Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does 'ambulacrum' refer to?
What does 'ambulacrum' refer to?
- A type of larva
- Radiating grooves where podia of the water-vascular system project (correct)
- A structure related to respiration
- A type of digestive gland
What is the ambulacral groove?
What is the ambulacral groove?
A groove along each ambulacrum containing rows of tube feet.
What are tube feet used for?
What are tube feet used for?
Locomotion, clinging, food handling, and respiration.
What is the function of the radial nerve?
What is the function of the radial nerve?
What are pedicellariae?
What are pedicellariae?
What is the role of papulae?
What is the role of papulae?
What is a madreporite?
What is a madreporite?
What is the water-vascular system?
What is the water-vascular system?
What are Polian vesicles used for?
What are Polian vesicles used for?
What are ossicles?
What are ossicles?
What are radial canals?
What are radial canals?
What do lateral canals connect?
What do lateral canals connect?
What is the ampulla?
What is the ampulla?
What is the cardiac stomach?
What is the cardiac stomach?
What is autotomy?
What is autotomy?
What are pyloric ceca?
What are pyloric ceca?
What is the pyloric stomach?
What is the pyloric stomach?
What are somatocoels?
What are somatocoels?
What is an axocoel?
What is an axocoel?
What is the hydrocoel?
What is the hydrocoel?
What is a bipinnaria?
What is a bipinnaria?
What are Ophiuroidea?
What are Ophiuroidea?
Match the following descriptions with their corresponding terms:
Match the following descriptions with their corresponding terms:
What are oral tentacles?
What are oral tentacles?
What is a respiratory tree?
What is a respiratory tree?
What is a cloaca?
What is a cloaca?
What is an auricularia?
What is an auricularia?
What are Cuvierian tubules?
What are Cuvierian tubules?
What describes Holothuroidea?
What describes Holothuroidea?
What defines Crinoidea?
What defines Crinoidea?
What is significant about Asteroidea?
What is significant about Asteroidea?
What does 'triploblastic' refer to?
What does 'triploblastic' refer to?
What is the Echinodermata?
What is the Echinodermata?
What is pentaradial symmetry?
What is pentaradial symmetry?
What type of symmetry do echinoderm larvae exhibit?
What type of symmetry do echinoderm larvae exhibit?
What is a Deuterostome?
What is a Deuterostome?
What are dermal papulae?
What are dermal papulae?
What is Aristotle's lantern?
What is Aristotle's lantern?
Study Notes
Echinoderms Overview
- Echinoderms belong to the phylum Echinodermata, characterized by their unique features and structures.
Unique Features
- Pentaradial symmetry: Adults exhibit this type of symmetry, while their larvae demonstrate bilateral symmetry.
- Triploblastic: Echinoderms develop from three germ layers during embryonic development.
- Deuterostome development: They exhibit deuterostomic cleavage patterns.
Key Anatomical Structures
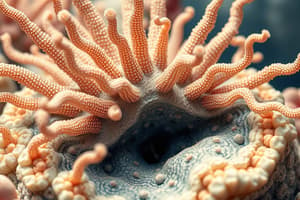
- Ambulacrum: Radiating grooves with projecting podia from the water-vascular system.
- Ambulacral groove: Central groove of each ambulacrum containing tube feet flanked by movable spines.
- Tube feet: Serve multiple purposes including locomotion, adhesion, feeding, and respiration.
Water-Vascular System
- Madreporite: A sievelike structure serving as the entry point for the water-vascular system.
- Polian vesicles: Fluid reservoirs connected to the ring canal of the water-vascular system.
- Ossicles: Calcareous plates forming the body structure, often projecting spines.
Circulatory Elements
- Radial canal: Canals radiating from the ring canal along the ambulacra.
- Lateral canal: Connects radial canals to tube feet.
- Ampulla: Muscular vesicle above tube feet aiding in movement and function.
Digestive System
- Cardiac stomach: Can be everted for digestion and enzymatic breakdown of food.
- Pyloric stomach: Connected to digestive glands where extensive digestion occurs.
- Pyloric ceca: Digestive glands facilitating nutrient absorption.
Respiratory Structures
- Papulae: Projections aiding gas exchange by increasing respiratory surface area.
- Respiratory tree: Unique structure in some echinoderms for respiration, leading to the cloaca.
Defensive Mechanisms
- Autotomy: Ability to sever parts of their body for defense.
- Cuvierian tubules: Sticky, toxic structures expelled to deter predators.
Major Classes of Echinoderms
- Asteroidea (Sea Stars): Have variable arms, open ambulacral grooves with suckered tube feet, and can prey by everting their stomachs.
- Ophiuroidea (Brittle Stars): Characterized by a distinct central disc, autotomous limbs, and lack of suckers on tube feet.
- Echinoidea (Sea Urchins & Sand Dollars): No arms with fused ossicle plates forming a "test," equipped with moveable spines and suckered tube feet.
- Holothuroidea (Sea Cucumbers): Elongated body plan with no arms, utilized for respiration with a unique respiratory tree.
- Crinoidea (Sea Lilies & Feather Stars): Flower-shaped bodies with arms bearing food grooves and tube feet, anchored by flexible appendages called cirri.
Larval Forms
- Bipinnaria: Free-swimming, bilateral larva of asteroids.
- Auricularia: Free-swimming larva of Holothuroidea that develops into adult forms.
Additional Concepts
- Pedicellariae: Small pincher-like structures for defense and maintenance.
- Dermal papulae: Flesh-like projections acting in respiration.
- Aristotle's lantern: A specialized jaw mechanism found in Echinoidea for feeding.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Test your knowledge of Echinoderms with these flashcards focused on chapter 14. Each card features a key term and its definition, enhancing your understanding of this fascinating group of marine animals. Perfect for studying and memorization.