Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main function of simple squamous epithelium?
What is the main function of simple squamous epithelium?
- Secretion and absorption
- Propels mucus and debris
- Protection against mechanical stress
- Allows passage of materials by filtration and diffusion (correct)
Where is simple cuboidal epithelium commonly found?
Where is simple cuboidal epithelium commonly found?
- Serosal membranes
- Lining of the heart
- Alveoli of lungs
- Kidney tubules (correct)
Which characteristic differentiates ciliated simple columnar epithelium from non-ciliated types?
Which characteristic differentiates ciliated simple columnar epithelium from non-ciliated types?
- Location in the body
- Shape of the cells
- Presence of cilia (correct)
- Function of secretion
Which of the following is a function of ciliated simple columnar epithelium?
Which of the following is a function of ciliated simple columnar epithelium?
What type of cells comprise simple squamous epithelium?
What type of cells comprise simple squamous epithelium?
What is the primary function of blood tissue in the cardiovascular system?
What is the primary function of blood tissue in the cardiovascular system?
What is a characteristic feature of hyaline cartilage?
What is a characteristic feature of hyaline cartilage?
Which type of connective tissue is characterized as the most widely distributed in the body?
Which type of connective tissue is characterized as the most widely distributed in the body?
Where is areolar connective tissue primarily located?
Where is areolar connective tissue primarily located?
Which of the following functions is associated with hyaline cartilage?
Which of the following functions is associated with hyaline cartilage?
What components are found in blood tissue?
What components are found in blood tissue?
In which location would you find fibrocartilage?
In which location would you find fibrocartilage?
What characteristic of areolar connective tissue enables it to soak up excess fluid?
What characteristic of areolar connective tissue enables it to soak up excess fluid?
What is a primary component of the matrix in hyaline cartilage?
What is a primary component of the matrix in hyaline cartilage?
Which statement about the lacunae in hyaline cartilage is correct?
Which statement about the lacunae in hyaline cartilage is correct?
What type of fibers becomes visible during the clotting process in blood tissue?
What type of fibers becomes visible during the clotting process in blood tissue?
What layer of areolar connective tissue is located directly beneath the epidermis?
What layer of areolar connective tissue is located directly beneath the epidermis?
What characteristic describes the matrix in areolar connective tissue?
What characteristic describes the matrix in areolar connective tissue?
What is the primary function of reticular connective tissue?
What is the primary function of reticular connective tissue?
Which of the following components are found in bone (osseous) tissue?
Which of the following components are found in bone (osseous) tissue?
What are lacunae in bone tissue?
What are lacunae in bone tissue?
In which of the following locations would you find nervous tissue?
In which of the following locations would you find nervous tissue?
Which characteristic is NOT associated with nervous tissue?
Which characteristic is NOT associated with nervous tissue?
What type of support do neuroglia provide in nervous tissue?
What type of support do neuroglia provide in nervous tissue?
Which of the following structures is unique to bone tissue?
Which of the following structures is unique to bone tissue?
What is the major function of reticular connective tissue in lymph nodes?
What is the major function of reticular connective tissue in lymph nodes?
What is the primary function of pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
What is the primary function of pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
Where is ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium primarily located?
Where is ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium primarily located?
What are the surface cells of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium primarily characterized as?
What are the surface cells of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium primarily characterized as?
Which feature is NOT associated with pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
Which feature is NOT associated with pseudostratified columnar epithelium?
What is the main function of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
What is the main function of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
Which of the following is a unique characteristic of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
Which of the following is a unique characteristic of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium?
In terms of structure, what distinguishes pseudostratified columnar epithelium from simple columnar epithelium?
In terms of structure, what distinguishes pseudostratified columnar epithelium from simple columnar epithelium?
Which type of epithelium primarily serves in secretion and propulsion of mucus?
Which type of epithelium primarily serves in secretion and propulsion of mucus?
Flashcards
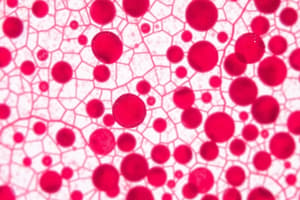
Blood
Blood
A fluid connective tissue composed of blood cells suspended in plasma. It transports nutrients, waste products, and respiratory gasses throughout the body.
Blood Plasma
Blood Plasma
The liquid matrix of blood, containing dissolved proteins, nutrients, and waste products.
Red Blood Cells (RBC)
Red Blood Cells (RBC)
Blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body. They lack a nucleus and contain hemoglobin, a protein that binds to oxygen.
White Blood Cells (WBC)
White Blood Cells (WBC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Platelets
Platelets
Signup and view all the flashcards
Areolar Connective Tissue
Areolar Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lamina Propria
Lamina Propria
Signup and view all the flashcards
Edema
Edema
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reticular Connective Tissue
Reticular Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stroma
Stroma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bone
Bone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteocytes
Osteocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lacunae
Lacunae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lamellae
Lamellae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Canaliculi
Canaliculi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nervous Tissue
Nervous Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurons
Neurons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neuroglia
Neuroglia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyaline Cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratified Squamous Epithelium (Keratinized)
Stratified Squamous Epithelium (Keratinized)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Goblet Cells
Goblet Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cilia
Cilia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Blood (Vascular Tissue)
- Composed of blood cells suspended in liquid matrix called blood plasma.
- Soluble fibers visible only during clotting.
- Functions to transport nutrients, wastes, and respiratory gases.
- Found in blood vessels.
- Key cell types: Red Blood Cells (RBC), White Blood Cells (WBC), and platelets.
Areolar Connective Tissue
- Most widespread connective tissue.
- Soft, pliable texture resembling "cobwebs."
- Serves as universal packing material and holds organs in place.
- Contains a layer known as lamina propria beneath the epidermis, supporting all skin membranes.
- Features a loose network of all fiber types and can absorb excess fluid, causing edema.
Reticular Connective Tissue
- Characterized by a delicate network of interwoven reticular fibers with reticular cells.
- Functions to form stroma, providing structural support to organs.
- Located in lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow.
Bone (Osseous Tissue)
- Comprises osteocytes (bone cells) located in lacunae.
- Features a hard matrix of calcium salts and a high content of collagen fibers.
- Functions to protect and support the body.
- Found in all bones, with key features: lacunae, lamellae, and canaliculi.
Nervous Tissue
- Functions to receive and conduct electrochemical impulses throughout the body.
- Key properties: irritability and conductivity.
- Composed of neurons and neuroglia, with neuroglia serving protective and supportive roles for neurons.
- Located in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
Hyaline Cartilage
- Most common type of cartilage with hidden abundant collagen fibers in a glassy matrix.
- Functions to aid smooth movement of bones at joints.
- Found in trachea, at the juncture of ribs with the breastbone, and at the ends of long bones.
- Major component of the fetal skeleton and located in growth plates of long bones.
Fibrocartilage
- Highly compressible, acting as a cushion within joints.
- Functions to manage compression forces and reduce stress.
- Found in intervertebral discs of the spinal column and areas needing heavy cushioning.
Simple Squamous Epithelium
- Single layer of flattened cells with disc-shaped nuclei.
- Functions in filtration and diffusion of materials.
- Present in kidney glomeruli, alveoli, heart lining, and serosa.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- Single layer of cube-shaped cells with large spherical nuclei.
- Functions in secretion and absorption.
- Located in kidney tubules, ducts, and the surface of ovaries.
Simple Columnar Epithelium
- Single layer of taller cells with round to oval nuclei, some may have cilia.
- Functions in the secretion of mucus; ciliated type propels mucus.
- Non-ciliated type found from stomach to anal canal; ciliated type found in bronchi and uterine tubes.
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
- Single layer of cells differing in height, containing goblet cells and cilia.
- Functions in mucus secretion and propulsion via ciliary action.
- Non-ciliated type located in male's sperm-carrying ducts; ciliated type found in trachea and bronchi.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium (Keratinized)
- Thick membrane of several layers, with basal cells being cuboidal or columnar and surface cells flattened.
- Functions to waterproof and reduce evaporation from underlying tissues.
- Key component of the epidermis and external skin, with non-keratinized versions found in the vagina.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz explores the structure and function of blood tissue, including the role of blood plasma and the characteristics of soluble fibers during clotting. Participants will learn about blood cells and their vital role in transportation within the body.