Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the tiny hair in the nostrils and Bronchi?
What is the primary function of the tiny hair in the nostrils and Bronchi?
- To move oxygen into the bloodstream
- To warm the air we inhale
- To produce mucus
- To filter the air we inhale and obstruct dust particles (correct)
How many lobes does the right lung have?
How many lobes does the right lung have?
- Two
- Three (correct)
- Five
- Four
What is the role of the Diaphragm in the breathing process?
What is the role of the Diaphragm in the breathing process?
- To filter the air we inhale
- To separate the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity (correct)
- To produce mucus
- To exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide
What happens in the alveoli?
What happens in the alveoli?
Why is the left lung smaller in size?
Why is the left lung smaller in size?
How many times does a person breathe approximately in one day?
How many times does a person breathe approximately in one day?
What happens to the air when it passes through the windpipe?
What happens to the air when it passes through the windpipe?
What is the purpose of the mucus in the bronchi?
What is the purpose of the mucus in the bronchi?
What is the function of the cilia in the bronchi?
What is the function of the cilia in the bronchi?
What is unique about the lungs?
What is unique about the lungs?
What is the location of the diaphragm?
What is the location of the diaphragm?
What happens to the diaphragm when we breathe out?
What happens to the diaphragm when we breathe out?
What is the purpose of the alveoli?
What is the purpose of the alveoli?
What separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity?
What separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
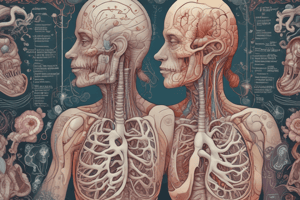
Human Respiratory System
- The human body needs oxygen to breathe, and it gets oxygen from the air around us.
- Without oxygen, the body would be like a car without fuel, and it's essential for survival.
Breathing Process
- When we breathe in, oxygen is taken in through the nostrils, where tiny hair obstructs dust particles.
- The air then passes through the windpipe (Trachea), which filters the air we inhale.
- The Trachea branches out into two tubes called Bronchi, where tiny hair called Cilia move back and forth to move mucus inside.
- The mucus is a sticky substance that collects germs and other particles that might harm the lungs.
Lungs
- The Bronchi carry air into each lung, with the right lung having three lobes and the left lung having two lobes.
- The left lung is slightly smaller in size to give space to the heart.
- The lobes are filled with small and spongy air sacs called alveoli, where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide happens.
- It is here that the blood picks up oxygen and lets go of carbon dioxide.
Diaphragm
- The Diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located beneath the lungs that contracts when we breathe in and expands when we breathe out.
- It separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity.
Trivia
- The lungs are the only organs that can float on water.
- A person breathes approximately 20,000 times in one day.
Human Respiratory System
- Oxygen is essential for human survival, and the body obtains it from the air.
- The absence of oxygen would render the body unable to function, similar to a car without fuel.
Breathing Process
- Oxygen is inhaled through the nostrils, where tiny hair obstructs dust particles.
- The air then passes through the trachea, which filters the inhaled air.
- The trachea branches into two tubes called bronchi, where cilia (tiny hair) move back and forth to move mucus inside.
- Mucus is a sticky substance that collects germs and other particles that might harm the lungs.
Lungs
- The bronchi carry air into each lung, with the right lung having three lobes and the left lung having two lobes.
- The left lung is smaller in size to accommodate the heart.
- The lobes are filled with small, spongy air sacs called alveoli, where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.
- It is in the alveoli that the blood picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide.
Diaphragm
- The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located beneath the lungs that contracts during inhalation and expands during exhalation.
- The diaphragm separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity.
Trivia
- The lungs are capable of floating on water due to their unique structure.
- An average person takes approximately 20,000 breaths in a day.
Human Respiratory System
- Oxygen is essential for human survival, and the body obtains it from the air.
- The absence of oxygen would render the body unable to function, similar to a car without fuel.
Breathing Process
- Oxygen is inhaled through the nostrils, where tiny hair obstructs dust particles.
- The air then passes through the trachea, which filters the inhaled air.
- The trachea branches into two tubes called bronchi, where cilia (tiny hair) move back and forth to move mucus inside.
- Mucus is a sticky substance that collects germs and other particles that might harm the lungs.
Lungs
- The bronchi carry air into each lung, with the right lung having three lobes and the left lung having two lobes.
- The left lung is smaller in size to accommodate the heart.
- The lobes are filled with small, spongy air sacs called alveoli, where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged.
- It is in the alveoli that the blood picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide.
Diaphragm
- The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located beneath the lungs that contracts during inhalation and expands during exhalation.
- The diaphragm separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity.
Trivia
- The lungs are capable of floating on water due to their unique structure.
- An average person takes approximately 20,000 breaths in a day.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.