaden the learning experience.
- They are no longer realistic reproductions.
- Employs highly abstract representations in some situations
- Examples include charts, graphs, maps, and diagrams.
Verbal Symbols
- Are not like the objects or ideas they stand for.
- Do not contain contain visual cues to their meaning.
- Can be a word (book), idea (freedom of speech), principle (the principle of balance), or formula (e=mc2).
The Eight (8) M's of Teaching
- Milieu - the learning environment
- Matter - the content of learning
- Method- teaching and learning activities
- Material- the resource of learning
- Media – communication system
- Motivation – arousing and sustaining interest in learning
- Mastery – internalization of learning
- Measurement - evidence that learning took place
Implications of Cone of Experience on Teaching and Learning
- Avoid using only one medium of communication. Instead, use varied instructional materials to help students conceptualize his experience.
- Avoid teaching directly at the symbolic level if there is inadequate concrete understanding. Students’ concepts will then lack real roots in experience.
- Don't get stuck in the concrete (meaning too focused on one way of thinking). Bring students to the abstract level to develop higher order.
Jerome Bruner's Three-Tiered Model of Learning
- Enactive: Learning through actions and direct manipulation.
- Iconic: Learning through visual images and diagrams.
- Symbolic: Learning through language, symbols, and abstract thinking.
Enactive Stage
- Focuses on learning through experiences and actions and is critical for early learning through building foundational knowledge.
- Solving puzzles or counting using fingers highlights the role of tactile and motor skills in cognitive development.
- Learners engage the world physically; Actions, rather than words, drive understanding.
- Children learn concepts manipulating objects forming mental models.
- Skills developed from early stages underpin future complex learning, essential for life success.
Iconic Stage
- Learners grasp knowledge through visual tools, such as images and diagrams, rather than physical actions.
- Visual tools/aids represent data visually, enhance understanding, are more accessible, easier to remember for learners, encourage creativity and critical thinking, boost understanding, and is especially effective in STEM.
Symbolic Stage
- A significant shift in cognitive development, learners begin to express ideas using language, symbols and abstract concepts.
- Symbolic thinking is essential for abstract reasoning and higher learning.
- Individuals manipulate symbols, words, and numbers mentally without needing physical objects.
- Abstract thought enables problem-solving, scientific theories work, and literary analysis engagement .
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.