Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which level of organization consists of cells made up of molecules?
Which level of organization consists of cells made up of molecules?
- Chemical level
- Cellular level (correct)
- Organ level
- Tissue level
What is the correct sequence of biological organization levels from simplest to most complex?
What is the correct sequence of biological organization levels from simplest to most complex?
- Molecules, Atoms, Organ level, Tissue level, Organismal level
- Atoms, Molecules, Cellular level, Tissue level, Organ level (correct)
- Atoms, Molecules, Tissues, Organ level, Organismal level
- Cellular level, Tissues, Organ system level, Organismal level, Organ level
What type of tissue is smooth muscle tissue classified as?
What type of tissue is smooth muscle tissue classified as?
- Muscle tissue (correct)
- Nervous tissue
- Connective tissue
- Epithelial tissue
How are organs defined in the context of biological organization?
How are organs defined in the context of biological organization?
Which level of organization includes the heart and blood vessels?
Which level of organization includes the heart and blood vessels?
What is the relationship between atoms and molecules in biological organization?
What is the relationship between atoms and molecules in biological organization?
Which statement best describes the tissue level of organization?
Which statement best describes the tissue level of organization?
At what level of organization do different organ systems come together to form a complete living entity?
At what level of organization do different organ systems come together to form a complete living entity?
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
Which structure is NOT part of the digestive system?
Which structure is NOT part of the digestive system?
During which process does gas exchange occur?
During which process does gas exchange occur?
Which of the following organs is part of the respiratory system?
Which of the following organs is part of the respiratory system?
What are the indigestible materials that the digestive system eliminates called?
What are the indigestible materials that the digestive system eliminates called?
What is the role of the small intestine in the digestive system?
What is the role of the small intestine in the digestive system?
Which of the following organs assists in the removal of carbon dioxide from the blood?
Which of the following organs assists in the removal of carbon dioxide from the blood?
What is the main function of the pharynx?
What is the main function of the pharynx?
What does the term 'superior' refer to in directional anatomy?
What does the term 'superior' refer to in directional anatomy?
In anatomical terms, which term describes a position farthest from the point of attachment of a limb?
In anatomical terms, which term describes a position farthest from the point of attachment of a limb?
Which directional term describes a position that is closer to the midline of the body?
Which directional term describes a position that is closer to the midline of the body?
What does the term 'deep' indicate in anatomical language?
What does the term 'deep' indicate in anatomical language?
Which term is used to describe the backside of the body?
Which term is used to describe the backside of the body?
What is the role of hormones in growth?
What is the role of hormones in growth?
What is considered the most abundant chemical in the human body?
What is considered the most abundant chemical in the human body?
What is the normal body temperature in Celsius for human survival?
What is the normal body temperature in Celsius for human survival?
Which of the following is not a necessary life function?
Which of the following is not a necessary life function?
Which body system is responsible for making oxygen available through chemical reactions?
Which body system is responsible for making oxygen available through chemical reactions?
What is the anatomical position?
What is the anatomical position?
Why is atmospheric pressure important for survival?
Why is atmospheric pressure important for survival?
What is the primary purpose of using special anatomical terminology?
What is the primary purpose of using special anatomical terminology?
What are the two main body cavities?
What are the two main body cavities?
Which cavity houses the brain?
Which cavity houses the brain?
What separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity?
What separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity?
Which of the following organs is housed within the abdominopelvic cavity?
Which of the following organs is housed within the abdominopelvic cavity?
What is the role of body cavities?
What is the role of body cavities?
Which subdivision of the dorsal body cavity houses the spinal cord?
Which subdivision of the dorsal body cavity houses the spinal cord?
Which of the following statements is true regarding the ventral body cavity?
Which of the following statements is true regarding the ventral body cavity?
Which organ is NOT found in the thoracic cavity?
Which organ is NOT found in the thoracic cavity?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Levels of Organization
- Atoms combine to form molecules, which make up cells at the chemical and cellular levels.
- Tissues consist of similar types of cells and are organized into different types of tissues at the tissue level.
- Organs are formed from multiple tissue types and operate as part of organ systems.
- The organismal level encompasses all organ systems working together.
Organ Systems Overview
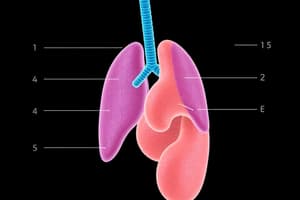
- Respiratory System:
- Maintains oxygen supply and carbon dioxide removal.
- Gaseous exchanges occur in the air sacs of the lungs.
- Digestive System:
- Includes mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, and accessory organs.
- Breaks down food, absorbs nutrients into the bloodstream, and eliminates waste material.
Necessary Life Functions
- Reproduction:
- Cellular level: Involves new cell production for growth and repair.
- Organismal level: Managed by the reproductive system.
- Growth:
- Results in increased cell or body size, regulated by hormones.
Survival Needs
- Nutrients:
- Essential for energy and cell structure; includes carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, and minerals.
- Oxygen:
- Vital for chemical reactions, supplied by respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
- Water:
- Comprises 60-80% of body weight, vital for bodily functions and chemical reactions.
- Normal Body Temperature:
- Optimal at 37ºC (98.6ºF); deviations affect chemical reactions.
- Atmospheric Pressure:
- Necessary for effective gas exchange.
Language of Anatomy
- Specialized terminology clarifies position, direction, and structure to avoid misunderstandings.
- Anatomical Position:
- Standard position: Standing, arms at sides, palms facing forward.
Directional Terms
- Superior (cranial): Above or toward the head.
- Inferior (caudal): Below or toward the feet.
- Anterior (ventral): Front of the body.
- Posterior (dorsal): Back of the body.
- Medial: Toward the midline.
- Lateral: Away from the midline.
- Proximal: Closer to point of attachment or body trunk.
- Distal: Farther from point of attachment or body trunk.
- Superficial (external): Towards the body surface.
- Deep (internal): Away from the body surface.
Regional Terms
- Divides the body into anatomical landmarks for reference.
Body Cavities
- Two main cavities:
- Dorsal: Contains cranial (brain) and spinal (spinal cord) cavities, protected by skull and vertebrae.
- Ventral: Contains thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities, separated by the diaphragm.
Protection of Organs
- Body cavities provide varying degrees of protection to the organs contained within.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.