Podcast
Questions and Answers
What structure is primarily responsible for synthesizing proteins in eukaryotic cells?
What structure is primarily responsible for synthesizing proteins in eukaryotic cells?
- Mitochondrion
- Nucleus
- Golgi apparatus
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (correct)
Which type of epithelium is characterized by its multiple layers of cells and is designed to provide protection?
Which type of epithelium is characterized by its multiple layers of cells and is designed to provide protection?
- Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- Transitional epithelium
- Stratified squamous epithelium (correct)
- Simple cuboidal epithelium
What type of connective tissue contains elastic fibers and allows for flexibility?
What type of connective tissue contains elastic fibers and allows for flexibility?
- Dense irregular connective tissue
- Hyaline cartilage
- Adipose tissue
- Elastic connective tissue (correct)
Which of the following types of muscle tissue is characterized by striations and is under voluntary control?
Which of the following types of muscle tissue is characterized by striations and is under voluntary control?
What type of cartilage is found in areas that require sturdiness and support, such as the ribs and trachea?
What type of cartilage is found in areas that require sturdiness and support, such as the ribs and trachea?
What structure in bone is primarily responsible for the transport of blood vessels and nerves?
What structure in bone is primarily responsible for the transport of blood vessels and nerves?
Which type of blood cell is primarily involved in the immune response and fighting infections?
Which type of blood cell is primarily involved in the immune response and fighting infections?
What is the primary function of the goblet cells in epithelial tissue?
What is the primary function of the goblet cells in epithelial tissue?
Flashcards
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranous sacs and tubules that extends throughout the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. It is involved in protein synthesis, folding, modification, and transport, as well as lipid metabolism and detoxification.
What are mitochondria?
What are mitochondria?
The mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell responsible for aerobic respiration, producing ATP through the breakdown of glucose.
What is the nucleus?
What is the nucleus?
The nucleus is the control center of the cell, containing the genetic material (DNA) organized into chromosomes. It is responsible for regulating gene expression and cell division.
What is simple cuboidal epithelium?
What is simple cuboidal epithelium?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is simple columnar epithelium?
What is simple columnar epithelium?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is stratified squamous epithelium?
What is stratified squamous epithelium?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Golgi apparatus?
What is the Golgi apparatus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is loose connective tissue?
What is loose connective tissue?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
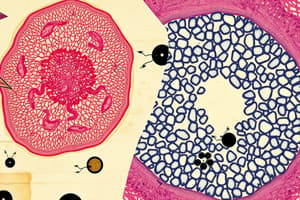
Electron Micrographs of Cellular Structures
- Images show various cell components at high magnification using electron microscopy
- Examples include mitochondrion, RER, Golgi Apparatus, centriole, nucleus, nucleolus, and chromatin
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- A single layer of cube-shaped cells forms this tissue
- Found in glands and lining kidney tubules
Simple Columnar Epithelium
- A single layer of column-shaped cells
- Commonly found lining the digestive tract
Pseudostratified Columnar Ciliated Epithelium
- Appears layered but all cells touch the basement membrane
- Cilia and goblet cells are present, aiding in movement and secretion
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
- Multiple layers of flattened cells
- Found in areas needing protection from abrasion, such as the skin
Stratified Squamous Keratinized Epithelium
- Outermost layer of stratified squamous tissue is composed of keratin
- Specialized for protection against wear and tear
Transitional Epithelium
- Cells change shape depending on the stretch state of the organ
- Seen in organs subject to expansion and contraction, like the urinary bladder
Loose Connective Tissue
- A flexible tissue with a network of fibers and cells
- Supports and connects other tissues
Macrophage EM
- Macrophages are a type of white blood cell involved in phagocytosis and immune response
- Electron micrograph shows the structural features of the cell
Plasma Cells EM
- Plasma cells are lymphocytes that produce antibodies.
- Their EM features reflect active protein synthesis
Mast Cells EM
- Mast cells are immune cells involved in allergic reactions
- Their EM characteristics are noted
Elastic Connective Tissue
- Tissue with elastic fibers for recoil and stretch
- Found in organs needed for expansion and contraction
Collagenous Connective Tissue
- Tissue with collagen fibers providing strength and support
- Present in tendons and ligaments
White Fat Sudan III
- A special stain highlighting fat droplets in white adipose tissue
- The stain shows fatty vesicles or vacuoles filled with triglycerides
Hyaline Cartilage
- A flexible cartilage with chondrocytes located in lacunae
- Shows structural characteristics of the tissue, including cells and matrix
Elastic Cartilage
- Cartilage with elastic fibers providing flexibility to the structure
- Features of elastic fibers are revealed clearly
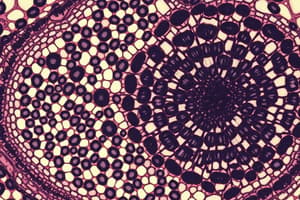
Compact Bone
- Hard, dense tissue with Haversian canals for blood vessels and nerves
- Shows Haversian systems and Volkmann canals
Spongy Bone
- Light, porous bone supporting cancellous bone marrow
- Shows supporting framework
Blood Film
- A thin blood smear viewed under a microscope
- Used to identify blood cells' shape, size, and presence
Red Blood Cells
- Disc-shaped cells without nuclei in mammals
- Seen in various magnification (light microscope, EM) showing cell traits
Neutrophils
- Granulocytes in the blood involved in immune responses against bacterial infections
- Their structural components as seen using microscopy are highlighted
Eosinophils
- Granulocytes in the blood playing a role in immune responses to parasites and allergic reactions
- Features of eosinophils are shown
Basophils
- Granulocytes involved in allergic reactions and inflammatory responses
- Visual appearance of cells is denoted
Monocytes
- Macrophages that phagocytize pathogens.
- Shown at the light microscope magnification
Medium Sized Artery and Vein
- Detailed structure, including the tunica intima, media, and adventitia
- Differences between artery and vein are shown in image
Aorta
- Largest artery in the body, featuring multiple layers
- Image highlights the prominent layers in the aorta
Skeletal Muscle (LS)
- Long, cylindrical, striated muscle cells
- The macroscopic or light microscopic view shows fiber arrangements
Skeletal Muscle (EM)
- Detailed view of muscle structure showing sarcomeres, Z-lines, dark and light bands
- Microscopic features of the myofibrils
Skeletal Muscle (TS)
- Transverse section of skeletal muscle showcasing fascicles; bundles of muscle fibers
- Macroscopic appearance or light microscopic appearance is highlighted
Neuron
- Neuron is a nerve cell comprising axon, dendrites, and cell body
- The position and structure of these components in a nerve cell is noted
TS Nerve Trunk (osmic acid)
- Cross-section of a nerve trunk showing bundled nerve fibers, myelin, and Schwann cells
TS Spinal Cord
- The spinal cord has white and gray matter
- Highlights the areas of white and gray matter
Lymph Node
- Shows cortex and medulla
- Location of the components in the lymph node is identified
Thick Skin
- Thick skin includes keratin, epidermis, and dermis
- The different layers are detailed
Thin Skin
- Thin skin contains epidermis, dermis, and hair follicles
- Positions of the components are indicated
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz focuses on key concepts from Biology Chapter 5, particularly on cell structures and various types of tissues. Test your knowledge on protein synthesis, epithelial layers, connective tissue, muscle tissue, cartilage, and functions of specific cells. Perfect for reinforcing your understanding of histology and cellular biology.