Podcast
Questions and Answers
What characterizes active transport compared to passive transport?
What characterizes active transport compared to passive transport?
- Active transport does not require energy.
- Active transport moves molecules against the concentration gradient. (correct)
- Active transport involves the random movement of molecules.
- Active transport provides larger spaces for particle movement.
Why is maintaining the internal cellular environment important for metabolism?
Why is maintaining the internal cellular environment important for metabolism?
- It allows cells to perform photosynthesis.
- It helps cells create more proteins.
- It ensures specific conditions for cellular processes. (correct)
- It prevents the import of waste materials.
What processes do cells use to import and export materials?
What processes do cells use to import and export materials?
- Endocytosis and exocytosis (correct)
- Filtration and evaporation
- Diffusion and osmosis
- Condensation and sublimation
How do endotherms regulate their body temperature?
How do endotherms regulate their body temperature?
What might happen if a cell fails to remove waste products efficiently?
What might happen if a cell fails to remove waste products efficiently?
What role does protein synthesis play in cellular function?
What role does protein synthesis play in cellular function?
What would be the consequence of failing to maintain homeostasis within cells?
What would be the consequence of failing to maintain homeostasis within cells?
What is the primary function of the plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells?
What is the primary function of the plasma membrane in eukaryotic cells?
Which process allows small molecules to pass through the plasma membrane without any input of energy?
Which process allows small molecules to pass through the plasma membrane without any input of energy?
What term describes the balance created across the plasma membrane due to molecular movement?
What term describes the balance created across the plasma membrane due to molecular movement?
Facilitated diffusion requires which of the following to assist the movement of larger, polar molecules?
Facilitated diffusion requires which of the following to assist the movement of larger, polar molecules?
What is homeostasis in the context of cellular environments?
What is homeostasis in the context of cellular environments?
In eukaryotic cells, which type of molecules are most likely to pass through the plasma membrane freely?
In eukaryotic cells, which type of molecules are most likely to pass through the plasma membrane freely?
Which of the following statements best describes diffusion?
Which of the following statements best describes diffusion?
What is the significance of the thin structure of the plasma membrane?
What is the significance of the thin structure of the plasma membrane?
Study Notes
Cell Membranes and Internal Environments
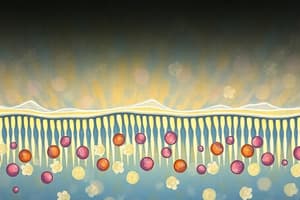
- Cell membranes act as barriers, separating the cell's internal environment from its external surroundings.
- Maintaining this difference is crucial for growth, reproduction, and homeostasis.
- Homeostasis refers to maintaining stable internal conditions, despite external changes.
Molecular Transport: Passive Transport
- Eukaryotic cells (plants, animals, fungi) are surrounded by a plasma membrane regulating the internal environment.
- Small molecules cross the membrane via diffusion (passive transport), moving from high to low concentration until equilibrium is reached.
- Facilitated diffusion uses transport proteins to help larger, polar molecules cross the membrane; still passive transport.
Molecular Transport: Active Transport
- Active transport requires energy to move molecules against their concentration gradient (from low to high concentration).
- Active transport mechanisms include pumping molecules through transport proteins.
- Exocytosis exports material out of the cell; endocytosis imports material into the cell.
Importance of Internal Regulation for Growth and Reproduction
- A properly controlled internal environment is essential for proper cell function, hence organism survival.
- Cellular processes require specific conditions (sugar levels, temperature, oxygen, water balance).
- Metabolism, crucial for maintaining body temperature (endotherms generate internal heat), relies on a stable internal environment.
- Waste removal via molecular transport is also vital to prevent cellular buildup.
- Protein synthesis, essential for growth, repair, and numerous bodily functions, depends on maintaining homeostasis.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz covers key concepts about cell membranes and their role in maintaining internal environments. It includes discussions on molecular transport methods such as passive and active transport. Test your understanding of how cells regulate their internal conditions and the importance of homeostasis.