Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the endothelial cells in the inner wall of blood vessels?
What is the primary function of the endothelial cells in the inner wall of blood vessels?
- To enhance platelet aggregation
- To produce clotting factors
- To synthesize collagen fibers
- To regulate the entry and exit of materials into and out of the bloodstream (correct)
What is the primary mechanism by which endothelial cells prevent blood coagulation?
What is the primary mechanism by which endothelial cells prevent blood coagulation?
- By forming a platelet plug
- By releasing thrombin
- By secreting chemical signals that prevent blood coagulation (correct)
- By secreting clotting factors
What is the result of endothelial damage in a blood vessel?
What is the result of endothelial damage in a blood vessel?
- Formation of a platelet plug that prevents blood flow out of the vessel (correct)
- Enhanced platelet aggregation
- Decreased release of thrombin
- Increased production of clotting factors
What is the role of clotting factors in the coagulation process?
What is the role of clotting factors in the coagulation process?
What is the result of thrombin activity in the coagulation process?
What is the result of thrombin activity in the coagulation process?
What could be a potential cause of excessive bleeding in a patient with a cut?
What could be a potential cause of excessive bleeding in a patient with a cut?
What would be the effect of heightened levels of serum antibodies against clotting factors?
What would be the effect of heightened levels of serum antibodies against clotting factors?
What is the primary function of platelets in the coagulation process?
What is the primary function of platelets in the coagulation process?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Endothelial Cells and Blood Vessels
- A single layer of endothelial cells forms the inner wall of all blood vessels, regulating entry and exit of materials into and out of the bloodstream.
- Endothelial cells secrete chemical signals that generally prevent blood coagulation (clotting).
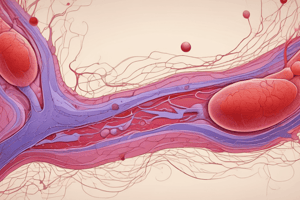
Blood Coagulation Cascade
- Injury to a blood vessel exposes connective tissue (collagen fibers), leading to platelet binding and aggregation, forming a platelet plug (clot).
- Platelets and endothelial cells near the damage site release signals that enhance platelet aggregation.
- Clotting factors (mainly synthesized in the liver) become activated in response to platelet aggregation, leading to thrombin formation.
- Thrombin induces protein strands (fibrin) to form an adhesive mesh-like structure over the platelet plug, reinforcing the clot.
Impaired Blood Clotting
- Reduced liver function can decrease clotting factor production, impairing blood clotting.
- Reduced platelet production can also impair blood clotting.
- Heightened levels of serum antibodies against clotting factors can promote their destruction, impairing clot formation.
Macrophages and Clot Formation
- Macrophages, phagocytic immune cells, engulf and destroy foreign pathogens and damaged cells.
- Macrophages can contribute to clot formation by secreting procoagulant molecules and destroying pathogens entering the body through the cut.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.