Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main arterial supply for the anterior cerebral arteries (ACA) and the middle cerebral arteries (MCA)?
What is the main arterial supply for the anterior cerebral arteries (ACA) and the middle cerebral arteries (MCA)?
- Vertebral arteries
- Internal carotid arteries (correct)
- Internal jugular arteries
- External carotid arteries
Which arteries enter the skull via foramen magnum and are the main supply for the posterior cerebral arteries (PCA)?
Which arteries enter the skull via foramen magnum and are the main supply for the posterior cerebral arteries (PCA)?
- Internal carotid arteries
- Renal arteries
- External carotid arteries
- Vertebral arteries (correct)
Which signals play a role in regulating coronary blood flow based on the metabolic demands of the myocardium?
Which signals play a role in regulating coronary blood flow based on the metabolic demands of the myocardium?
- Myogenic mechanism
- Metabolic signals (correct)
- Endothelial substances
- Sympathetic input
What condition may develop if there is stasis of blood in the lower limbs?
What condition may develop if there is stasis of blood in the lower limbs?
What is a possible consequence of impaired venous drainage in the lower limbs?
What is a possible consequence of impaired venous drainage in the lower limbs?
What condition is associated with the development of varicose veins?
What condition is associated with the development of varicose veins?
Autoregulation of blood flow is primarily influenced by:
Autoregulation of blood flow is primarily influenced by:
What is the role of nitric oxide (NO) in autoregulation of blood flow?
What is the role of nitric oxide (NO) in autoregulation of blood flow?
The increased shearing forces on endothelial cells caused by increased perfusion pressure lead to the increased synthesis of:
The increased shearing forces on endothelial cells caused by increased perfusion pressure lead to the increased synthesis of:
Which of the following is NOT a signal of the tissue's metabolic status in autoregulation of blood flow?
Which of the following is NOT a signal of the tissue's metabolic status in autoregulation of blood flow?
Which of the following is NOT an endothelial factor involved in autoregulation of blood flow?
Which of the following is NOT an endothelial factor involved in autoregulation of blood flow?
What triggers the release of nitric oxide from endothelial cells?
What triggers the release of nitric oxide from endothelial cells?
Which molecule is responsible for the production of nitric oxide in endothelial cells?
Which molecule is responsible for the production of nitric oxide in endothelial cells?
Which of the following are important regulators of coronary blood flow?
Which of the following are important regulators of coronary blood flow?
Which receptors mediate vasodilation in coronary arterioles in response to sympathetic input?
Which receptors mediate vasodilation in coronary arterioles in response to sympathetic input?
Which neural input can influence the dilation of coronary arterioles?
Which neural input can influence the dilation of coronary arterioles?
Which arteries are responsible for supplying blood to the brain?
Which arteries are responsible for supplying blood to the brain?
What is formed when the Vertebral Arteries re-join?
What is formed when the Vertebral Arteries re-join?
How do the Internal Carotid Arteries enter the skull?
How do the Internal Carotid Arteries enter the skull?
Where do the Vertebral Arteries enter the skull?
Where do the Vertebral Arteries enter the skull?
Which vein sits under the sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscle?
Which vein sits under the sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscle?
The internal jugular vein (IJV) runs from:
The internal jugular vein (IJV) runs from:
The external jugular vein (EJV) is located:
The external jugular vein (EJV) is located:
How can the internal jugular vein (IJV) be accessed?
How can the internal jugular vein (IJV) be accessed?
What potential complication can result from injury to the external jugular vein (EJV)?
What potential complication can result from injury to the external jugular vein (EJV)?
Which vein is associated with the jugular venous pulse (JVP)?
Which vein is associated with the jugular venous pulse (JVP)?
True or False: The internal jugular vein is a vein without valves.
True or False: The internal jugular vein is a vein without valves.
What happens to the jugular venous pulse when pressure changes occur on the right side of circulation?
What happens to the jugular venous pulse when pressure changes occur on the right side of circulation?
At what angle of body positioning is the jugular venous pulse (JVP) in the internal jugular vein just visible above the clavicle in a normal individual?
At what angle of body positioning is the jugular venous pulse (JVP) in the internal jugular vein just visible above the clavicle in a normal individual?
Elevated jugular venous pulse can be seen in which condition?
Elevated jugular venous pulse can be seen in which condition?
What causes the jugular venous pulse to be elevated in heart failure?
What causes the jugular venous pulse to be elevated in heart failure?
Which vein is less useful when estimating jugular venous pressure due to the presence of valves?
Which vein is less useful when estimating jugular venous pressure due to the presence of valves?
What might be heard on auscultation of the renal arteries?
What might be heard on auscultation of the renal arteries?
Where do the renal arteries branch off from?
Where do the renal arteries branch off from?
What type of arteries are the renal arteries?
What type of arteries are the renal arteries?
Which blood vessels supply the kidneys?
Which blood vessels supply the kidneys?
Which artery supplies the posterior left ventricle?
Which artery supplies the posterior left ventricle?
Which artery gives off the posterior interventricular artery?
Which artery gives off the posterior interventricular artery?
Which artery supplies most of the right ventricle?
Which artery supplies most of the right ventricle?
The left coronary artery splits into which two branches?
The left coronary artery splits into which two branches?
Which artery supplies the anterior left ventricle?
Which artery supplies the anterior left ventricle?
Which artery is responsible for the arterial supply to the lower limbs?
Which artery is responsible for the arterial supply to the lower limbs?
Which of the following is a key step in the examination of the peripheral vasculature?
Which of the following is a key step in the examination of the peripheral vasculature?
In individuals with peripheral vascular disease, what can be observed regarding the pulses in the lower limbs?
In individuals with peripheral vascular disease, what can be observed regarding the pulses in the lower limbs?
Which analysis can be performed to assess peripheral vascular health?
Which analysis can be performed to assess peripheral vascular health?
What are the three factors that venous drainage of the lower limbs depends on?
What are the three factors that venous drainage of the lower limbs depends on?
What is the Circle of Willis and why is it advantageous?
What is the Circle of Willis and why is it advantageous?
What can an elevated jugular vein pulse indicate?
What can an elevated jugular vein pulse indicate?
Where are renal arteries located and what is their function?
Where are renal arteries located and what is their function?
What are some symptoms of reduced blood flow to the brain?
What are some symptoms of reduced blood flow to the brain?
What are some symptoms of reduced renal blood flow?
What are some symptoms of reduced renal blood flow?
What is autoregulation of blood flow and how is it maintained?
What is autoregulation of blood flow and how is it maintained?
What are some symptoms of reduced blood flow to the brain?
What are some symptoms of reduced blood flow to the brain?
What are some symptoms of reduced renal blood flow?
What are some symptoms of reduced renal blood flow?
What is the main supply for the posterior cerebral arteries (PCA)?
What is the main supply for the posterior cerebral arteries (PCA)?
Where do renal veins drain into?
Where do renal veins drain into?
What are the symptoms of reduced blood flow to the brain?
What are the symptoms of reduced blood flow to the brain?
What are the symptoms of reduced renal blood flow?
What are the symptoms of reduced renal blood flow?
What mechanisms maintain autoregulation of blood flow?
What mechanisms maintain autoregulation of blood flow?
Flashcards
ACA and MCA arterial supply
ACA and MCA arterial supply
Internal carotid arteries
PCA arterial supply
PCA arterial supply
Vertebral arteries
Coronary blood flow regulation
Coronary blood flow regulation
Metabolic signals
Vasodilator in autoregulation
Vasodilator in autoregulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Triggers of nitric oxide release
Triggers of nitric oxide release
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nitric oxide production
Nitric oxide production
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neural input influencing coronary arterioles
Neural input influencing coronary arterioles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vertebral Arteries
Vertebral Arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Entry of Vertebral Arteries
Entry of Vertebral Arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vein under SCM
Vein under SCM
Signup and view all the flashcards
IJV course
IJV course
Signup and view all the flashcards
EJV location
EJV location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vein for JVP
Vein for JVP
Signup and view all the flashcards
IJV valves?
IJV valves?
Signup and view all the flashcards
JVP pressure change on right side
JVP pressure change on right side
Signup and view all the flashcards
JVP visibility angle
JVP visibility angle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Auscultation of renal arteries
Auscultation of renal arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal arteries branch off from
Renal arteries branch off from
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal arteries
Renal arteries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior left ventricle blood supply
Posterior left ventricle blood supply
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior interventricular artery origin
Posterior interventricular artery origin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Left coronary artery splits
Left coronary artery splits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anterior left ventricle blood supply
Anterior left ventricle blood supply
Signup and view all the flashcards
Artery supplying lower limbs
Artery supplying lower limbs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Factors of venous drainage
Factors of venous drainage
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Circle of Willis
What is the Circle of Willis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is the JVP elevated in heart failure?
Why is the JVP elevated in heart failure?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Blood Supply and Control of Blood Flow to the Heart, Brain, Kidneys and Lower Limbs
- Major arterial supply and venous drainage of the heart, brain, kidneys, and lower limbs are described.
- Deficiency of supply of oxygenated blood to the heart, brain, kidneys, and lower limbs is related to symptoms and signs in patients.
- Mechanisms of how blood flow is controlled are described.
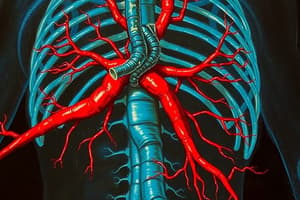
- Internal carotid arteries are the main supply for the anterior cerebral arteries (ACA) and the middle cerebral arteries (MCA).
- Vertebral arteries enter the skull via foramen magnum, and the main supply for the posterior cerebral arteries (PCA).
- The Circle of Willis is advantageous because it allows for collateral circulation.
- The jugular vein pulse is elevated in heart failure and can be used to estimate jugular venous pressure.
- Renal arteries are direct branches off the abdominal aorta and sit at vertebral level L1.
- Renal veins drain directly into the inferior vena cava (IVC).
- Reduced blood flow to the brain can cause loss of motor function, syncope, sensory loss, visual field loss, confusion, temporary loss of consciousness, blindness, amnesia, ataxia, behavioral change, and problems with balance.
- Reduced renal blood flow can cause malignant hypertension, high blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fatigue, sleep problems, changes in how much you urinate, decreased mental sharpness, muscle twitches and cramps, swelling of feet and ankles, and persistent itching.
- Autoregulation of blood flow is maintained at a constant level over a wide range of perfusion pressures, and it is controlled by neural and hormonal influences and intrinsic myogenic mechanisms of the arteriolar smooth muscle.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.