Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which cranial nerve is responsible for the sense of smell?
Which cranial nerve is responsible for the sense of smell?
- Olfactory (correct)
- Oculomotor
- Optic
- Trigeminal
The cerebellum is located anterior to the cerebrum.
The cerebellum is located anterior to the cerebrum.
False (B)
What is the primary function of the medulla oblongata?
What is the primary function of the medulla oblongata?
Controls vital aspects of cardiovascular and respiratory function
The _________ is the band of white matter responsible for communication between the hemispheres of the brain.
The _________ is the band of white matter responsible for communication between the hemispheres of the brain.
Match the following parts of the brain with their primary functions:
Match the following parts of the brain with their primary functions:
What is the primary function of the thalamus?
What is the primary function of the thalamus?
The pia mater is the most superficial covering of the brain and spinal cord.
The pia mater is the most superficial covering of the brain and spinal cord.
What are the paired glands located atop the kidneys called?
What are the paired glands located atop the kidneys called?
The ______ secretes hormones like thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
The ______ secretes hormones like thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
Match the following parts of the spinal cord with their descriptions:
Match the following parts of the spinal cord with their descriptions:
Which part of the brain is responsible for processing visual information?
Which part of the brain is responsible for processing visual information?
The hypothalamus is located superior to the thalamus.
The hypothalamus is located superior to the thalamus.
What fills the subarachnoid space?
What fills the subarachnoid space?
The ______ secretes hormones like aldosterone to regulate sodium and potassium levels.
The ______ secretes hormones like aldosterone to regulate sodium and potassium levels.
Which cells are primarily found in the parathyroid glands?
Which cells are primarily found in the parathyroid glands?
What is the primary role of the optic chiasma in the visual pathway?
What is the primary role of the optic chiasma in the visual pathway?
Describe the function of the corpus callosum.
Describe the function of the corpus callosum.
In what way does the trigeminal nerve contribute to facial function?
In what way does the trigeminal nerve contribute to facial function?
How does the cerebellum contribute to movement?
How does the cerebellum contribute to movement?
What functions are associated with the medulla oblongata?
What functions are associated with the medulla oblongata?
What are the primary functions of the occipital lobe?
What are the primary functions of the occipital lobe?
How does the thalamus contribute to information processing in the brain?
How does the thalamus contribute to information processing in the brain?
What is the role of the hypothalamus in maintaining homeostasis?
What is the role of the hypothalamus in maintaining homeostasis?
Describe the composition and function of the spinal cord's grey matter.
Describe the composition and function of the spinal cord's grey matter.
What distinguishes the white matter from the grey matter in the spinal cord?
What distinguishes the white matter from the grey matter in the spinal cord?
Identify the three meninges and describe their arrangement relative to the brain.
Identify the three meninges and describe their arrangement relative to the brain.
What is the primary function of the adrenal gland's zona fasciculata?
What is the primary function of the adrenal gland's zona fasciculata?
Explain the significance of the thyroid follicles in hormone production.
Explain the significance of the thyroid follicles in hormone production.
Where is the central canal located, and what is its function?
Where is the central canal located, and what is its function?
What is the role of the spinal ganglion in the spinal nerves?
What is the role of the spinal ganglion in the spinal nerves?
The sensory nerve for vision originates in the ______ and is triggered when light hits photoreceptors in the eye.
The sensory nerve for vision originates in the ______ and is triggered when light hits photoreceptors in the eye.
The ______ is a band of white matter that facilitates communication between the two hemispheres of the brain.
The ______ is a band of white matter that facilitates communication between the two hemispheres of the brain.
The ______ is responsible for controlling vital aspects of cardiovascular and respiratory function.
The ______ is responsible for controlling vital aspects of cardiovascular and respiratory function.
The ______ lobe is located inferior to the frontal lobe and is associated with auditory processing.
The ______ lobe is located inferior to the frontal lobe and is associated with auditory processing.
The ______ connects the medulla oblongata to the cerebellum and higher brain centers.
The ______ connects the medulla oblongata to the cerebellum and higher brain centers.
The ______ is responsible for the regulation of circadian rhythm, thirst, hunger, and body temperature.
The ______ is responsible for the regulation of circadian rhythm, thirst, hunger, and body temperature.
The ______ lobe is primarily involved in processing visual information.
The ______ lobe is primarily involved in processing visual information.
The outer region of the spinal cord, known as ______, is responsible for high-speed conduction of nerve impulses.
The outer region of the spinal cord, known as ______, is responsible for high-speed conduction of nerve impulses.
The ______ mater is the most superficial membrane surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
The ______ mater is the most superficial membrane surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
The ______ is located at the center of the grey matter and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
The ______ is located at the center of the grey matter and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
The ______ glands are responsible for secreting melatonin.
The ______ glands are responsible for secreting melatonin.
The anterior (motor) nerve root contains axons of ______ neurons.
The anterior (motor) nerve root contains axons of ______ neurons.
The ______ produces thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) hormones.
The ______ produces thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) hormones.
The ______ space is located between the pia mater and the arachnoid mater and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
The ______ space is located between the pia mater and the arachnoid mater and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
The ______ is a mass of grey matter in the spinal cord responsible for processing of information.
The ______ is a mass of grey matter in the spinal cord responsible for processing of information.
Flashcards
Olfactory Bulb Function
Olfactory Bulb Function
Sensory nerve for smell originating from the nasal mucosa and terminating in the cerebral hemisphere.
Optic Nerve Function
Optic Nerve Function
Sensory nerve for vision that originates in the retina and responds to light.
Oculomotor Nerve Function
Oculomotor Nerve Function
Motor nerve originating from the midbrain controlling extrinsic eye muscles.
Trigeminal Nerve Function
Trigeminal Nerve Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebellum Function
Cerebellum Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Grey Matter (Spinal Cord)
Grey Matter (Spinal Cord)
Signup and view all the flashcards
White Matter (Spinal Cord)
White Matter (Spinal Cord)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Central Canal (Spinal Cord)
Central Canal (Spinal Cord)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anterior (Motor) Nerve Root
Anterior (Motor) Nerve Root
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior (Sensory) Nerve Root
Posterior (Sensory) Nerve Root
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thalamus
Thalamus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypothalamus
Hypothalamus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pineal Gland
Pineal Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dura Mater
Dura Mater
Signup and view all the flashcards
Subarachnoid Space
Subarachnoid Space
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebral Cortex
Cerebral Cortex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Optic Chiasma
Optic Chiasma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Midbrain Function
Midbrain Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pons Function
Pons Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medulla Oblongata Function
Medulla Oblongata Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cerebrum Gyri & Sulci
Cerebrum Gyri & Sulci
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the thalamus?
What is the function of the thalamus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the pineal gland?
What is the function of the pineal gland?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the anterior horns of the spinal cord?
What is the function of the anterior horns of the spinal cord?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the posterior horns of the spinal cord?
What is the function of the posterior horns of the spinal cord?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the dura mater?
What is the function of the dura mater?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the arachnoid mater?
What is the function of the arachnoid mater?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the pia mater?
What is the function of the pia mater?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the thyroid gland?
What is the function of the thyroid gland?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the adrenal glands?
What is the function of the adrenal glands?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the olfactory bulb responsible for?
What is the olfactory bulb responsible for?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trigeminal Nerve: Mixed
Trigeminal Nerve: Mixed
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corpus Callosum Function
Corpus Callosum Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Occipital Lobe
Occipital Lobe
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pituitary Gland
Pituitary Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anterior Horns (Spinal Cord)
Anterior Horns (Spinal Cord)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Horns (Spinal Cord)
Posterior Horns (Spinal Cord)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Brain Structures
- Olfactory Bulbs: Sensory nerves for smell, originating in nasal mucosa and terminating in anterior cerebral hemisphere. Olfactory tract carries information to the temporal lobe for interpretation.
- Olfactory Tract: Carries smell information to the temporal lobe.
- Optic Nerve: Sensory nerve for vision, originating in the retina. Activated by light hitting photoreceptors.
- Optic Chiasma: Where optic nerves converge, forming an X-shape.
- Oculomotor Nerve: Motor nerve originating in the midbrain, controlling extrinsic eye muscles.
- Trigeminal Nerve: Mixed cranial nerve (motor and sensory) arising from midbrain/pons junction. Sensory portion interacts with facial sensation from oral/nasal areas; motor part influences chewing and swallowing.
- Midbrain: Situated under the diencephalon, involved in eye movement, vision, and hearing. Anterior portion carries nerve pathways; posterior portion receives sensory reflexes.
- Cerebellum: Located posterior to cerebrum, separated by transverse fissure, responsible for movement control.
- Pons: Connects medulla oblongata and cerebellum to higher brain centers.
- Medulla Oblongata: Located between pons and spinal cord, controls vital functions like cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
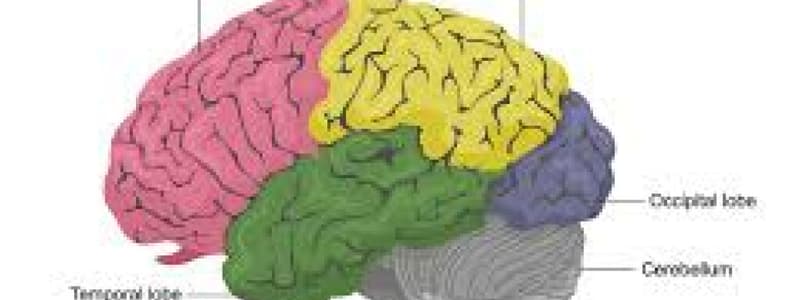
Cerebral Lobes
- Cerebrum: Outer gyri, defined by sulci/fissures; divides into lobes:
- Frontal Lobe: Anteriormost; contains primary motor area and motor speech area.
- Parietal Lobe: Posterior to frontal lobe, includes primary somatosensory area, somatosensory association area, and gustatory area.
- Temporal Lobe: Located inferior to frontal and parietal lobes; includes primary auditory, auditory association areas, and olfactory areas.
- Occipital Lobe: Posteriormost, contains primary visual area and visual association areas.
Diencephalon
- Thalamus: Located within the centre of the cerebrum; processes, integrates, and relays information to the cerebral cortex. Situated in the diencephalon's walls.
- Hypothalamus: Located inferior to thalamus; responsible for regulating circadian rhythm, thirst, hunger, body temperature, and controls the pituitary gland.
- Pituitary Gland: Located just below the hypothalamus; it is a component of the endocrine system.
Spinal Cord and Nerves
- Spinal Cord:
- Grey Matter: "H"-shaped inner region, processes information (anterior and posterior horns).
- White Matter: Outer region, high-speed nerve impulse conductors separated by grey matter horns.
- Central Canal: Filled with cerebrospinal fluid, continuous with brain cavities.
- Spinal Nerves: 31 pairs in total.
- Anterior Nerve Root: Motor axons carrying impulses to effectors (muscles/glands).
- Posterior Nerve Root: Sensory axons with a ganglion for sensory neurons carrying information towards the spinal cord.
Brain Meninges
- Dura Mater: Dense irregular connective tissue; outermost covering.
- Epidural Space: Between vertebrae & dura mater, filled with connective, vascular, and adipose tissues.
- Arachnoid Mater: Thin, elastic membrane (middle layer).
- Subdural Space: Separates dura and arachnoid mater.
- Subarachnoid Space: Between pia and arachnoid mater; contains cerebrospinal fluid.
- Pia Mater: Deepest vascularized layer (innermost), closely adhering to brain/spinal cord.
Thyroid Gland
- Thyroid Follicles: Spherical sacs with follicular cells producing thyroid hormones (T3 and T4).
- Colloid: The space in the center of follicles containing precursor material for T3 and T4 hormones.
- Parafollicular Cells: Produce calcitonin.
- Parathyroid Glands: Four small masses posterior to the thyroid; produce hormones regulating calcium.
Adrenal Glands
- Zona Glomerulosa: Outer layer, secretes mineralocorticoids (e.g., aldosterone).
- Zona Fasciculata: Secretes glucocorticoids (e.g., cortisol).
- Zona Reticularis: Secretes androgens (hormones influencing male traits).
- Adrenal Medulla: The innermost layer, secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.