Podcast
Questions and Answers
What initiates the transmission of information between neurons?
What initiates the transmission of information between neurons?
- Dendrites
- Neuron proliferation
- Axon branches
- Electrical impulses (correct)
What role do neurotransmitters play in the brain?
What role do neurotransmitters play in the brain?
- They prune unnecessary synapses
- They transmit messages across synapses (correct)
- They initiate neuron proliferation
- They form the fatty sheath of myelination
What is the purpose of myelination in neurons?
What is the purpose of myelination in neurons?
- To initiate neuron proliferation
- To improve the speed of transmission (correct)
- To transmit electrical impulses
- To connect neurons into networks
Why is there neuron pruning during brain development?
Why is there neuron pruning during brain development?
What happens to neurons during the first two years of brain development?
What happens to neurons during the first two years of brain development?
What results from neuron proliferation before birth?
What results from neuron proliferation before birth?
What is the function of the synapse in neuron communication?
What is the function of the synapse in neuron communication?
How do neurons typically change over time during brain development?
How do neurons typically change over time during brain development?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Development of the Brain
- The development of the brain begins soon after conception.
- Neurons or nerve cells develop and are responsible for storing and transmitting messages throughout the brain system.
Neuron Development
- Between 100 and 200 billion neurons are present at birth, which is the majority of neurons needed for growth and development.
Neural Transmission
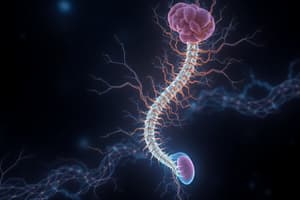
- Information is transmitted between neurons via an axon, a long arm-like projection.
- When a neuron is activated, an electrical impulse travels along the axon and crosses the synapse between it and the adjacent neuron.
- The synapse forms a junction between neurons, and the message is received by the branch-like dendrites of the neighbouring neuron.
Neuron Growth and Complexity
- Over time, neurons develop in size and complexity, growing axon branches and dendrites that connect to other cells.
- Thousands of neurons connect to each other, forming networks that interact with other networks.
Myelination
- A process of myelination occurs, insulating the axon in a fatty sheath that improves the speed of transmission across the neural networks by up to 100 times.
Synaptic Development
- During the first two years, an estimated million or more synapses are formed every second.
- The developing brain produces many more neurons and synapses than are eventually used or needed.
Neuron Pruning
- Some neurons die off naturally, and unused or unnecessary synapses are pruned.
- The adult brain contains only about half the number of neurons generated during the developmental phase.
- This pruning enables faster and more efficient communication between the remaining cells and allows new connections to develop.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.