Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary role of osteoblasts in bone formation?
What is the primary role of osteoblasts in bone formation?
- To fill trabecular spaces and form osteons (correct)
- To initiate apoptosis of chondrocytes
- To remodel spongy bone into medullary cavities
- To invade periosteal buds during ossification
What is the function of the periosteum in bone development?
What is the function of the periosteum in bone development?
- To act as a scaffold for cartilage formation
- To provide a protective layer surrounding the bone (correct)
- To facilitate nutrient artery invasion
- To promote the death of chondrocytes
Which process describes the gradual replacement of cartilage by bone during development?
Which process describes the gradual replacement of cartilage by bone during development?
- Intramembranous ossification
- Resorption
- Endochondral ossification (correct)
- Bone remodeling
How does Wolff's law relate to bone remodeling?
How does Wolff's law relate to bone remodeling?
Which step involves the invasion of a nutrient artery during endochondral ossification?
Which step involves the invasion of a nutrient artery during endochondral ossification?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for increasing blood calcium levels when detected by the parathyroid glands?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for increasing blood calcium levels when detected by the parathyroid glands?
What structural feature characterizes flat bones during development?
What structural feature characterizes flat bones during development?
Which cells are responsible for remodeling spongy bone into medullary cavities?
Which cells are responsible for remodeling spongy bone into medullary cavities?
What is the primary function of red marrow in the human body?
What is the primary function of red marrow in the human body?
In which location is yellow marrow primarily found in adults?
In which location is yellow marrow primarily found in adults?
Which blood cell type is primarily produced by red marrow?
Which blood cell type is primarily produced by red marrow?
What is the process of ossification responsible for in skeletal development?
What is the process of ossification responsible for in skeletal development?
What role does yellow marrow play in the body under specific conditions?
What role does yellow marrow play in the body under specific conditions?
During which developmental phase does endochondral ossification begin?
During which developmental phase does endochondral ossification begin?
Which of the following bones is primarily formed through intramembranous ossification?
Which of the following bones is primarily formed through intramembranous ossification?
What occurs during the calcification step of intramembranous ossification?
What occurs during the calcification step of intramembranous ossification?
Flashcards
Bone Marrow
Bone Marrow
A vital tissue found in bone cavities, responsible for blood cell production (hematopoiesis) and overall bone health.
Red Marrow
Red Marrow
The active blood-producing tissue found in bones, primarily in children and specific locations in adults. It generates red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Yellow Marrow
Yellow Marrow
A type of marrow primarily found in adults, composed of fat and reticular tissue. It stores fat and can revert to red marrow during anemia.
What are the three types of blood cells produced in red marrow?
What are the three types of blood cells produced in red marrow?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ossification
Ossification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intramembranous Ossification
Intramembranous Ossification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endochondral Ossification
Endochondral Ossification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Steps of Intramembranous Ossification
Steps of Intramembranous Ossification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteoprogenitor Cells
Osteoprogenitor Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spicules
Spicules
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trabeculae
Trabeculae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Periosteum
Periosteum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteon
Osteon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bone Collar
Bone Collar
Signup and view all the flashcards
Periosteal Bud
Periosteal Bud
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epiphysis
Epiphysis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Bone Marrow
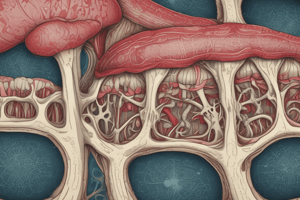
- Bone marrow is found within long bones and spongy bone.
- It plays a crucial role in hematopoiesis, the creation of blood cells.
- Red marrow produces red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets.
- RBCs transport oxygen, WBCs fight infection, and platelets aid in clotting.
- Red marrow is present in nearly all bones in children.
- Adult red marrow locations include skull, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, pelvic girdle, and proximal ends of humerus and femur.
- Yellow marrow is mostly found in adults, composed of adipose cells and does not create blood cells.
- Yellow marrow can convert to red marrow under conditions of anemia to increase blood cell production.
Bone Development - Ossification
- Ossification (osteogenesis) is the formation of bone in prenatal and postnatal development.
- Intramembranous Ossification forms flat bones (skull, mandible, clavicles).
- It also impacts the thickness and support of long bones.
- Intramembranous ossification steps:
- Mesenchymal cells form an ossification center.
- Osteoblasts secrete osteoid, then become osteocytes in lacunae.
- Spicules form, connecting around blood vessels to become trabeculae.
- Osteoblasts fill spaces to form osteons; mature compact bone develops.
- Flat bones have a compact-spongy-compact structure.
- Endochondral Ossification replaces cartilage with bone; begins around 6-8 weeks fetal development.
- Endochondral ossification steps:
- Mesenchymal cells form a hyaline cartilage model.
- Chondrocytes die, leaving cavities for diaphysis elongation.
- A perichondrial collar supports structure.
- A nutrient artery invades cavities, forming spongy bone.
- Osteoclasts remodel spongy bone to form a medullary cavity.
- Secondary ossification centers develop in epiphyses, with growth plates for lengthwise growth.
Bone Remodeling
- Bone remodeling is a continuous process where bone tissue is absorbed and deposited throughout life.
- About 10% of the skeleton is remodeled each year.
- It repairs microfractures, mobilizes minerals, and adapts to stress (Wolff's law).
Hormonal Regulation of Bone
- Calcium imbalances trigger hormonal responses to regulate blood calcium levels.
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is released when blood calcium is low.
- Osteoclasts release calcium into the bloodstream.
- Kidneys retain calcium and excrete phosphate to increase blood calcium levels.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.